|
Storkerson Bay
Storkerson Bay is a Canadian Arctic waterway in the Northwest Territories The Northwest Territories (abbreviated ''NT'' or ''NWT''; french: Territoires du Nord-Ouest, formerly ''North-Western Territory'' and ''North-West Territories'' and namely shortened as ''Northwest Territory'') is a federal territory of Canada. .... It is an arm of Amundsen Gulf on central western Banks Island. Historically, it has been a wintering area for Inuvialuit families. References Bays of the Northwest Territories Geography of the Inuvialuit Settlement Region {{NorthwestTerritories-geo-stub ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Northern Canada
Northern Canada, colloquially the North or the Territories, is the vast northernmost region of Canada variously defined by geography and politics. Politically, the term refers to the three Provinces_and_territories_of_Canada#Territories, territories of Canada: Yukon, Northwest Territories and Nunavut. This area covers about 48 per cent of Canada's total land area, but has less than 1 per cent of demographics of Canada, Canada's population. The terms "northern Canada" or "the North" may be used in contrast with ''the far north'', which may refer to the Canadian Arctic, the portion of Canada that lies north of the Arctic Circle, east of Alaska and west of Greenland. However, in many other uses the two areas are treated as a single unit. __TOC__ Definitions Subdivisions As a social rather than political region, the Canadian North is often subdivided into two distinct regions based on climate, the ''near north'' and the ''far north''. The different climates of these two regions ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Waterway
A waterway is any navigable body of water. Broad distinctions are useful to avoid ambiguity, and disambiguation will be of varying importance depending on the nuance of the equivalent word in other languages. A first distinction is necessary between maritime shipping routes and waterways used by inland water craft. Maritime shipping routes cross oceans and seas, and some lakes, where navigability is assumed, and no engineering is required, except to provide the draft for deep-sea shipping to approach seaports (channels), or to provide a short cut across an isthmus; this is the function of ship canals. Dredged channels in the sea are not usually described as waterways. There is an exception to this initial distinction, essentially for legal purposes, see under international waters. Where seaports are located inland, they are approached through a waterway that could be termed "inland" but in practice is generally referred to as a "maritime waterway" (examples Seine Maritime, Loir ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Northwest Territories
The Northwest Territories (abbreviated ''NT'' or ''NWT''; french: Territoires du Nord-Ouest, formerly ''North-Western Territory'' and ''North-West Territories'' and namely shortened as ''Northwest Territory'') is a federal territory of Canada. At a land area of approximately and a 2016 census population of 41,790, it is the second-largest and the most populous of the three territories in Northern Canada. Its estimated population as of 2022 is 45,605. Yellowknife is the capital, most populous community, and only city in the territory; its population was 19,569 as of the 2016 census. It became the territorial capital in 1967, following recommendations by the Carrothers Commission. The Northwest Territories, a portion of the old North-Western Territory, entered the Canadian Confederation on July 15, 1870. Since then, the territory has been divided four times to create new provinces and territories or enlarge existing ones. Its current borders date from April 1, 1999, when the ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
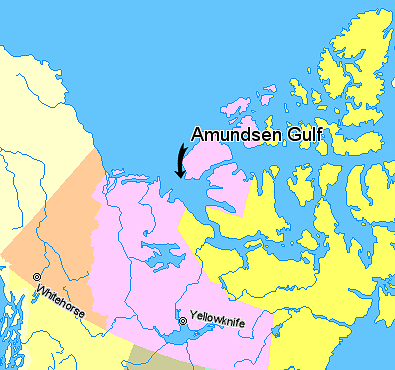
Amundsen Gulf
Amundsen Gulf is a gulf located mainly in the Inuvik Region, Northwest Territories, Canada with a small section in the Kitikmeot Region of Nunavut. It lies between Banks Island and Victoria Island and the mainland. It is approximately in length and about across where it meets the Beaufort Sea. The Amundsen Gulf was explored by Norwegian explorer Roald Amundsen between 1903 and 1906. The gulf is at the western end of the famous Northwest Passage, a route from the Atlantic Ocean to the Pacific. Few people live along the shores of the gulf, but there are a few towns and communities, including Sachs Harbour, Ulukhaktok, and Paulatuk. Heading north in the gulf one would find the Prince of Wales Strait. Heading southeast and east, the gulf leads through the Dolphin and Union Strait, past Simpson Bay and into the Coronation Gulf. From there one would go through the Dease Strait and into the Queen Maud Gulf, and eventually head northeast into the Victoria Strait. Heading west and nor ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Banks Island
Banks Island is one of the larger members of the Arctic Archipelago. Situated in the Inuvik Region, and part of the Inuvialuit Settlement Region, of the Northwest Territories, it is separated from Victoria Island to its east by the Prince of Wales Strait and from the mainland by Amundsen Gulf to its south. The Beaufort Sea lies to its west, and to its northeast M'Clure Strait separates the island from Prince Patrick Island and Melville Island. It is home to at least fourteen mammal species including the Peary caribou, barren-ground caribou, and polar bears. At one time over 68,000 muskoxen lived on the island, the majority of the world's population. However, the bacterium ''Erysipelothrix rhusiopathiae'' has led to a sharp decline in their numbers. The island is the summer home to hundreds of thousands of migratory birds who nest at Banks Island Migratory Bird Sanctuary No. 1 and Banks Island Migratory Bird Sanctuary No. 2. As of the 2016 census it had a human population ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Inuvialuit
The Inuvialuit (sing. Inuvialuk; ''the real people'') or Western Canadian Inuit are Inuit who live in the western Canadian Arctic region. They, like all other Inuit, are descendants of the Thule who migrated eastward from Alaska Alaska ( ; russian: Аляска, Alyaska; ale, Alax̂sxax̂; ; ems, Alas'kaaq; Yup'ik: ''Alaskaq''; tli, Anáaski) is a state located in the Western United States on the northwest extremity of North America. A semi-exclave of the U.S., .... Their homeland – the Inuvialuit Settlement Region – covers the Arctic Ocean coastline area from the Alaskan border, east through the Beaufort Sea and beyond the Amundsen Gulf which includes some of the western Arctic Archipelago, Canadian Arctic Islands, as well as the inland community of Aklavik and part of Yukon. The land was demarked in 1984 by the Inuvialuit Final Agreement. History and migration The Inuvialuit Settlement Region was primarily inhabited by ''Siglit'' Inuit until their number ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Bays Of The Northwest Territories
A bay is a recessed, coastal body of water that directly connects to a larger main body of water, such as an ocean, a lake, or another bay. A large bay is usually called a gulf, sea, sound, or bight. A cove is a small, circular bay with a narrow entrance. A fjord is an elongated bay formed by glacial action. A bay can be the estuary of a river, such as the Chesapeake Bay, an estuary of the Susquehanna River. Bays may also be nested within each other; for example, James Bay is an arm of Hudson Bay in northeastern Canada. Some large bays, such as the Bay of Bengal and Hudson Bay, have varied marine geology. The land surrounding a bay often reduces the strength of winds and blocks waves. Bays may have as wide a variety of shoreline characteristics as other shorelines. In some cases, bays have beaches, which "are usually characterized by a steep upper foreshore with a broad, flat fronting terrace".Maurice Schwartz, ''Encyclopedia of Coastal Science'' (2006), p. 129. Bays were s ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |