|
Structural Inheritance
Structural inheritance or cortical inheritance is the transmission of an epigenetic trait in a living organism by a self-perpetuating spatial structures. This is in contrast to the transmission of digital information such as is found in DNA sequences, which accounts for the vast majority of known genetic variation. Examples of structural inheritance include the propagation of prions, the infectious proteins of diseases such as scrapie (in sheep and goats), bovine spongiform encephalopathy ('mad cow disease') and Creutzfeldt–Jakob disease (although the protein-only hypothesis of prion transmission has been considered contentious until recently). Prions based on heritable protein structure also exist in yeast. Structural inheritance has also been seen in the orientation of cilia in protozoans such as ''Paramecium'' and ''Tetrahymena'', and 'handedness' of the spiral of the cell in ''Tetrahymena'', and shells of snails. Some organelles also have structural inheritance, such as the ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Organelle
In cell biology, an organelle is a specialized subunit, usually within a cell, that has a specific function. The name ''organelle'' comes from the idea that these structures are parts of cells, as organs are to the body, hence ''organelle,'' the suffix ''-elle'' being a diminutive. Organelles are either separately enclosed within their own lipid bilayers (also called membrane-bound organelles) or are spatially distinct functional units without a surrounding lipid bilayer (non-membrane bound organelles). Although most organelles are functional units within cells, some function units that extend outside of cells are often termed organelles, such as cilia, the flagellum and archaellum, and the trichocyst. Organelles are identified by microscopy, and can also be purified by cell fractionation. There are many types of organelles, particularly in eukaryotic cells. They include structures that make up the endomembrane system (such as the nuclear envelope, endoplasmic reticulum, and G ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Origination Of Organismal Form
''Origination of Organismal Form: Beyond the Gene in Developmental and Evolutionary Biology'' is an anthology published in 2003 edited by Gerd B. Müller and Stuart A. Newman. The book is the outcome of the 4th Altenberg Workshop in Theoretical Biology on "Origins of Organismal Form: Beyond the Gene Paradigm", hosted in 1999 at the Konrad Lorenz Institute for Evolution and Cognition Research. It has been cited over 200 times and has a major influence on extended evolutionary synthesis research. Description of the book The book explores the multiple factors that may have been responsible for the origination of biological form in multicellular life. These biological forms include limbs, segmented structures, and different body symmetries. It explores why the basic body plans of nearly all multicellular life arose in the relatively short time span of the Cambrian Explosion. The authors focus on physical factors (structuralism) other than changes in an organism's genome that may ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Newsweek
''Newsweek'' is an American weekly online news magazine co-owned 50 percent each by Dev Pragad, its president and CEO, and Johnathan Davis (businessman), Johnathan Davis, who has no operational role at ''Newsweek''. Founded as a weekly print magazine in 1933, it was widely distributed during the 20th century, and had many notable editors-in-chief. The magazine was acquired by The Washington Post Company in 1961, and remained under its ownership until 2010. Revenue declines prompted The Washington Post Company to sell it, in August 2010, to the audio pioneer Sidney Harman for a purchase price of one dollar and an assumption of the magazine's liabilities. Later that year, ''Newsweek'' merged with the news and opinion website ''The Daily Beast'', forming The Newsweek Daily Beast Company. ''Newsweek'' was jointly owned by the estate of Harman and the diversified American media and Internet company IAC (company), IAC. ''Newsweek'' continued to experience financial difficulties, whic ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Extended Evolutionary Synthesis
