|
Stereoselective
In chemistry, stereoselectivity is the property of a chemical reaction in which a single reactant forms an unequal mixture of stereoisomers during a non-stereospecific creation of a new stereocenter or during a non-stereospecific transformation of a pre-existing one. The selectivity arises from differences in steric and electronic effects in the mechanistic pathways leading to the different products. Stereoselectivity can vary in degree but it can never be total since the activation energy difference between the two pathways is finite. Both products are at least possible and merely differ in amount. However, in favorable cases, the minor stereoisomer may not be detectable by the analytic methods used. An enantioselective reaction is one in which one enantiomer is formed in preference to the other, in a reaction that creates an optically active product from an achiral starting material, using either a chiral catalyst, an enzyme or a chiral reagent. The degree of selectivity is measu ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Stereospecificity
In chemistry, stereospecificity is the property of a reaction mechanism that leads to different stereoisomeric reaction products from different stereoisomeric reactants, or which operates on only one (or a subset) of the stereoisomers."Overlap Control of Carbanionoid Reactions. I. Stereoselectivity in Alkaline Epoxidation," Zimmerman, H. E.; Singer, L.; Thyagarajan, B. S. J. Am. Chem. Soc., 1959, 81, 108-116.Eliel, E., "Stereochemistry of Carbon Compound", McGraw-Hill, 1962 pp 434-436 In contrast, stereoselectivity is the property of a reactant mixture where a non-stereospecific mechanism allows for the formation of multiple products, but where one (or a subset) of the products is favored by factors, such as steric access, that are independent of the mechanism. A stereospecific mechanism ''specifies'' the stereochemical outcome of a given reactant, whereas a stereoselective reaction ''selects'' products from those made available by the same, non-specific mechanism acting on a g ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
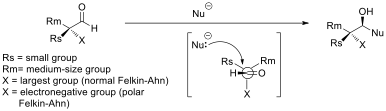
Cram's Rule
In stereochemistry, asymmetric induction (also enantioinduction) describes the preferential formation in a chemical reaction of one enantiomer or diastereoisomer over the other as a result of the influence of a optical isomerism, chiral feature present in the Substrate (chemistry), substrate, reagent, catalyst or environment. Asymmetric induction is a key element in asymmetric synthesis. Asymmetric induction was introduced by Hermann Emil Fischer based on his work on carbohydrates. Several types of induction exist. Internal asymmetric induction makes use of a chiral center bound to the reactive center through a covalent bond and remains so during the reaction. The starting material is often derived from chiral pool synthesis. In relayed asymmetric induction the chiral information is introduced in a separate step and removed again in a separate chemical reaction. Special synthons are called chiral auxiliary, chiral auxiliaries. In external asymmetric induction chiral information ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Pinoresinol
Pinoresinol is a tetrahydrofuran lignan found in ''Styrax sp.'', ''Forsythia suspensa, and in Forsythia koreana''. It is also found in the caterpillar of the cabbage butterfly, ''Pieris rapae'' where it serves as a defence against ants. In food, it is found in sesame seed, in ''Brassica'' vegetables and in olive oil. Pinoresinol has also been found to be toxic to larvae of the milkweed bug Oncopeltus fasciatus and of the haematophagous insect Rhodnius prolixus, which is a vector of chagas disease. Currently, pinoresinol is isolated from plants with low efficiency and low yield. Biosynthesis A first dirigent protein was discovered in '' Forsythia intermedia''. This protein has been found to direct the stereoselective biosynthesis of (+)-pinoresinol from coniferyl alcohol monomers. Recently, a second, enantiocomplementary dirigent protein was identified in ''Arabidopsis thaliana'', which directs enantioselective synthesis of (-)-pinoresinol. Pharmacology Pinoresinol inhib ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Kinetic Resolution
In organic chemistry, kinetic resolution is a means of differentiating two enantiomers in a racemic mixture. In kinetic resolution, two enantiomers react with different reaction rates in a chemical reaction with a chiral catalyst or reagent, resulting in an enantioenriched sample of the less reactive enantiomer. As opposed to chiral resolution, kinetic resolution does not rely on different physical properties of diastereomeric products, but rather on the different chemical properties of the racemic starting materials. The enantiomeric excess (ee) of the unreacted starting material continually rises as more product is formed, reaching 100% just before full completion of the reaction. Kinetic resolution relies upon differences in reactivity between enantiomers or enantiomeric complexes. Kinetic resolution can be used for the preparation of chiral molecules in organic synthesis. Kinetic resolution reactions utilizing purely synthetic reagents and catalysts are much less common tha ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Dirigent Protein
Dirigent proteins are members of a class of proteins which dictate the stereochemistry of a compound synthesized by other enzymes. The first dirigent protein was discovered in ''Forsythia intermedia''. This protein has been found to direct the stereoselective biosynthesis of (+)-pinoresinol from coniferyl alcohol monomers: Lignan biosynthesis is catalysed by oxidative enzymes. In the test tube the reaction results in a heteregenous mixture of dimeric compounds. When a dirigent protein is present during the reaction, one stereoisomer of one compound is highly enriched. Dirigent proteins appear to possess no oxidative radical forming activity of their own; in the absence of oxidative enzyme, no reaction will occur. Recently, a second, enantiocomplementary dirigent protein was identified in ''Arabidopsis thaliana'', which directs enantioselective synthesis of (-)-pinoresinol. Activity In lignan biosynthesis, oxidative enzymes perform proton coupled electron transfer to remove ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
T-butyl
In organic chemistry, butyl is a four-carbon alkyl radical or substituent group with general chemical formula , derived from either of the two isomers (''n''-butane and isobutane) of butane. The isomer ''n''-butane can connect in two ways, giving rise to two "-butyl" groups: * If it connects at one of the two terminal carbon atoms, it is normal butyl or ''n''-butyl: (preferred IUPAC name: butyl) * If it connects at one of the non-terminal (internal) carbon atoms, it is secondary butyl or ''sec''-butyl: (preferred IUPAC name: butan-2-yl) The second isomer of butane, isobutane, can also connect in two ways, giving rise to two additional groups: * If it connects at one of the three terminal carbons, it is isobutyl: (preferred IUPAC name: 2-methylpropyl) * If it connects at the central carbon, it is tertiary butyl, ''tert''-butyl or ''t''-butyl: (preferred IUPAC name: ''tert''-butyl) Nomenclature According to IUPAC nomenclature, "isobutyl", "''sec''-butyl", and "''tert''-b ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Stereogenic
In stereochemistry, a stereocenter of a molecule is an atom (center), axis or plane that is the focus of stereoisomerism; that is, when having at least three different groups bound to the stereocenter, interchanging any two different groups creates a new stereoisomer. Stereocenters are also referred to as stereogenic centers. A stereocenter is geometrically defined as a point (location) in a molecule; a stereocenter is usually but not always a specific atom, often carbon. Stereocenters can exist on chiral or achiral molecules; stereocenters can contain single bonds or double bonds. The number of hypothetical stereoisomers can be predicted by using 2''n'', with ''n'' being the number of tetrahedral stereocenters; however, exceptions such as meso compounds can reduce the prediction to below the expected 2''n''. Chirality centers are a type of stereocenter with four different substituent groups; chirality centers are a specific subset of stereocenters because they can only hav ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Sharpless Asymmetric Dihydroxylation
Sharpless asymmetric dihydroxylation (also called the Sharpless bishydroxylation) is the chemical reaction of an alkene with osmium tetroxide in the presence of a chiral quinine ligand to form a vicinal diol. The reaction has been applied to alkenes of virtually every substitution, often high enantioselectivities are realized, with the chiral outcome controlled by the choice of dihydroquinidine (DHQD) vs dihydroquinine (DHQ) as the ligand. Asymmetric dihydroxylation reactions are also highly site selective, providing products derived from reaction of the most electron-rich double bond in the substrate. It is common practice to perform this reaction using a catalytic amount of osmium tetroxide, which after reaction is regenerated with reoxidants such as potassium ferricyanide or ''N''-methylmorpholine ''N''-oxide. This dramatically reduces the amount of the highly toxic and very expensive osmium tetroxide needed. These four reagents are commercially available premixed (" AD- ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |