|
Stemming Over Ruilverkaveling In Tubbergen (Twente) Boer Demonstreren Tegen Ste, Bestanddeelnr 925-2
In linguistic morphology and information retrieval, stemming is the process of reducing inflected (or sometimes derived) words to their word stem, base or root form—generally a written word form. The stem need not be identical to the morphological root of the word; it is usually sufficient that related words map to the same stem, even if this stem is not in itself a valid root. Algorithms for stemming have been studied in computer science since the 1960s. Many search engines treat words with the same stem as synonyms as a kind of query expansion, a process called conflation. A computer program or subroutine that stems word may be called a ''stemming program'', ''stemming algorithm'', or ''stemmer''. Examples A stemmer for English operating on the stem ''cat'' should identify such strings as ''cats'', ''catlike'', and ''catty''. A stemming algorithm might also reduce the words ''fishing'', ''fished'', and ''fisher'' to the stem ''fish''. The stem need not be a word, for example ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Linguistic Morphology
In linguistics, morphology () is the study of words, how they are formed, and their relationship to other words in the same language. It analyzes the structure of words and parts of words such as stems, root words, prefixes, and suffixes. Morphology also looks at parts of speech, intonation and stress, and the ways context can change a word's pronunciation and meaning. Morphology differs from morphological typology, which is the classification of languages based on their use of words, and lexicology, which is the study of words and how they make up a language's vocabulary. While words, along with clitics, are generally accepted as being the smallest units of syntax, in most languages, if not all, many words can be related to other words by rules that collectively describe the grammar for that language. For example, English speakers recognize that the words ''dog'' and ''dogs'' are closely related, differentiated only by the plurality morpheme "-s", only found bound to noun phr ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Michael Lesk
Michael E. Lesk (born 1945) is an American computer scientist. Biography In the 1960s, Michael Lesk worked for the SMART Information Retrieval System project, wrote much of its retrieval code and did many of the retrieval experiments, as well as obtaining a BA degree in Physics and Chemistry from Harvard College in 1964 and a PhD from Harvard University in Chemical Physics in 1969. From 1970 to 1984, Lesk worked at Bell Labs in the group that built Unix. Lesk wrote Unix tools for word processing (''tbl'', ''refer'', and the standard ''ms'' macro package, all for ''troff''), for compiling (''Lex''), and for networking (''uucp''). He also wrote the Portable I/O Library (the predecessor to stdio.h in C) and contributed significantly to the development of the C language preprocessor. In 1984, he left to work for Bellcore, where he managed the computer science research group. There, Lesk worked on specific information systems applications, mostly with geography (a system for drivi ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
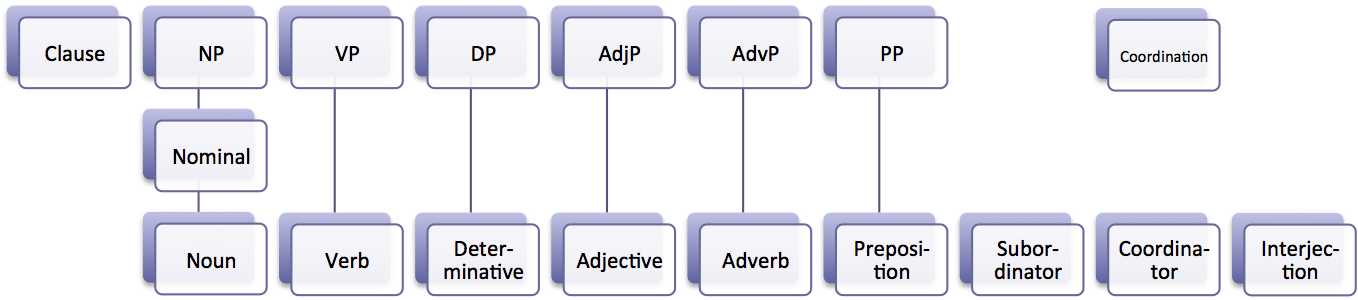
Part Of Speech
In grammar, a part of speech or part-of-speech (abbreviated as POS or PoS, also known as word class or grammatical category) is a category of words (or, more generally, of lexical items) that have similar grammatical properties. Words that are assigned to the same part of speech generally display similar syntactic behavior (they play similar roles within the grammatical structure of sentences), sometimes similar morphological behavior in that they undergo inflection for similar properties and even similar semantic behavior. Commonly listed English parts of speech are noun, verb, adjective, adverb, pronoun, preposition, conjunction, interjection, numeral, article, and determiner. Other terms than ''part of speech''—particularly in modern linguistic classifications, which often make more precise distinctions than the traditional scheme does—include word class, lexical class, and lexical category. Some authors restrict the term ''lexical category'' to refer only to a particular ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Lemmatisation
Lemmatisation ( or lemmatization) in linguistics is the process of grouping together the inflected forms of a word so they can be analysed as a single item, identified by the word's lemma, or dictionary form. In computational linguistics, lemmatisation is the algorithmic process of determining the lemma of a word based on its intended meaning. Unlike stemming, lemmatisation depends on correctly identifying the intended part of speech and meaning of a word in a sentence, as well as within the larger context surrounding that sentence, such as neighboring sentences or even an entire document. As a result, developing efficient lemmatisation algorithms is an open area of research. Description In many languages, words appear in several ''inflected'' forms. For example, in English, the verb 'to walk' may appear as 'walk', 'walked', 'walks' or 'walking'. The base form, 'walk', that one might look up in a dictionary, is called the ''lemma'' for the word. The association of the base form ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Lemmatisation
Lemmatisation ( or lemmatization) in linguistics is the process of grouping together the inflected forms of a word so they can be analysed as a single item, identified by the word's lemma, or dictionary form. In computational linguistics, lemmatisation is the algorithmic process of determining the lemma of a word based on its intended meaning. Unlike stemming, lemmatisation depends on correctly identifying the intended part of speech and meaning of a word in a sentence, as well as within the larger context surrounding that sentence, such as neighboring sentences or even an entire document. As a result, developing efficient lemmatisation algorithms is an open area of research. Description In many languages, words appear in several ''inflected'' forms. For example, in English, the verb 'to walk' may appear as 'walk', 'walked', 'walks' or 'walking'. The base form, 'walk', that one might look up in a dictionary, is called the ''lemma'' for the word. The association of the base form ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Lexical Category