The extended evolutionary synthesis consists of a set of theoretical concepts argued to be more comprehensive than the earlier modern synthesis of evolutionary biology that took place between 1918 and 1942. The extended evolutionary synthesis was called for in the 1950s by C. H. Waddington, argued for on the basis of punctuated equilibrium by Stephen Jay Gould and Niles Eldredge in the 1980s, and was reconceptualized in 2007 by Massimo Pigliucci and Gerd B. Müller. Notably, Dr. Müller concluded from this research that Natural Selection has no way of explaining speciation, saying: “selection has no innovative capacity...the generative and the ordering aspects of morphological evolution are thus absent from evolutionary theory.” The extended evolutionary synthesis revisits the relative importance of different factors at play, examining several assumptions of the earlier synthesis, and augmenting it with additional causative factors. It includes multilevel selection, transgene ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Protozoa
Protozoa (singular: protozoan or protozoon; alternative plural: protozoans) are a group of single-celled eukaryotes, either free-living or parasitic, that feed on organic matter such as other microorganisms or organic tissues and debris. Historically, protozoans were regarded as "one-celled animals", because they often possess animal-like behaviours, such as motility and predation, and lack a cell wall, as found in plants and many algae. When first introduced by Georg Goldfuss (originally spelled Goldfuß) in 1818, the taxon Protozoa was erected as a class within the Animalia, with the word 'protozoa' meaning "first animals". In later classification schemes it was elevated to a variety of higher ranks, including phylum, subkingdom and kingdom, and sometimes included within Protoctista or Protista. The approach of classifying Protozoa within the context of Animalia was widespread in the 19th and early 20th century, but not universal. By the 1970s, it became usual to require th ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Tracy Sonneborn
Tracy Morton Sonneborn (October 19, 1905 – January 26, 1981) was an American biologist. His life's study was ciliated protozoa of the group ''Paramecium''. Education Sonneborn attended the Baltimore City Public Schools and graduated from the Baltimore City College (high school) in 1922. As an adolescent, Sonneborn was interested in the humanities and considered becoming a rabbi. After taking a biology course taught by E. A. Andrews, his interest in literature was eclipsed by his interest in science. He earned a B.A. from Johns Hopkins University in 1925 and a Ph.D in 1928. His graduate work, supervised by Herbert S. Jennings, focused on the flatworm ''Stenostomum''. Career Sonneborn spent 1928 and 1929 researching the ciliate ''Colpidium'' with Jennings as a National Research Council fellow. He remained at Hopkins until 1939, with appointments as research assistant, research associate, and associate. He was offered a faculty position at Indiana University, where he serv ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Base Pair
A base pair (bp) is a fundamental unit of double-stranded nucleic acids consisting of two nucleobases bound to each other by hydrogen bonds. They form the building blocks of the DNA double helix and contribute to the folded structure of both DNA and RNA. Dictated by specific hydrogen bonding patterns, "Watson–Crick" (or "Watson–Crick–Franklin") base pairs (guanine–cytosine and adenine–thymine) allow the DNA helix to maintain a regular helical structure that is subtly dependent on its nucleotide sequence. The Complementarity (molecular biology), complementary nature of this based-paired structure provides a redundant copy of the genetic information encoded within each strand of DNA. The regular structure and data redundancy provided by the DNA double helix make DNA well suited to the storage of genetic information, while base-pairing between DNA and incoming nucleotides provides the mechanism through which DNA polymerase replicates DNA and RNA polymerase transcribes DNA in ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Plasma Membrane
