|
Stickies (papermaking)
When recycling post-consumer paper, stickies are tacky substances contained in the paper pulp and process water systems of paper machines. Stickies have the potential to contaminate the components either within or around the equipment necessary in the Stages of Manufacturing that a Paper Mill follows in its Developed Process, but would have otherwise excluded it in its routine cleaning and maintenance procedures. Contaminations of paper that are classified as tacky are also called stickies. The main sources for stickies are recycled paper, waxes, and soft adhesives. Composition Stickies are an indefinite mixture of organic compounds, with the main part being different esters. The components might stem from: *Printing inks *Coating binders (synthetic latex) *Waxes *Hot melt adhesive and unsupported pressure-sensitive adhesives * Plastics *Wet strength resins * Pitch * Papermaking additives Properties Stickies that pass through a slotted plate screen of 0.10 - 0.15 mm are called ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Pulp (paper)
Pulp is a lignocellulosic fibrous material prepared by chemically or mechanically separating cellulose fibers from wood, fiber crops, waste paper, or rags. Mixed with water and other chemical or plant-based additives, pulp is the major raw material used in papermaking and the industrial production of other paper products. History Before the widely acknowledged invention of papermaking by Cai Lun in China around 105 AD, paper-like writing materials such as papyrus and amate were produced by ancient civilizations using plant materials which were largely unprocessed. Strips of bark or bast material were woven together, beaten into rough sheets, dried, and polished by hand. Pulp used in modern and traditional papermaking is distinguished by the process which produces a finer, more regular slurry of cellulose fibers which are pulled out of solution by a screen and dried to form sheets or rolls. The earliest paper produced in China consisted of bast fibers from the paper mulberr ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Wet Strength
The wet strength of paper and paperboard is a measure of how well the web of fibers holding the paper together can resist a force of rupture when the paper is wet. Wet strength is routinely expressed as the ratio of wet to dry Tensile strength, tensile force at break. With combined board such as corrugated fiberboard or with laminations, wet strength also includes the ability to stay intact under humid or wet conditions. Wet strength adhesives are often needed. Mechanism The cellulose fibreweb of paper is mainly held together by hydrogen bonds. These are dependent on physical contact between the fibres and can be broken by wetting of the fibres. The residual strength of a wetted paper can be less than 10% of the original strength. Various techniques, such as refining of the pulp (paper), pulp and wet pressing on the paper machine can be used to reduce the strength loss of the paper upon wetting. To improve the wet strength it is common to use chemicals. The use of chemicals c ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Charge (physics)
In physics, a charge is any of many different quantities, such as the electric charge in electromagnetism or the color charge in quantum chromodynamics. Charges correspond to the time-invariant generators of a symmetry group, and specifically, to the generators that commute with the Hamiltonian. Charges are often denoted by the letter ''Q'', and so the invariance of the charge corresponds to the vanishing commutator ,H0, where H is the Hamiltonian. Thus, charges are associated with conserved quantum numbers; these are the eigenvalues ''q'' of the generator ''Q''. Abstract definition Abstractly, a charge is any generator of a continuous symmetry of the physical system under study. When a physical system has a symmetry of some sort, Noether's theorem implies the existence of a conserved current. The thing that "flows" in the current is the "charge", the charge is the generator of the (local) symmetry group. This charge is sometimes called the Noether charge. Thus, for exampl ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
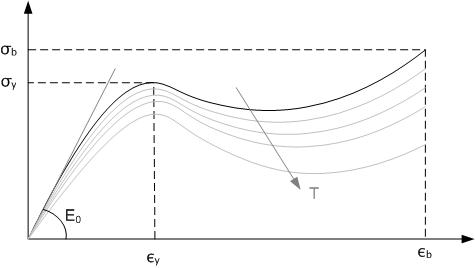
Temperature
Temperature is a physical quantity that expresses quantitatively the perceptions of hotness and coldness. Temperature is measured with a thermometer. Thermometers are calibrated in various temperature scales that historically have relied on various reference points and thermometric substances for definition. The most common scales are the Celsius scale with the unit symbol °C (formerly called ''centigrade''), the Fahrenheit scale (°F), and the Kelvin scale (K), the latter being used predominantly for scientific purposes. The kelvin is one of the seven base units in the International System of Units (SI). Absolute zero, i.e., zero kelvin or −273.15 °C, is the lowest point in the thermodynamic temperature scale. Experimentally, it can be approached very closely but not actually reached, as recognized in the third law of thermodynamics. It would be impossible to extract energy as heat from a body at that temperature. Temperature is important in all fields of natur ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Thermoplastic
A thermoplastic, or thermosoft plastic, is any plastic polymer material that becomes pliable or moldable at a certain elevated temperature and solidifies upon cooling. Most thermoplastics have a high molecular weight. The polymer chains associate by intermolecular forces, which weaken rapidly with increased temperature, yielding a viscous liquid. In this state, thermoplastics may be reshaped and are typically used to produce parts by various polymer processing techniques such as injection molding, compression molding, calendering, and extrusion. Thermoplastics differ from thermosetting polymers (or "thermosets"), which form irreversible chemical bonds during the curing process. Thermosets do not melt when heated, but typically decompose and do not reform upon cooling. Above its glass transition temperature and below its melting point, the physical properties of a thermoplastic change drastically without an associated phase change. Some thermoplastics do not fully crystallize ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Deposits
A deposit account is a bank account maintained by a financial institution in which a customer can deposit and withdraw money. Deposit accounts can be savings accounts, Transaction account#Current accounts, current accounts or any of several other types of accounts explained below. Transactions on deposit accounts are recorded in a bank's books, and the resulting balance is recorded as a Liability (accounting), liability of the bank and represents an amount owed by the bank to the customer. In other words, the banker-customer (depositor) relationship is one of debtor-creditor. Some banks charge fees for transactions on a customer's account. Additionally, some banks pay customers Interest (finance), interest on their account balances. Types of accounts * How banking works In banking, the verbs "deposit" and "withdraw" mean a customer paying money into, and taking money out of, an account, respectively. From a legal and financial accounting standpoint, the noun "deposit" is used ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Flocculation
Flocculation, in the field of chemistry, is a process by which colloidal particles come out of suspension to sediment under the form of floc or flake, either spontaneously or due to the addition of a clarifying agent. The action differs from precipitation in that, prior to flocculation, colloids are merely suspended, under the form of a stable dispersion (where the internal phase (solid) is dispersed throughout the external phase (fluid) through mechanical agitation) and are not truly dissolved in solution. Coagulation and flocculation are important processes in water treatment with coagulation aimed to destabilize and aggregate particles through chemical interactions between the coagulant and colloids, and flocculation to sediment the destabilized particles by causing their aggregation into floc. Term definition According to the IUPAC definition, flocculation is "a process of contact and adhesion whereby the particles of a dispersion form larger-size clusters". Flocculation ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Deinking
Deinking is the industrial process of removing printing ink from paperfibers of recycled paper to make deinked pulp. The key in the deinking process is the ability to detach ink from the fibers. This is achieved by a combination of mechanical action and chemical means. In Europe the most common process is froth flotation deinking. Paper is one of the main targets for recycling. A concern about recycling wood pulp paper is that the fibers are degraded with each cycle and after being recycled 4–6 times the fibers become too short and weak to be useful in making paper. History Before the invention of the paper machine in 1799 the most common fibre source was recycled fibres from used textiles, hence the name rag paper. The rags were from hemp, linen and cotton. It was not until the introduction of wood pulp in 1843 that paper production was independent of recycled materials. Recycling of used paper before the industrialisation of paper production, rag paper was recycled to m ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Deinked Pulp
Pulp is a lignocellulosic fibrous material prepared by chemically or mechanically separating cellulose fibers from wood, fiber crops, waste paper, or rags. Mixed with water and other chemical or plant-based additives, pulp is the major raw material used in papermaking and the industrial production of other paper products. History Before the widely acknowledged invention of papermaking by Cai Lun in China around 105 AD, paper-like writing materials such as papyrus and amate were produced by ancient civilizations using plant materials which were largely unprocessed. Strips of bark or bast material were woven together, beaten into rough sheets, dried, and polished by hand. Pulp used in modern and traditional papermaking is distinguished by the process which produces a finer, more regular slurry of cellulose fibers which are pulled out of solution by a screen and dried to form sheets or rolls. The earliest paper produced in China consisted of bast fibers from the paper mulberry ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Nanometer
330px, Different lengths as in respect to the molecular scale. The nanometre (international spelling as used by the International Bureau of Weights and Measures; SI symbol: nm) or nanometer (American and British English spelling differences#-re, -er, American spelling) is a units of measurement, unit of length in the International System of Units (SI), equal to one billionth (short scale) of a metre () and to 1000 picometres. One nanometre can be expressed in scientific notation as , and as metres. History The nanometre was formerly known as the millimicrometre – or, more commonly, the millimicron for short – since it is of a micron (micrometre), and was often denoted by the symbol mμ or (more rarely and confusingly, since it logically should refer to a ''millionth'' of a micron) as μμ. Etymology The name combines the SI prefix ''nano-'' (from the Ancient Greek , ', "dwarf") with the parent unit name ''metre'' (from Greek , ', "unit of measurement"). ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Papermaking
Papermaking is the manufacture of paper and cardboard, which are used widely for printing, writing, and packaging, among many other purposes. Today almost all paper is made using industrial machinery, while handmade paper survives as a specialized craft and a medium for artistic expression. In papermaking, a dilute suspension consisting mostly of separate cellulose fibres in water is drained through a sieve-like screen, so that a mat of randomly interwoven fibres is laid down. Water is further removed from this sheet by pressing, sometimes aided by suction or vacuum, or heating. Once dry, a generally flat, uniform and strong sheet of paper is achieved. Before the invention and current widespread adoption of automated machinery, all paper was made by hand, formed or laid one sheet at a time by specialized laborers. Even today those who make paper by hand use tools and technologies quite similar to those existing hundreds of years ago, as originally developed in China and other ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Pitch (resin)
Pitch is a viscoelastic polymer which can be natural or manufactured, derived from petroleum, coal tar, or plants. Various forms of pitch may also be called tar, bitumen, or asphalt. Pitch produced from plants is also known as resin. Some products made from plant resin are also known as rosin. Uses Pitch was traditionally used to help caulk the seams of wooden sailing vessels (see shipbuilding), and to coat earthenware vessels for the preservation of wine. Pitch may also be used to waterproof wooden containers and in the making of torches. Petroleum-derived pitch is black in colour, hence the adjectival phrase, "pitch-black". The viscoelastic properties of pitch make it well suited for the polishing of high-quality optical lenses and mirrors. In use, the pitch is formed into a lap or polishing surface, which is charged with iron oxide ( Jewelers' rouge) or cerium oxide. The surface to be polished is pressed into the pitch, then rubbed against the surface so formed. The ability ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |

.jpg)