In grammar, a part of speech or part-of-speech (abbreviated as POS or PoS, also known as word class or grammatical category) is a category of words (or, more generally, of lexical items) that have similar grammatical properties. Words that are assigned to the same part of speech generally display similar syntactic behavior (they play similar roles within the grammatical structure of sentences), sometimes similar morphological behavior in that they undergo inflection for similar properties and even similar semantic behavior. Commonly listed English parts of speech are noun, verb, adjective, adverb, pronoun, preposition, conjunction, interjection, numeral, article, and determiner. Other terms than ''part of speech''—particularly in modern linguistic classifications, which often make more precise distinctions than the traditional scheme does—include word class, lexical class, and lexical category. Some authors restrict the term ''lexical category'' to refer only to a partic ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Part-of-speech Tagging
In corpus linguistics, part-of-speech tagging (POS tagging or PoS tagging or POST), also called grammatical tagging is the process of marking up a word in a text (corpus) as corresponding to a particular part of speech, based on both its definition and its context. A simplified form of this is commonly taught to school-age children, in the identification of words as nouns, verbs, adjectives, adverbs, etc. Once performed by hand, POS tagging is now done in the context of computational linguistics, using algorithms which associate discrete terms, as well as hidden parts of speech, by a set of descriptive tags. POS-tagging algorithms fall into two distinctive groups: rule-based and stochastic. E. Brill's tagger, one of the first and most widely used English POS-taggers, employs rule-based algorithms. Principle Part-of-speech tagging is harder than just having a list of words and their parts of speech, because some words can represent more than one part of speech at different times, ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Lookup Table
In computer science, a lookup table (LUT) is an array that replaces runtime computation with a simpler array indexing operation. The process is termed as "direct addressing" and LUTs differ from hash tables in a way that, to retrieve a value v with key k, a hash table would store the value v in the slot h(k) where h is a hash function i.e. k is used to compute the slot, while in the case of LUT, the value v is stored in slot k, thus directly addressable. The savings in processing time can be significant, because retrieving a value from memory is often faster than carrying out an "expensive" computation or input/output operation. The tables may be precalculated and stored in static program storage, calculated (or "pre-fetched") as part of a program's initialization phase ( memoization), or even stored in hardware in application-specific platforms. Lookup tables are also used extensively to validate input values by matching against a list of valid (or invalid) items in an array and ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Christopher D
Christopher is the English version of a Europe-wide name derived from the Greek name Χριστόφορος (''Christophoros'' or '' Christoforos''). The constituent parts are Χριστός (''Christós''), "Christ" or "Anointed", and φέρειν (''phérein''), "to bear"; hence the "Christ-bearer". As a given name, 'Christopher' has been in use since the 10th century. In English, Christopher may be abbreviated as "Chris", "Topher", and sometimes " Kit". It was frequently the most popular male first name in the United Kingdom, having been in the top twenty in England and Wales from the 1940s until 1995, although it has since dropped out of the top 100. The name is most common in England and not so common in Wales, Scotland, or Ireland. People with the given name Antiquity and Middle Ages * Saint Christopher (died 251), saint venerated by Catholics and Orthodox Christians * Christopher (Domestic of the Schools) (fl. 870s), Byzantine general * Christopher Lekapenos (died 931) ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Snowball Programming Language
Snowball is a small string processing programming language designed for creating stemming algorithms for use in information retrieval."Snowball" Martin Porter, web page. Retrieved 2 September 2014. The Snowball compiler translates a Snowball script (a .sbl file) into program in , , Ada, C#, Go, Javascript, Object Pascal, Python or Rust. For ANSI C, each Snowball script produces a program file and corresponding header file (with .c and . ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
BSD Licenses
BSD licenses are a family of permissive free software licenses, imposing minimal restrictions on the use and distribution of covered software. This is in contrast to copyleft licenses, which have share-alike requirements. The original BSD license was used for its namesake, the Berkeley Software Distribution (BSD), a Unix-like operating system. The original version has since been revised, and its descendants are referred to as modified BSD licenses. BSD is both a license and a class of license (generally referred to as BSD-like). The modified BSD license (in wide use today) is very similar to the license originally used for the BSD version of Unix. The BSD license is a simple license that merely requires that all code retain the BSD license notice if redistributed in source code format, or reproduce the notice if redistributed in binary format. The BSD license (unlike some other licenses e.g. GPL) does not require that source code be distributed at all. Terms In addition to ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Free Software
Free software or libre software is computer software distributed under terms that allow users to run the software for any purpose as well as to study, change, and distribute it and any adapted versions. Free software is a matter of liberty, not price; all users are legally free to do what they want with their copies of a free software (including profiting from them) regardless of how much is paid to obtain the program.Selling Free Software (gnu.org) Computer programs are deemed "free" if they give end-users (not just the developer) ultimate control over the software and, subsequently, over their devices. The right to study and modify a computer program entails that |