The cell membrane (also known as the plasma membrane (PM) or cytoplasmic membrane, and historically referred to as the plasmalemma) is a biological membrane that separates and protects the interior of all cells from the outside environment (the extracellular space). The cell membrane consists of a lipid bilayer, made up of two layers of phospholipids with cholesterols (a lipid component) interspersed between them, maintaining appropriate membrane fluidity at various temperatures. The membrane also contains membrane proteins, including integral proteins that span the membrane and serve as membrane transporters, and peripheral proteins that loosely attach to the outer (peripheral) side of the cell membrane, acting as enzymes to facilitate interaction with the cell's environment. Glycolipids embedded in the outer lipid layer serve a similar purpose. The cell membrane controls the movement of substances in and out of cells and organelles, being selectively permeable to ions an ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Cell (biology)
The cell is the basic structural and functional unit of life forms. Every cell consists of a cytoplasm enclosed within a membrane, and contains many biomolecules such as proteins, DNA and RNA, as well as many small molecules of nutrients and metabolites.Cell Movements and the Shaping of the Vertebrate Body in Chapter 21 of Molecular Biology of the Cell '' fourth edition, edited by Bruce Alberts (2002) published by Garland Science. The Alberts text discusses how the "cellular building blocks" move to shape developing embryos. It is also common to describe small molecules such as ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Centriole
In cell biology a centriole is a cylindrical organelle composed mainly of a protein called tubulin. Centrioles are found in most eukaryotic cells, but are not present in conifers (Pinophyta), flowering plants (angiosperms) and most fungi, and are only present in the male gametes of charophytes, bryophytes, seedless vascular plants, cycads, and ''Ginkgo''. A bound pair of centrioles, surrounded by a highly ordered mass of dense material, called the pericentriolar material (PCM), makes up a structure called a centrosome. Centrioles are typically made up of nine sets of short microtubule triplets, arranged in a cylinder. Deviations from this structure include crabs and ''Drosophila melanogaster'' embryos, with nine doublets, and '' Caenorhabditis elegans'' sperm cells and early embryos, with nine singlets. Additional proteins include centrin, cenexin and tektin. The main function of centrioles is to produce cilia during interphase and the aster and the spindle during cell divis ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
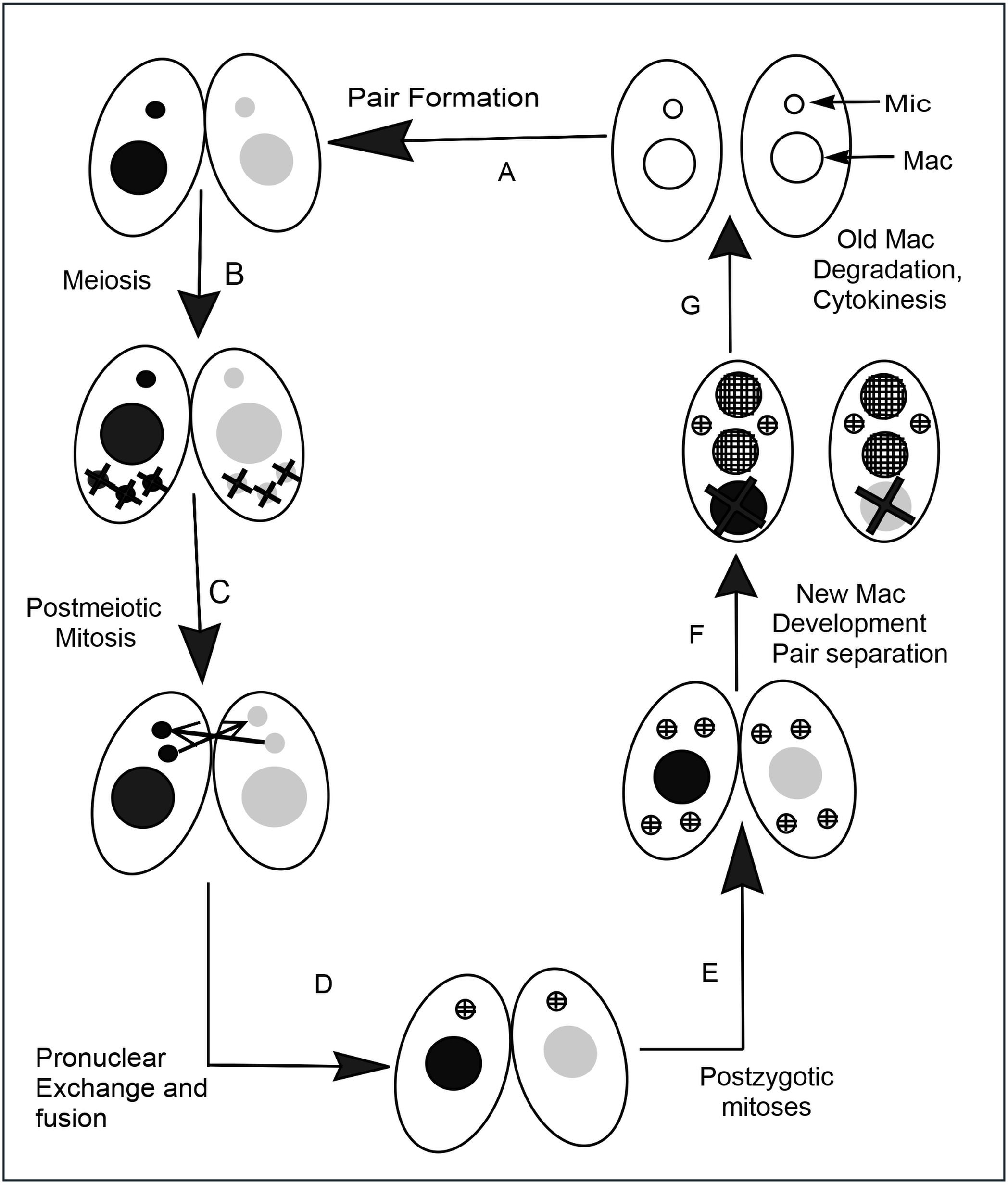
Tetrahymena
''Tetrahymena'', a Unicellular organism, unicellular eukaryote, is a genus of free-living ciliates. The genus Tetrahymena is the most widely studied member of its phylum. It can produce, store and react with different types of hormones. Tetrahymena cells can recognize both related and hostile cells. They can also switch from commensalism, commensalistic to pathogenic modes of survival. They are common in freshwater lakes, ponds, and streams. ''Tetrahymena'' species used as model organisms in biomedical research are ''T. thermophila'' and ''T. pyriformis''. ''T. thermophila'': a model organism in experimental biology As a ciliated protozoan, ''Tetrahymena thermophila'' exhibits nuclear dimorphism: two types of cell Cell nucleus, nuclei. They have a bigger, Somatic cell, non-germline macronucleus and a small, germline micronucleus in each cell at the same time and these two carry out different functions with distinct cytological and biological properties. This unique vers ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |