|
Stenosis Of Pulmonary Artery
Stenosis of the pulmonary artery is a condition where the pulmonary artery is subject to an abnormal constriction (or stenosis). Peripheral pulmonary artery stenosis may occur as an isolated event or in association with Alagille syndrome, Berardinelli-Seip congenital lipodystrophy type 1, Costello syndrome, Keutel syndrome, nasodigitoacoustic syndrome (Keipert syndrome), Noonan syndrome or Williams syndrome. It should not be confused with a pulmonary valve stenosis, which is in the heart, but can have similar hemodynamic effects. Both stenosis of the pulmonary artery and pulmonary valve stenosis are causes of pulmonic stenosis Pulmonic stenosis, is a dynamic or fixed obstruction of flow from the right ventricle of the heart to the pulmonary artery. It is usually first diagnosed in childhood. Signs and symptoms Cause Pulmonic stenosis is usually due to isolated valvula ....In some cases it is treated with surgery. References External links Congenital vascular defects [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
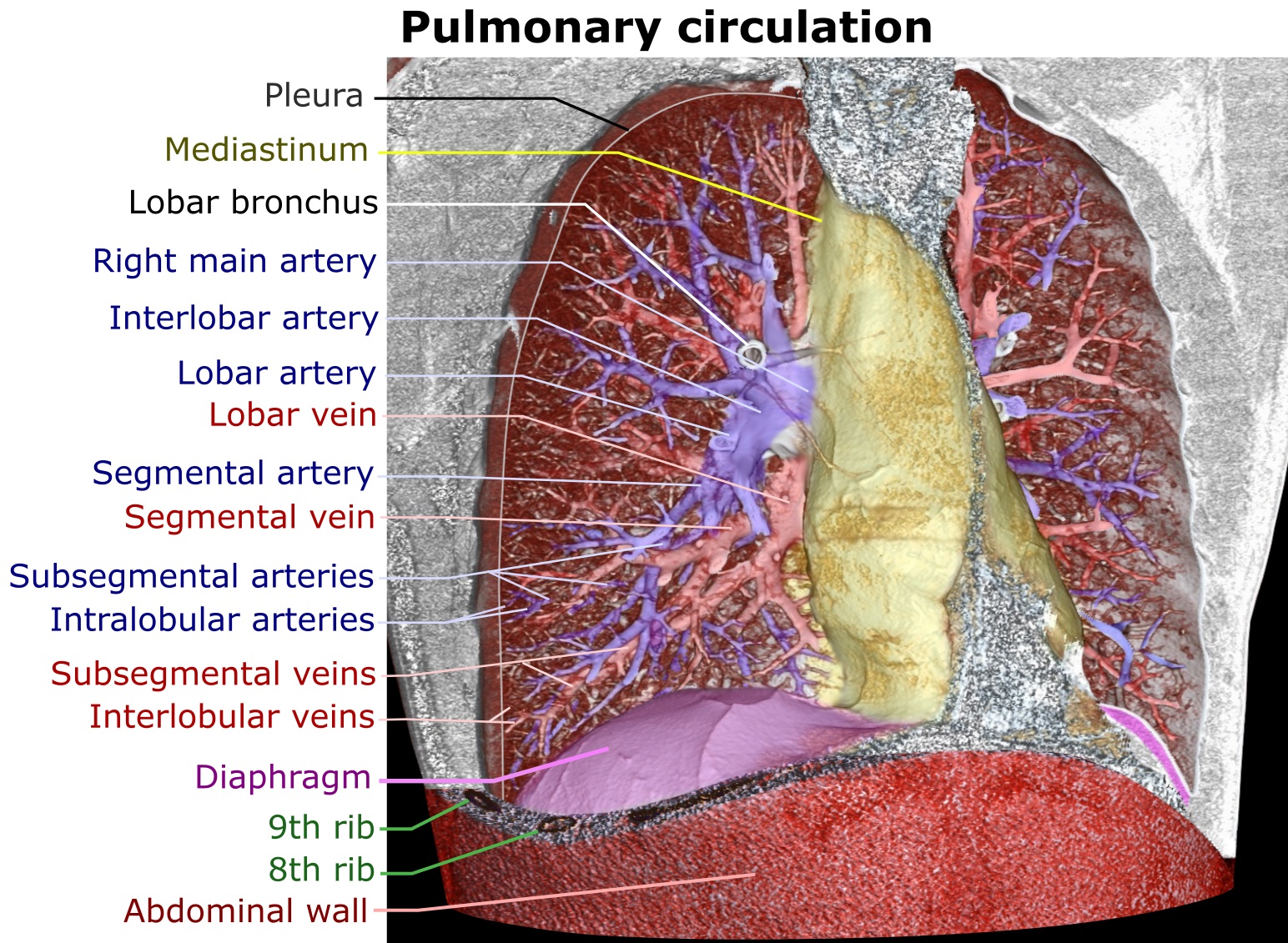
Pulmonary Artery
A pulmonary artery is an artery in the pulmonary circulation that carries deoxygenated blood from the right side of the heart to the lungs. The largest pulmonary artery is the ''main pulmonary artery'' or ''pulmonary trunk'' from the heart, and the smallest ones are the arterioles, which lead to the capillaries that surround the pulmonary alveoli. Structure The pulmonary arteries are blood vessels that carry systemic venous blood from the right ventricle of the heart to the microcirculation of the lungs. Unlike in other organs where arteries supply oxygenated blood, the blood carried by the pulmonary arteries is deoxygenated, as it is venous blood returning to the heart. The main pulmonary arteries emerge from the right side of the heart, and then split into smaller arteries that progressively divide and become arterioles, eventually narrowing into the capillary microcirculation of the lungs where gas exchange occurs. Pulmonary trunk In order of blood flow, the pulmonary art ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Stenosis
A stenosis (from Ancient Greek στενός, "narrow") is an abnormal narrowing in a blood vessel or other tubular organ or structure such as foramina and canals. It is also sometimes called a stricture (as in urethral stricture). ''Stricture'' as a term is usually used when narrowing is caused by contraction of smooth muscle (e.g. achalasia, prinzmetal angina); ''stenosis'' is usually used when narrowing is caused by lesion that reduces the space of lumen (e.g. atherosclerosis). The term coarctation is another synonym, but is commonly used only in the context of aortic coarctation. Restenosis is the recurrence of stenosis after a procedure. Types The resulting syndrome depends on the structure affected. Examples of vascular stenotic lesions include: * Intermittent claudication (peripheral artery stenosis) * Angina ( coronary artery stenosis) * Carotid artery stenosis which predispose to (strokes and transient ischaemic episodes) * Renal artery stenosis The types of sten ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
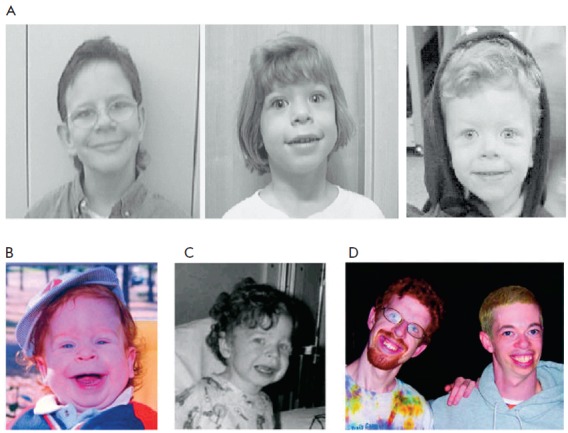
Alagille Syndrome
Alagille syndrome is a genetic disorder that affects primarily the liver and the heart. Problems associated with the disorder generally become evident in infancy or early childhood. The disorder is inherited in an autosomal dominant pattern, and the estimated prevalence of Alagille syndrome is 1 in every 30,000 to 1 in every 40,000 live births. It is named after the French pediatrician Daniel Alagille, who first described the condition in 1969. Signs and symptoms The severity of the disorder can vary within the same family, with symptoms ranging from so mild as to go unnoticed, to severe heart and/or liver disease that requires transplantation. It is uncommon, but Alagille syndrome can be a life-threatening disease with a mortality rate of 10%. The majority of deaths from ALGS are typically due to heart complications or chronic liver failure. Liver Signs and symptoms arising from liver damage in Alagille syndrome may include a yellowish tinge in the skin and the whites of t ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Lipodystrophy
Lipodystrophy syndromes are a group of genetic or acquired disorders in which the body is unable to produce and maintain healthy fat tissue. The medical condition is characterized by abnormal or degenerative conditions of the body's adipose tissue. A more specific term, ''lipoatrophy ("lipo" is Greek for "fat", and "dystrophy" is Greek for "abnormal or degenerative condition")'', is used when describing the loss of fat from one area (usually the face). This condition is also characterized by a lack of circulating leptin which may lead to osteosclerosis. The absence of fat tissue is associated with insulin resistance, hypertriglyceridemia, non-alcoholic fatty liver disease (NAFLD) and metabolic syndrome. Types Lipodystrophy can be divided into the following types: *Congenital lipodystrophy syndromes **Congenital generalized lipodystrophy (Berardinelli-Seip syndrome) **Familial partial lipodystrophy **Marfanoid–progeroid–lipodystrophy syndrome ** Chronic atypical neutrophilic d ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Costello Syndrome
Costello syndrome, also called faciocutaneoskeletal syndrome or FCS syndrome, is a rare genetic disorder that affects many parts of the body. It is characterized by delayed development and intellectual disabilities, distinctive facial features, unusually flexible joints, and loose folds of extra skin, especially on the hands and feet.James, William; Berger, Timothy; Elston, Dirk (2005). ''Andrews' Diseases of the Skin: Clinical Dermatology''. (10th ed.). Saunders. . Heart abnormalities are common, including a very fast heartbeat (tachycardia), structural heart defects, and overgrowth of the heart muscle (hypertrophic cardiomyopathy). Infants with Costello syndrome may be large at birth, but grow more slowly than other children and have difficulty feeding. Later in life, people with this condition have relatively short stature and many have reduced levels of growth hormones. It is a RASopathy. Beginning in early childhood, people with specific mutations on the Costello syndrome gene ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Keutel Syndrome
Keutel syndrome (KS) is a rare autosomal recessive genetic disorder characterized by abnormal diffuse cartilage calcification, hypoplasia of the mid-face, peripheral pulmonary stenosis, hearing loss, short distal phalanges (tips) of the fingers and mild mental retardation. Individuals with KS often present with peripheral pulmonary stenosis, brachytelephalangism, sloping forehead, midface hypoplasia, and receding chin. It is associated with abnormalities in the gene coding for matrix gla protein, ''MGP''. Being an autosomal recessive disorder, it may be inherited from two unaffected, abnormal MGP-carrying parents. Thus, people who inherit two affected ''MGP'' alleles will likely inherit KS. It was first identified in 1972 as a novel rare genetic disorder sharing similar symptoms with chondrodysplasia punctata. Multiple forms of chondrodysplasia punctata share symptoms consistent with KS including abnormal cartilage calcification, forceful respiration, brachytelephalangism, hypoto ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Nasodigitoacoustic Syndrome
Nasodigitoacoustic syndrome, also called Keipert syndrome, is a rare congenital syndrome first described by J.A. Keipert and colleagues in 1973. The syndrome is characterized by a misshaped nose, broad thumbs and halluces (the big toes), brachydactyly, sensorineural hearing loss, facial features such as hypertelorism (unusually wide-set eyes), and developmental delay. It is believed to be inherited in an X-linked recessive manner, which means a genetic mutation causing the disorder is located on the X chromosome, and while two copies of the mutated gene must be inherited for a female to be born with the disorder, just one copy is sufficient to cause a male to be born with the disorder. Nasodigitoacoustic syndrome is likely caused by a mutated gene located on the X chromosome between positions Xq22.2–q28. The incidence of the syndrome has not been determined, but it is considered to affect less than 200,000 people in the United States, and no greater than 1 per 2,000 in Europ ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Noonan Syndrome
Noonan syndrome (NS) is a genetic disorder that may present with mildly unusual facial features, short height, congenital heart disease, bleeding problems, and skeletal malformations. Facial features include widely spaced eyes, light-colored eyes, low-set ears, a short neck, and a small lower jaw. Heart problems may include pulmonary valve stenosis. The breast bone may either protrude or be sunken, while the spine may be abnormally curved. Intelligence in the syndrome is often normal. Complications of NS can include leukemia. A number of genetic mutations can result in Noonan syndrome. The condition may be inherited from a person's parents as an autosomal dominant condition or occur as a new mutation. Noonan syndrome is a type of RASopathy, the underlying mechanism for which involves overactivation within the RAS/MAPK cell signaling pathway. The diagnosis may be suspected based on symptoms, medical imaging, and blood tests. Confirmation may be achieved with genetic tes ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Williams Syndrome
Williams syndrome (WS) is a genetic disorder that affects many parts of the body. Facial features frequently include a broad forehead, underdeveloped chin, short nose, and full cheeks. Mild to moderate intellectual disability is observed in people with WS, with particular challenges with visual spatial tasks such as drawing. Verbal skills are relatively unaffected. Many people with WS have an outgoing personality, an openness to engaging with other people, and a happy disposition. Medical issues with teeth, heart problems (especially supravalvular aortic stenosis), and periods of high blood calcium are common. Williams syndrome is caused by a genetic abnormality, specifically a deletion of about 27 genes from the long arm of one of the two chromosome 7s. Typically, this occurs as a random event during the formation of the egg or sperm from which a person develops. In a small number of cases, it is inherited from an affected parent in an autosomal dominant manner. The different ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Pulmonary Valve Stenosis
Pulmonary valve stenosis (PVS) is a heart valve disorder. Blood going from the heart to the lungs goes through the pulmonary valve, whose purpose is to prevent blood from flowing back to the heart. In pulmonary valve stenosis this opening is too narrow, leading to a reduction of flow of blood to the lungs. While the most common cause of pulmonary valve stenosis is congenital heart disease, it may also be due to a malignant carcinoid tumor. Both stenosis of the pulmonary artery and pulmonary valve stenosis are forms of pulmonic stenosis (nonvalvular and valvular, respectively) but pulmonary valve stenosis accounts for 80% of pulmonic stenosis. PVS was the key finding that led Jacqueline Noonan to identify the syndrome now called Noonan syndrome. Symptoms and signs Among some of the symptoms consistent with pulmonary valve stenosis are the following: * Heart murmur * Cyanosis * Dyspnea * Dizziness * Upper thorax pain * Developmental disorders Cause In regards to the cause of pul ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Heart
The heart is a muscular organ in most animals. This organ pumps blood through the blood vessels of the circulatory system. The pumped blood carries oxygen and nutrients to the body, while carrying metabolic waste such as carbon dioxide to the lungs. In humans, the heart is approximately the size of a closed fist and is located between the lungs, in the middle compartment of the chest. In humans, other mammals, and birds, the heart is divided into four chambers: upper left and right atria and lower left and right ventricles. Commonly the right atrium and ventricle are referred together as the right heart and their left counterparts as the left heart. Fish, in contrast, have two chambers, an atrium and a ventricle, while most reptiles have three chambers. In a healthy heart blood flows one way through the heart due to heart valves, which prevent backflow. The heart is enclosed in a protective sac, the pericardium, which also contains a small amount of fluid. The wall ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |