|
Stradbally (barony)
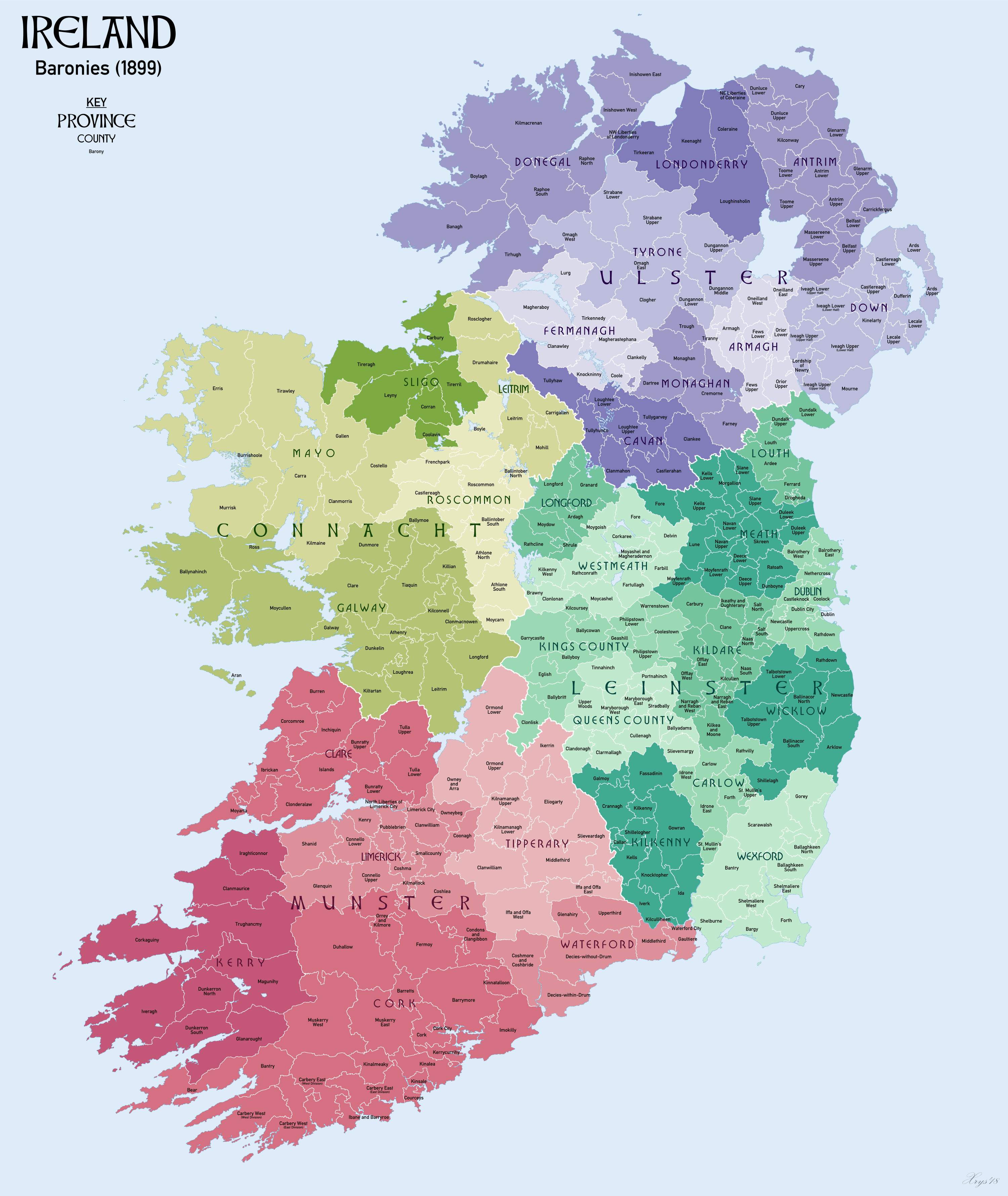
Stradbally () is a Barony (Ireland), barony in County Laois (formerly called ''Queen's County'' or ''County Leix''), Republic of Ireland. Etymology Stradbally barony is named after the town of Stradbally (literally meaning "one-street town"). Geography Stradbally is located in eastern County Laois, bounded to the south by Luggacurren, to the east by the River Barrow and to the west by Dunamase. History Stradbally barony was anciently known as ''Magh Druchtain'' ("plain of sweetness") and was ruled by a sept of the Ó Ceallaigh. It was also called Farran-O'Kelly ("men of O'Kelly"). According to the Annals of the Four Masters, in 1394, James Butler, 3rd Earl of Ormond "mustered a force, and marched into Leinster to spoil it; and he burned and spoiled Gailine, and the territory of O'Kelly of Magh Druchtain, and then returned home." It is referred to in the topographical poem ''Tuilleadh feasa ar Éirinn óigh'' (Giolla na Naomh Ó hUidhrín, d. 1420): ''Ós Muigh Drúchtain an ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Irish Language
Irish ( Standard Irish: ), also known as Gaelic, is a Goidelic language of the Insular Celtic branch of the Celtic language family, which is a part of the Indo-European language family. Irish is indigenous to the island of Ireland and was the population's first language until the 19th century, when English gradually became dominant, particularly in the last decades of the century. Irish is still spoken as a first language in a small number of areas of certain counties such as Cork, Donegal, Galway, and Kerry, as well as smaller areas of counties Mayo, Meath, and Waterford. It is also spoken by a larger group of habitual but non-traditional speakers, mostly in urban areas where the majority are second-language speakers. Daily users in Ireland outside the education system number around 73,000 (1.5%), and the total number of persons (aged 3 and over) who claimed they could speak Irish in April 2016 was 1,761,420, representing 39.8% of respondents. For most of recorded ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Annals Of The Four Masters
The ''Annals of the Kingdom of Ireland'' ( ga, Annála Ríoghachta Éireann) or the ''Annals of the Four Masters'' (''Annála na gCeithre Máistrí'') are chronicles of medieval Irish history. The entries span from the Deluge, dated as 2,242 years after creation to AD 1616. Publication delay Due to the criticisms by 17th century Irish historian Tuileagna Ó Maol Chonaire, the text was not published in the lifetimes of any of the participants. Text The annals are mainly a compilation of earlier annals, although there is some original work. They were compiled between 1632 and 1636, allegedly in a cottage beside the ruins of Donegal Abbey, just outside Donegal Town. At this time, however, the Franciscans had a house of refuge by the River Drowes in County Leitrim, just outside Ballyshannon, and it was here, according to others, that the ''Annals'' were compiled. [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
William Cosby
Brigadier-General William Cosby (1690–1736) was an Irish soldier who served as the British colonial governor of New York from 1732 to 1736. During his short term, Cosby was portrayed as one of the most oppressive governors in the Thirteen Colonies. In 1735, Cosby accused publisher John Peter Zenger of sedition and libel for publishing unflattering reports about Cosby. In spite of Cosby's efforts, Zenger was acquitted of all charges and the case helped to establish the concept of freedom of the press. Early life and military career William Cosby was born in Stradbally Hall, Queen's County, Ireland, in 1690. His father, Alexander Cosby of Stradbally, stemmed from a British family that emigrated to Ireland in 1590, by the first Alexander Cosby. His mother, Elizabeth L'Estrange, was from another family of the Protestant Ascendancy. In 1709, 19-year-old William Cosby travelled to Italy and earned money by gambling in card games. The next year he enlisted in the British Army at ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Francis Cosby
Francis Cosby (1510–1580) was an English soldier and settler in Ireland. He has been implicated in the Massacre of Mullaghmast. Life He was the second son of John Cosby of Great Leake, Nottingham. He settled in Ireland in the reign of Henry VIII. He was active in fighting on the edge of the English Pale, and was commended by the Lord Deputies Edward Bellingham and Thomas Radclyffe, 3rd Earl of Sussex. In 1558 Cosby was appointed general of the Kerne, and in 1562 was granted the suppressed abbey of Stradbally in Queen's County. In 1565 he became governor of Portlaoise, and seneschal of Queen's County. He helped to massacre, although the degree of his responsibility is not clear, many of the O'Mores at Mullaghmast, near Athy, who had been summoned to the fortress on avowedly peaceful business. The date 1577 in the ''Annals of the Four Masters'' is contradicted in the ''Annals of Lough Cé'' which says 1567. Cosby was not successful in repression in Queen's County. Rory Og ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
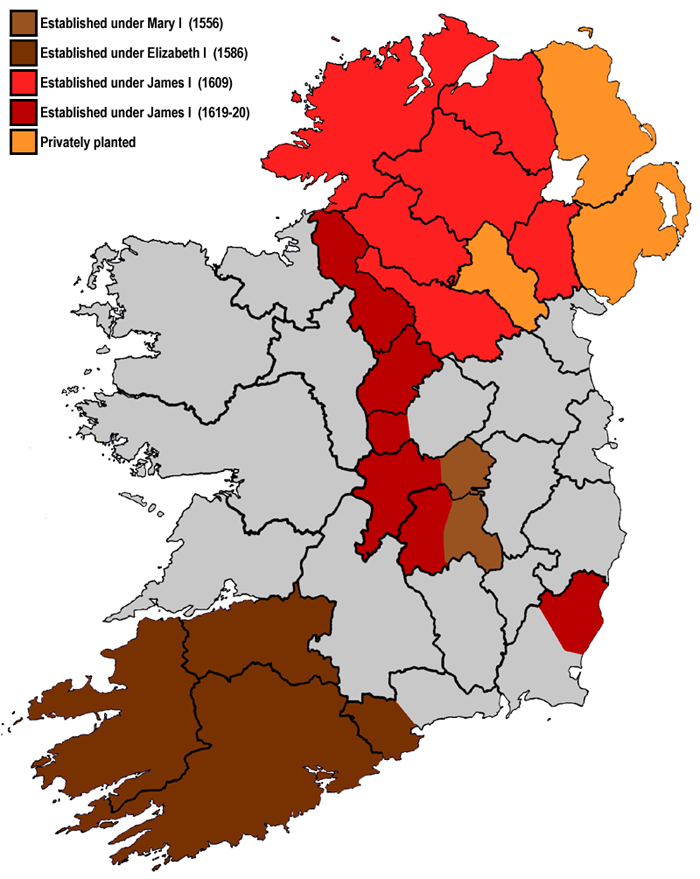
Laois-Offaly Plantation
Plantations in 16th- and 17th-century Ireland involved the confiscation of Irish-owned land by the English Crown and the colonisation of this land with settlers from Great Britain. The Crown saw the plantations as a means of controlling, anglicising and 'civilising' Gaelic Ireland. The main plantations took place from the 1550s to the 1620s, the biggest of which was the plantation of Ulster. The plantations led to the founding of many towns, massive demographic, cultural and economic changes, changes in land ownership and the landscape, and also to centuries of ethnic and sectarian conflict. They took place before and during the earliest English colonisation of the Americas, and a group known as the West Country Men were involved in both Irish and American colonization. There had been small-scale immigration from Britain since the 12th century, after the Anglo-Norman invasion. By the 15th century, direct English control had shrunk to an area called the Pale. In the 1540s th ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Atlantic Salmon
The Atlantic salmon (''Salmo salar'') is a species of ray-finned fish in the family Salmonidae. It is the third largest of the Salmonidae, behind Siberian taimen and Pacific Chinook salmon, growing up to a meter in length. Atlantic salmon are found in the northern Atlantic Ocean and in rivers that flow into it. Most populations are anadromous, hatching in streams and rivers but moving out to sea as they grow where they mature, after which the adults seasonally move upstream again to spawn. When the mature fish re-enter rivers to spawn, they change in colour and appearance. Some populations of this fish only migrate to large lakes, and are "landlocked", spending their entire lives in freshwater. Such populations are found throughout the range of the species. Unlike Pacific species of salmon, ''S. salar'' is iteroparous, which means it can survive spawning and return to sea to repeat the process again in another year. Such individuals can grow to extremely large sizes, althoug ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Giolla Na Naomh Ó HUidhrín
Giolla na Naomh O hUidhrin, Irish historian and poet, died 1420. O hUidhrin is known as the author of ''Tuilleadh feasa ar Éirinn óigh'', a topographical poem of a kind with Seán Mór Ó Dubhagáin's '' Triallam timcheall na Fodla'', of which it is a supplement. Although his obit is noted in all the main Irish annals A number of Irish annals, of which the earliest was the Chronicle of Ireland, were compiled up to and shortly after the end of the 17th century. Annals were originally a means by which monks determined the yearly chronology of feast days. Over t ..., indicating he was regarded as a noteworthy man, nothing further is known of him. References * ''O hUidhrin, Giolla-na-naomh'', Aidan Breen, in ''Dictionary of Irish Biography'', p. 574, Cambridge, 2009. 15th-century Irish historians 15th-century Irish poets 1420 deaths Year of birth unknown Irish male poets Irish-language writers {{Ireland-historian-stub ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Tuilleadh Feasa Ar Éirinn óigh
Tuilleadh feasa ar Éirinn óigh ("More knowledge on the entirety of Ireland") is a medieval Gaelic-Irish topographical text, composed by Giolla na Naomh Ó hUidhrín (died 1420). Overview ''Tuilleadh feasa ...'' is both a supplement and a continuation of Seán Mór Ó Dubhagáin's '' Triallam timcheall na Fodla''. Of the two, James Carney wrote: * "These two poems together constitute a compendium of the topography of pre-Norman Ireland, as seen, however, by poets who lived two centuries after the invasion. ''Triallam timcheall na Fodla'' ... is an account of the territories of the northern half of Ireland and Leinster, indicating the ruling family or families of each district. ''Tuilleadh feasa ar Éirinn óigh'' ... treats in similar fashion of the southern half of Ireland, including Leinster, of which we have therefore two independent accounts. The introductory stanzas of Ó hUidhrín's poem, in which he defines the scope of his work and its relation to that of his predecessor ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
James Butler, 3rd Earl Of Ormond
James Butler, 3rd Earl of Ormond (c. 1359 – 7 September 1405), was a noble in the Peerage of Ireland. He acceded to the title in 1382, and built Gowran Castle three years later in 1385 close to the centre of Gowran, making it his usual residence, whence his common epithet, ''The Earl of Gowran''. James died in Gowran Castle in 1405 and is buried in St. Mary's Collegiate Church, Gowran together with his father James Butler, 2nd Earl of Ormond, his grandfather James Butler, 1st Earl of Ormond and his great great grandfather Edmund Butler, Earl of Carrick and 6th Chief Butler of Ireland. James, the 2nd Earl, was usually called The Noble Earl, being a great-grandson, through his mother, Eleanor de Bohun, of King Edward I of England. Career In 1391, he purchased Kilkenny Castle from the Despencer family. He also built the castle of Dunfert (also called Danefort) and in 1386 founded a Friary of minorites at Aylesbury in Buckinghamshire. In 1384, he was deputy to Sir Philip Courtena ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Ó Ceallaigh
O'Kelly ( ga, i=no, Ó Ceallaigh, approximately ) is the name of a number of distinct septs in Ireland. Most prominent of these is the O'Kelly sept of the Uí Maine. Another sept is that of the kingdom of Kings of Brega, Brega, descended from the Uí Néill. A more minor sept of O'Kelly was that descended from the Uí Máil; this sept is referred to in Irish as the Uí Ceallaig Cualann, in reference to the region of their origin, Cualu. O'Kelly of Uí Maine The O'Kelly sept of Uí Maine is descended from Cellach mac Fíonachta, who lived in the 9th century. The first to bear the surname was Tadhg Mór Ua Cellaigh, Tadhg Mór Ó Ceallaigh, a grandson of the former who was slain in the Battle of Clontarf fighting on behest of his ally Brian Boru, king of Kingdom of Munster, Munster and high king of Ireland. The earliest parts of the O'Kelly genealogy are contained in the Book of Hy Many, which was written in the latter half of the 14th century on behest of the then archbishop of ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Barony (Ireland)
In Ireland, a barony ( ga, barúntacht, plural ) is a historical subdivision of a county, analogous to the hundreds into which the counties of England were divided. Baronies were created during the Tudor reconquest of Ireland, replacing the earlier cantreds formed after the original Norman invasion.Mac Cotter 2005, pp.327–330 Some early baronies were later subdivided into half baronies with the same standing as full baronies. Baronies were mainly cadastral rather than administrative units. They acquired modest local taxation and spending functions in the 19th century before being superseded by the Local Government (Ireland) Act 1898. Subsequent adjustments of county boundaries mean that some baronies now straddle two counties. The final catalogue of baronies numbered 331, with an average area of ; therefore, each county was divided, on average, into 10 or 11 baronies. Creation The island of Ireland was "shired" into counties in two distinct periods: the east and south duri ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |