|
Stochastic Dynamic Programming
Originally introduced by Richard E. Bellman in , stochastic dynamic programming is a technique for modelling and solving problems of decision making under uncertainty. Closely related to stochastic programming and dynamic programming, stochastic dynamic programming represents the problem under scrutiny in the form of a Bellman equation. The aim is to compute a policy prescribing how to act optimally in the face of uncertainty. A motivating example: Gambling game A gambler has $2, she is allowed to play a game of chance 4 times and her goal is to maximize her probability of ending up with a least $6. If the gambler bets $b on a play of the game, then with probability 0.4 she wins the game, recoup the initial bet, and she increases her capital position by $b; with probability 0.6, she loses the bet amount $b; all plays are pairwise independent. On any play of the game, the gambler may not bet more money than she has available at the beginning of that play.This problem is adapted ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] [Amazon] |
Richard E
Richard is a male given name. It originates, via Old French, from compound of the words descending from Proto-Germanic language">Proto-Germanic ''*rīk-'' 'ruler, leader, king' and ''*hardu-'' 'strong, brave, hardy', and it therefore means 'strong in rule'. Nicknames include " Richie", " Dick", " Dickon", " Dickie", " Rich", " Rick", "Rico (name), Rico", " Ricky", and more. Richard is a common English (the name was introduced into England by the Normans), German and French male name. It's also used in many more languages, particularly Germanic, such as Norwegian, Danish, Swedish, Icelandic, and Dutch, as well as other languages including Irish, Scottish, Welsh and Finnish. Richard is cognate with variants of the name in other European languages, such as the Swedish "Rickard", the Portuguese and Spanish "Ricardo" and the Italian "Riccardo" (see comprehensive variant list below). People named Richard Multiple people with the same name * Richard Andersen (other) * ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] [Amazon] |
Conditional Probability
In probability theory, conditional probability is a measure of the probability of an Event (probability theory), event occurring, given that another event (by assumption, presumption, assertion or evidence) is already known to have occurred. This particular method relies on event A occurring with some sort of relationship with another event B. In this situation, the event A can be analyzed by a conditional probability with respect to B. If the event of interest is and the event is known or assumed to have occurred, "the conditional probability of given ", or "the probability of under the condition ", is usually written as or occasionally . This can also be understood as the fraction of probability B that intersects with A, or the ratio of the probabilities of both events happening to the "given" one happening (how many times A occurs rather than not assuming B has occurred): P(A \mid B) = \frac. For example, the probability that any given person has a cough on any given day ma ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] [Amazon] |
Memoization
In computing, memoization or memoisation is an optimization technique used primarily to speed up computer programs by storing the results of expensive function calls to pure functions and returning the cached result when the same inputs occur again. Memoization has also been used in other contexts (and for purposes other than speed gains), such as in simple mutually recursive descent parsing. It is a type of caching, distinct from other forms of caching such as buffering and page replacement. In the context of some logic programming languages, memoization is also known as tabling. Etymology The term ''memoization'' was coined by Donald Michie in 1968 and is derived from the Latin word ('to be remembered'), usually truncated as ''memo'' in American English, and thus carries the meaning of 'turning he results ofa function into something to be remembered'. While ''memoization'' might be confused with ''memorization'' (because they are etymological cognates), ''memoization'' ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] [Amazon] |
Curse Of Dimensionality
The curse of dimensionality refers to various phenomena that arise when analyzing and organizing data in high-dimensional spaces that do not occur in low-dimensional settings such as the three-dimensional physical space of everyday experience. The expression was coined by Richard E. Bellman when considering problems in dynamic programming. The curse generally refers to issues that arise when the number of datapoints is small (in a suitably defined sense) relative to the intrinsic dimension of the data. Dimensionally cursed phenomena occur in domains such as numerical analysis, sampling, combinatorics, machine learning, data mining and databases. The common theme of these problems is that when the dimensionality increases, the volume of the space increases so fast that the available data become sparse. In order to obtain a reliable result, the amount of data needed often grows exponentially with the dimensionality. Also, organizing and searching data often relies on detecting a ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] [Amazon] |
Memoization
In computing, memoization or memoisation is an optimization technique used primarily to speed up computer programs by storing the results of expensive function calls to pure functions and returning the cached result when the same inputs occur again. Memoization has also been used in other contexts (and for purposes other than speed gains), such as in simple mutually recursive descent parsing. It is a type of caching, distinct from other forms of caching such as buffering and page replacement. In the context of some logic programming languages, memoization is also known as tabling. Etymology The term ''memoization'' was coined by Donald Michie in 1968 and is derived from the Latin word ('to be remembered'), usually truncated as ''memo'' in American English, and thus carries the meaning of 'turning he results ofa function into something to be remembered'. While ''memoization'' might be confused with ''memorization'' (because they are etymological cognates), ''memoization'' ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] [Amazon] |
Stochastic Dynamic Programming
Originally introduced by Richard E. Bellman in , stochastic dynamic programming is a technique for modelling and solving problems of decision making under uncertainty. Closely related to stochastic programming and dynamic programming, stochastic dynamic programming represents the problem under scrutiny in the form of a Bellman equation. The aim is to compute a policy prescribing how to act optimally in the face of uncertainty. A motivating example: Gambling game A gambler has $2, she is allowed to play a game of chance 4 times and her goal is to maximize her probability of ending up with a least $6. If the gambler bets $b on a play of the game, then with probability 0.4 she wins the game, recoup the initial bet, and she increases her capital position by $b; with probability 0.6, she loses the bet amount $b; all plays are pairwise independent. On any play of the game, the gambler may not bet more money than she has available at the beginning of that play.This problem is adapted ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] [Amazon] |
Markov Property
In probability theory and statistics, the term Markov property refers to the memoryless property of a stochastic process, which means that its future evolution is independent of its history. It is named after the Russian mathematician Andrey Markov. The term strong Markov property is similar to the Markov property, except that the meaning of "present" is defined in terms of a random variable known as a stopping time. The term Markov assumption is used to describe a model where the Markov property is assumed to hold, such as a hidden Markov model. A Markov random field extends this property to two or more dimensions or to random variables defined for an interconnected network of items. An example of a model for such a field is the Ising model. A discrete-time stochastic process satisfying the Markov property is known as a Markov chain. Introduction A stochastic process has the Markov property if the conditional probability distribution of future states of the process (cond ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] [Amazon] |
Stationary Process
In mathematics and statistics, a stationary process (also called a strict/strictly stationary process or strong/strongly stationary process) is a stochastic process whose statistical properties, such as mean and variance, do not change over time. More formally, the joint probability distribution of the process remains the same when shifted in time. This implies that the process is statistically consistent across different time periods. Because many statistical procedures in time series analysis assume stationarity, non-stationary data are frequently transformed to achieve stationarity before analysis. A common cause of non-stationarity is a trend in the mean, which can be due to either a unit root or a deterministic trend. In the case of a unit root, stochastic shocks have permanent effects, and the process is not mean-reverting. With a deterministic trend, the process is called trend-stationary, and shocks have only transitory effects, with the variable tending towards a determin ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] [Amazon] |
Stochastic Process
In probability theory and related fields, a stochastic () or random process is a mathematical object usually defined as a family of random variables in a probability space, where the index of the family often has the interpretation of time. Stochastic processes are widely used as mathematical models of systems and phenomena that appear to vary in a random manner. Examples include the growth of a bacterial population, an electrical current fluctuating due to thermal noise, or the movement of a gas molecule. Stochastic processes have applications in many disciplines such as biology, chemistry, ecology Ecology () is the natural science of the relationships among living organisms and their Natural environment, environment. Ecology considers organisms at the individual, population, community (ecology), community, ecosystem, and biosphere lev ..., neuroscience, physics, image processing, signal processing, stochastic control, control theory, information theory, computer scien ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] [Amazon] |
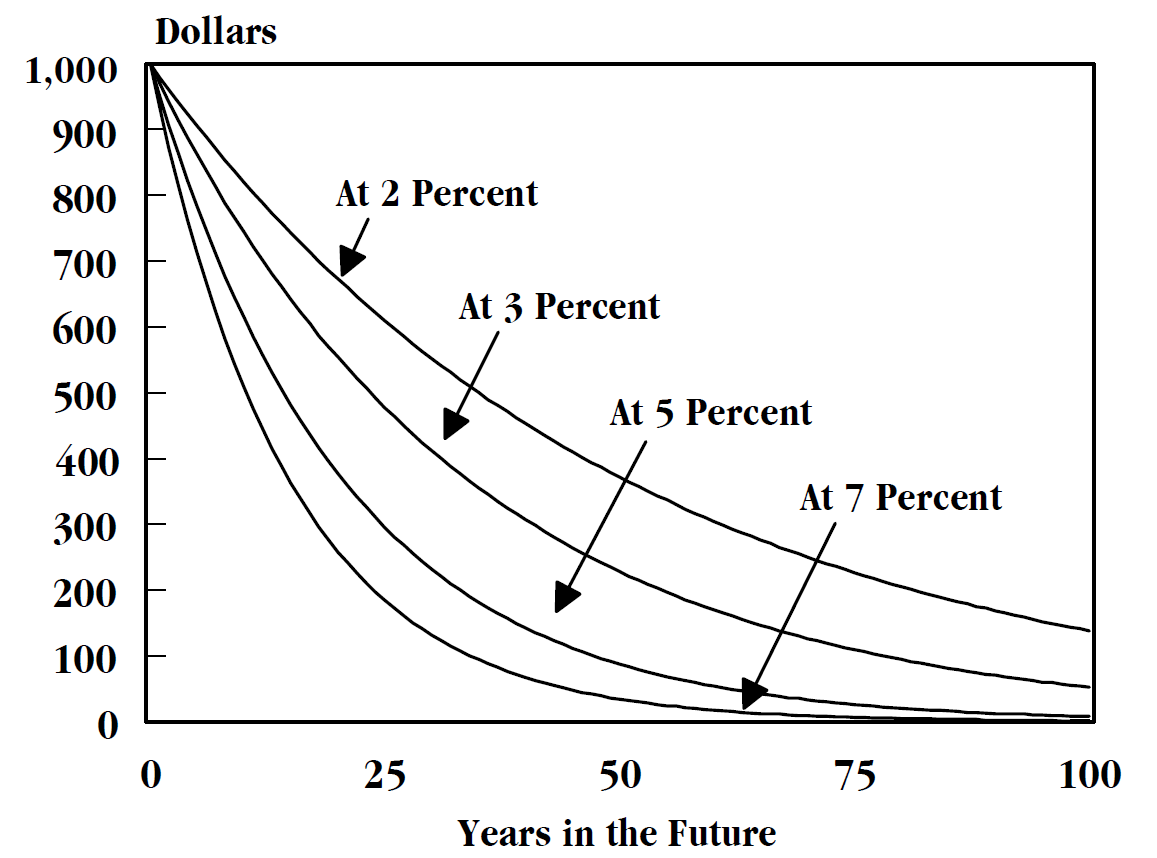
Discounting
In finance, discounting is a mechanism in which a debtor obtains the right to delay payments to a creditor, for a defined period of time, in exchange for a charge or fee.See "Time Value", "Discount", "Discount Yield", "Compound Interest", "Efficient Market", "Market Value" and "Opportunity Cost" in Downes, J. and Goodman, J. E. ''Dictionary of Finance and Investment Terms'', Baron's Financial Guides, 2003. Essentially, the party that owes money in the present purchases the right to delay the payment until some future date.See "Discount", "Compound Interest", "Efficient Markets Hypothesis", "Efficient Resource Allocation", "Pareto-Optimality", "Price", "Price Mechanism" and "Efficient Market" in Black, John, ''Oxford Dictionary of Economics'', Oxford University Press, 2002. This Financial transaction, transaction is based on the fact that most people prefer current interest to delayed interest because of Mortality salience, mortality effects, impatience effects, and Motivational sa ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] [Amazon] |
Decision Theory
Decision theory or the theory of rational choice is a branch of probability theory, probability, economics, and analytic philosophy that uses expected utility and probabilities, probability to model how individuals would behave Rationality, rationally under uncertainty. It differs from the Cognitive science, cognitive and Behavioural sciences, behavioral sciences in that it is mainly Prescriptive economics, prescriptive and concerned with identifying optimal decision, optimal decisions for a rational agent, rather than Descriptive economics, describing how people actually make decisions. Despite this, the field is important to the study of real human behavior by Social science, social scientists, as it lays the foundations to Mathematical model, mathematically model and analyze individuals in fields such as sociology, economics, criminology, cognitive science, moral philosophy and political science. History The roots of decision theory lie in probability theory, developed by Blai ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] [Amazon] |