|
Strategic Advisory Group Of Experts
The Strategic Advisory Group of Experts (SAGE) is the principal advisory group to World Health Organization (WHO) for vaccines and immunization. Established in 1999 through the merging of two previous committees, notably the Scientific Advisory Group of Experts (which served the Program for Vaccine Development) and the Global Advisory Group (which served the EPI program) by Director-General of the WHO Gro Harlem Brundtland. It is charged with advising WHO on overall global policies and strategies, ranging from vaccines and biotechnology, research and development, to delivery of immunization and its linkages with other health interventions. SAGE is concerned not just with childhood vaccines and immunization, but all vaccine-preventable diseases. SAGE provide global recommendations on immunization policy and such recommendations will be further translated by advisory committee at the country level. Membership The SAGE has 15 members, who are recruited and selected as acknowledged ex ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
World Health Organization
The World Health Organization (WHO) is a specialized agency of the United Nations responsible for international public health. The WHO Constitution states its main objective as "the attainment by all peoples of the highest possible level of health". Headquartered in Geneva, Switzerland, it has six regional offices and 150 field offices worldwide. The WHO was established on 7 April 1948. The first meeting of the World Health Assembly (WHA), the agency's governing body, took place on 24 July of that year. The WHO incorporated the assets, personnel, and duties of the League of Nations' Health Organization and the , including the International Classification of Diseases (ICD). Its work began in earnest in 1951 after a significant infusion of financial and technical resources. The WHO's mandate seeks and includes: working worldwide to promote health, keeping the world safe, and serve the vulnerable. It advocates that a billion more people should have: universal health care coverag ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
UNICEF
UNICEF (), originally called the United Nations International Children's Emergency Fund in full, now officially United Nations Children's Fund, is an agency of the United Nations responsible for providing Humanitarianism, humanitarian and Development aid, developmental aid to children worldwide. The agency is among the most widespread and recognizable social welfare organizations in the world, with a presence in 192 countries and territories. UNICEF's activities include providing immunizations and disease prevention, administering Antiretroviral drug, treatment for children and mothers with HIV, enhancing childhood and maternal nutrition, improving sanitation, promoting education, and providing emergency relief in response to disasters. UNICEF is the successor of the United Nations International Children's Emergency Fund, created on 11 December 1946, in New York, by the United Nations Relief and Rehabilitation Administration, U.N. Relief Rehabilitation Administration to provide ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
International Medical And Health Organizations
International is an adjective (also used as a noun) meaning "between nations". International may also refer to: Music Albums * ''International'' (Kevin Michael album), 2011 * ''International'' (New Order album), 2002 * ''International'' (The Three Degrees album), 1975 *''International'', 2018 album by L'Algérino Songs * The Internationale, the left-wing anthem * "International" (Chase & Status song), 2014 * "International", by Adventures in Stereo from ''Monomania'', 2000 * "International", by Brass Construction from ''Renegades'', 1984 * "International", by Thomas Leer from ''The Scale of Ten'', 1985 * "International", by Kevin Michael from ''International'' (Kevin Michael album), 2011 * "International", by McGuinness Flint from ''McGuinness Flint'', 1970 * "International", by Orchestral Manoeuvres in the Dark from '' Dazzle Ships'', 1983 * "International (Serious)", by Estelle from '' All of Me'', 2012 Politics * Political international, any transnational organization ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Health Policy
Health policy can be defined as the "decisions, plans, and actions that are undertaken to achieve specific healthcare goals within a society".World Health Organization''Health Policy'' accessed 22 March 2011(Web archive)/ref> According to the World Health Organization, an explicit health policy can achieve several things: it defines a vision for the future; it outlines priorities and the expected roles of different groups; and it builds consensus and informs people. Different approaches Health policy often refers to the health-related content of a policy. Understood in this sense, there are many categories of health policies, including global health policy, public health policy, mental health policy, health care services policy, insurance policy, personal healthcare policy, pharmaceutical policy, and policies related to public health such as vaccination policy, tobacco control policy or breastfeeding promotion policy. Health policy may also cover topics related to healthcar ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Public Health
Public health is "the science and art of preventing disease, prolonging life and promoting health through the organized efforts and informed choices of society, organizations, public and private, communities and individuals". Analyzing the determinants of health of a population and the threats it faces is the basis for public health. The ''public'' can be as small as a handful of people or as large as a village or an entire city; in the case of a pandemic it may encompass several continents. The concept of ''health'' takes into account physical, psychological, and social well-being.What is the WHO definition of health? from the Preamble to the Constitution of WHO as adopted by the International Health Conference, New York, 19 June - 22 July 1946; signed on ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Monkeypox
Monkeypox (also called mpox by the WHO) is an infectious viral disease that can occur in humans and some other animals. Symptoms include fever, swollen lymph nodes, and a rash that forms blisters and then crusts over. The time from exposure to onset of symptoms ranges from five to twenty-one days. The duration of symptoms is typically two to four weeks. There may be mild symptoms, and it may occur without any symptoms being apparent. The classic presentation of fever and muscle pains, followed by swollen glands, with lesions all at the same stage, has not been found to be common to all outbreaks. Cases may be severe, especially in children, pregnant women or people with suppressed immune systems. The disease is caused by the monkeypox virus, a zoonotic virus in the genus ''Orthopoxvirus''. The variola virus, the causative agent of smallpox, is also in this genus. Of the two types in humans, cladeII (formerly West African clade) causes a less severe disease than the Central A ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Smallpox Vaccine
The smallpox vaccine is the first vaccine to be developed against a contagious disease. In 1796, British physician Edward Jenner demonstrated that an infection with the relatively mild cowpox virus conferred immunity against the deadly smallpox virus. Cowpox served as a natural vaccine until the modern smallpox vaccine emerged in the 20th century. From 1958 to 1977, the World Health Organization (WHO) conducted a global vaccination campaign that eradicated smallpox, making it the only human disease to be eradicated. Although routine smallpox vaccination is no longer performed on the general public, the vaccine is still being produced to guard against bioterrorism, biological warfare, and monkeypox.Anderson MG, Frenkel LD, Homann S, and Guffey J. (2003), "A case of severe monkeypox virus disease in an American child: emerging infections and changing professional values"; '' Pediatr Infect Dis J'';22(12): 1093–96; discussion 1096–98. The term ''vaccine'' derives from the Latin ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Malaria Vaccine
A malaria vaccine is a vaccine that is used to prevent malaria. The only approved use of a vaccine outside the EU, as of 2022, is RTS,S, known by the brand name ''Mosquirix''. In October 2021, the WHO for the first time recommended the large-scale use of a malaria vaccine for children living in areas with moderate-to-high malaria transmission. Four injections are required for full protection. Research continues with other malaria vaccines. The most effective malaria vaccine is R21/Matrix-M, with a 77% efficacy rate shown in initial trials and significantly higher antibody levels than with the RTS,S vaccine. It is the first vaccine that meets the World Health Organization's (WHO) goal of a malaria vaccine with at least 75% efficacy. Approved vaccines RTS,S RTS,S, developed by PATH Malaria Vaccine Initiative (MVI) and GlaxoSmithKline (GSK) with support from the Bill and Melinda Gates Foundation, is the most recently developed recombinant vaccine. It consists of the ''P. falci ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Polio Vaccine
Polio vaccines are vaccines used to prevent poliomyelitis (polio). Two types are used: an inactivated poliovirus given by injection (IPV) and a weakened poliovirus given by mouth (OPV). The World Health Organization (WHO) recommends all children be fully vaccinated against polio. The two vaccines have eliminated polio from most of the world, and reduced the number of cases reported each year from an estimated 350,000 in 1988 to 33 in 2018. The inactivated polio vaccines are very safe. Mild redness or pain may occur at the site of injection. Oral polio vaccines cause about three cases of vaccine-associated paralytic poliomyelitis per million doses given. This compares with 5,000 cases per million who are paralysed following a polio infection. Both types of vaccine are generally safe to give during pregnancy and in those who have HIV/AIDS but are otherwise well. However, the emergence of circulating vaccine-derived poliovirus (cVDPV), a form of the vaccine virus that has rever ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Pneumococcal Vaccines
Pneumococcal vaccines are vaccines against the bacterium ''Streptococcus pneumoniae''. Their use can prevent some cases of pneumonia, meningitis, and sepsis. There are two types of pneumococcal vaccines: conjugate vaccines and polysaccharide vaccines. They are given by injection either into a muscle or just under the skin. The World Health Organization (WHO) recommends the use of the conjugate vaccine in the routine immunizations given to children. This includes those with HIV/AIDS. The recommended three or four doses are between 71 and 93% effective at preventing severe pneumococcal disease. The polysaccharide vaccines, while effective in healthy adults, are not effective in children less than two years old or those with poor immune function. These vaccines are generally safe. With the conjugate vaccine about 10% of babies develop redness at the site of injection, fever, or change in sleep. Severe allergies are very rare. Whole cell vaccinations were developed alongsid ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Meningococcal Vaccines
Meningococcal vaccine refers to any vaccine used to prevent infection by ''Neisseria meningitidis''. Different versions are effective against some or all of the following types of meningococcus: A, B, C, W-135, and Y. The vaccines are between 85 and 100% effective for at least two years. They result in a decrease in meningitis and sepsis among populations where they are widely used. They are given either by injection into a muscle or just under the skin. The World Health Organization recommends that countries with a moderate or high rate of disease or with frequent outbreaks should routinely vaccinate. In countries with a low risk of disease, they recommend that high risk groups should be immunized. In the African meningitis belt efforts to immunize all people between the ages of one and thirty with the meningococcal A conjugate vaccine are ongoing. In Canada and the United States the vaccines effective against four types of meningococcus (A, C, W, and Y) are recommended routi ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
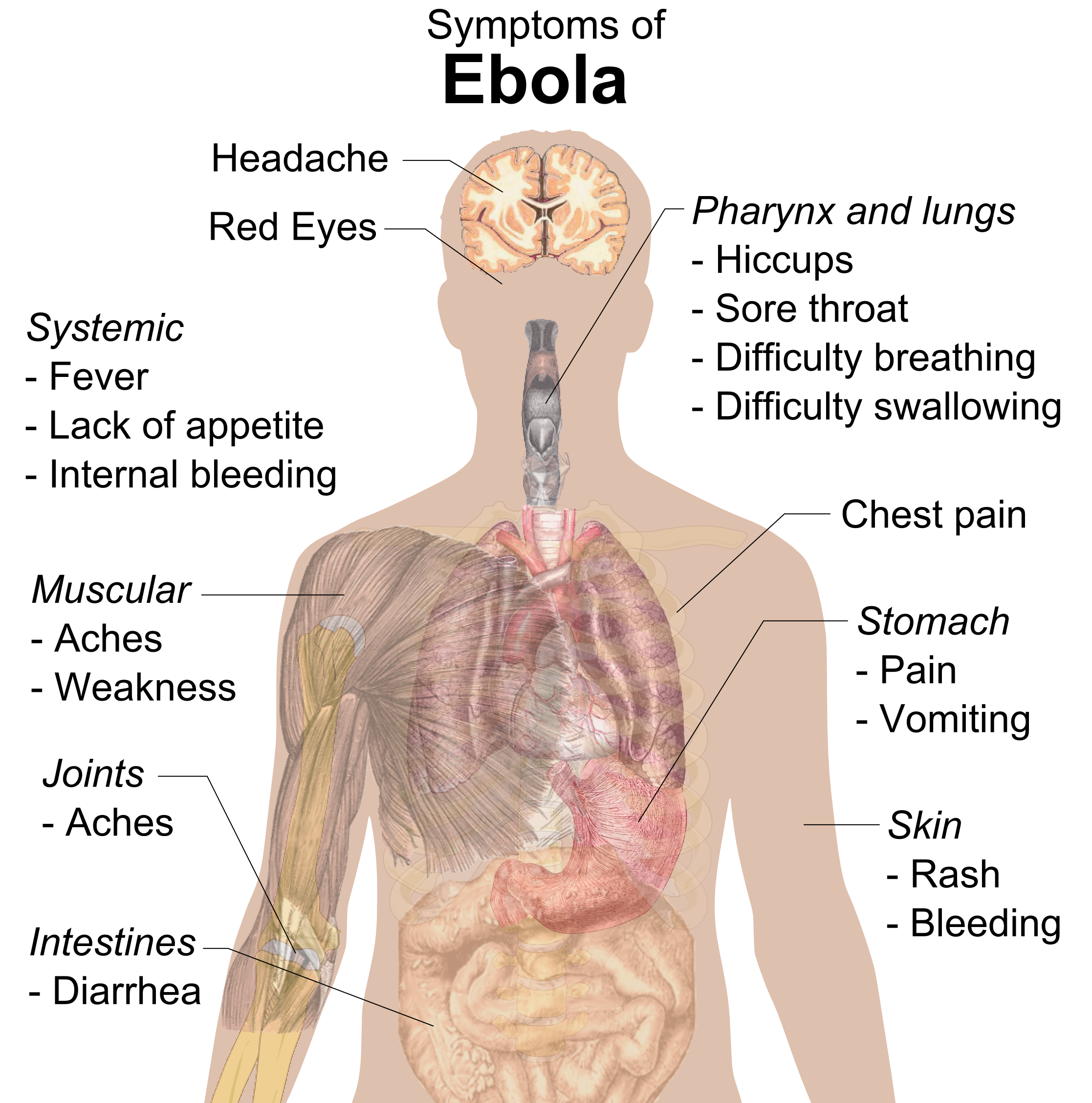
Ebola
Ebola, also known as Ebola virus disease (EVD) and Ebola hemorrhagic fever (EHF), is a viral hemorrhagic fever in humans and other primates, caused by ebolaviruses. Symptoms typically start anywhere between two days and three weeks after becoming infected with the virus. The first symptoms are usually fever, sore throat, muscle pain, and headaches. These are usually followed by vomiting, diarrhoea, rash and decreased liver and kidney function, at which point, some people begin to bleed both internally and externally. The disease kills between 25% and 90% of those infected – about 50% on average. Death is often due to shock from fluid loss, and typically occurs between six and 16 days after the first symptoms appear. Early treatment of symptoms increases the survival rate considerably compared to late start. The virus spreads through direct contact with body fluids, such as blood from infected humans or other animals, or from contact with items that have recently been conta ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |








.jpg)