|
Stefan Uroš V
Saint Stefan Uroš V ( sr-cyrl, Свети Стефан Урош V, ; 13362/4 December 1371), known in historiography and folk tradition as Uroš the Weak ( sr-cyr, Урош Нејаки, Uroš Nejaki), was the second Emperor (Tsar) of the Serbian Empire (1355–1371), and before that he was Serbian King and co-ruler (since 1346) with his father, Emperor Stefan Dušan. Early life Stefan Uroš V was the only son of Stefan Uroš IV Dušan by Helena of Bulgaria, the sister of Ivan Alexander of Bulgaria. He had been crowned as king (second highest title) in the capacity of heir and co-ruler after Dušan was crowned emperor in 1346. Although by the time of his succession as sole ruler and emperor in 1355 Stefan Uroš V was no longer a minor, he remained heavily dependent on his mother and various members of the court. Reign left, 200px, Depiction in the Visoki_Dečani.html" ;"title="Serbian Orthodox Monastery of Visoki Dečani">Serbian Orthodox Monastery of Visoki Dečani, Serbia ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Saint
In religious belief, a saint is a person who is recognized as having an exceptional degree of holiness, likeness, or closeness to God. However, the use of the term ''saint'' depends on the context and denomination. In Catholic, Eastern Orthodox, Anglican, Oriental Orthodox, and Lutheran doctrine, all of their faithful deceased in Heaven are considered to be saints, but some are considered worthy of greater honor or emulation. Official ecclesiastical recognition, and consequently a public cult of veneration, is conferred on some denominational saints through the process of canonization in the Catholic Church or glorification in the Eastern Orthodox Church after their approval. While the English word ''saint'' originated in Christianity, historians of religion tend to use the appellation "in a more general way to refer to the state of special holiness that many religions attribute to certain people", referring to the Jewish tzadik, the Islamic walī, the Hindu rishi or ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Ivan Alexander Of Bulgaria
Ivan Alexander ( bg, Иван Александър, transliterated ''Ivan Aleksandǎr'', ; original spelling: ІѠАНЪ АЛЄѮАНдРЪ), also sometimes Anglicized as John Alexander, ruled as Emperor (''Tsar'') of Bulgaria from 1331 to 1371,Lalkov, ''Rulers of Bulgaria'', pp. 42–43. during the Second Bulgarian Empire. The date of his birth is unknown. He died on 17 February 1371. The long reign of Ivan Alexander is considered a transitional period in Bulgarian medieval history. Ivan Alexander began his rule by dealing with internal problems and external threats from Bulgaria's neighbours, the Byzantine Empire and Serbia, as well as leading his empire into a period of economic recovery and cultural and religious renaissance.''Bǎlgarite i Bǎlgarija'', 2.1 However, the emperor was later unable to cope with the mounting incursions of Ottoman forces, Hungarian invasions from the northwest and the Black Death. In an ill-fated attempt to combat these problems, he divided the ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Despotate Of Epirus
The Despotate of Epirus ( gkm, Δεσποτᾶτον τῆς Ἠπείρου) was one of the Greek successor states of the Byzantine Empire established in the aftermath of the Fourth Crusade in 1204 by a branch of the Angelos dynasty. It claimed to be the legitimate successor of the Byzantine Empire, along with the Empire of Nicaea and the Empire of Trebizond, its rulers briefly proclaiming themselves as Emperors in 1227–1242 (during which it is most often called the Empire of Thessalonica). The term "Despotate of Epirus" is, like "Byzantine Empire" itself, a modern historiographic convention and not a name in use at the time. The Despotate was centred on the region of Epirus, encompassing also Albania and the western portion of Greek Macedonia and also included Thessaly and western Greece as far south as Nafpaktos. Through a policy of aggressive expansion under Theodore Komnenos Doukas the Despotate of Epirus also briefly came to incorporate central Macedonia, with the ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Zeta (crown Land)
Zeta ( sr-cyrl, Зета) as a crown land was a medieval region and province of the Serbian state ( Principality, Kingdom, and Empire) of the Nemanjić dynasty, from the end of the 12th century, up to the middle of the 14th century. During that period, regional administration in Zeta was often bestowed to various members of the ruling dynasty, who administered the region as a crown land. Name At the time of Mihailo I, Zeta was a župa within Duklja and was also known as Luška župa. From the end of the 11th century, the name began to be used to refer to the whole of Duklja, at first in Kekaumenos's military manual, written in the 1080s. Over the following decades, the term ''Zeta'' gradually replaced ''Duklja'' to denote the region. History Serbian Prince Desa Urošević conquered Duklja and Travunia in 1148, combining the title as "''Prince of Primorje''" (the Maritime) and co-ruled Serbia with his brother Uroš II Prvoslav from 1149 to 1153, and alone until 1162. In 1190 ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Skoplje
Skopje ( , , ; mk, Скопје ; sq, Shkup) is the capital and largest city of North Macedonia. It is the country's political, cultural, economic, and academic centre. The territory of Skopje has been inhabited since at least 4000 BC; remains of Neolithic settlements have been found within the old Kale Fortress that overlooks the modern city centre. Originally a Paeonian city, Scupi became the capital of Dardania in the second century BC. On the eve of the 1st century AD, the settlement was seized by the Romans and became a military camp. When the Roman Empire was divided into eastern and western halves in 395 AD, Scupi came under Byzantine rule from Constantinople. During much of the early medieval period, the town was contested between the Byzantines and the Bulgarian Empire, whose capital it was between 972 and 992. From 1282, the town was part of the Serbian Empire, and acted as its capital city from 1346 to 1371. In 1392, Skopje was conquered by the Ottoman Turks, ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Kastoria
Kastoria ( el, Καστοριά, ''Kastoriá'' ) is a city in northern Greece in the modern regions of Greece, region of Western Macedonia. It is the capital of Kastoria (regional unit), Kastoria regional unit, in the Geographic regions of Greece, geographic region of Macedonia (Greece), Macedonia. It is situated on a promontory on the western shore of Lake Orestiada, in a valley surrounded by limestone mountains. The town is known for its many Byzantine Empire, Byzantine churches, Byzantine architecture, Byzantine and Ottoman architecture, Ottoman-era domestic architecture, its lake and its fur clothing industry. Name The city is first mentioned in 550 AD, by Procopius as follows: "There was a certain city in Thessaly, Diocletianopolis by name, which had been prosperous in ancient times, but with the passage of time and the assaults of the barbarians it had been destroyed, and for a very long time it had been destitute of inhabitants; and a certain lake chances to be clo ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Acarnania
Acarnania ( el, Ἀκαρνανία) is a region of west-central Greece that lies along the Ionian Sea, west of Aetolia, with the Achelous River for a boundary, and north of the gulf of Calydon, which is the entrance to the Gulf of Corinth. Today it forms the western part of the regional unit of Aetolia-Acarnania. The capital and principal city in ancient times was Stratos. The north side of Acarnania of the Corinthian Gulf was considered part of the region of Epirus. Acarnania's foundation in Greek mythology was traditionally ascribed to Acarnan, son of Alcmaeon. History Pre-Peloponnesian War The name of Acarnania appears to have been unknown in the earliest times. Homer (8th century BC) only calls the country opposite Ithaca and Cephalonia, under the general name of "Epeirus" (῎ηπειρος), or the mainland, although he frequently mentions the Aetolians. The country is said to have been originally inhabited by the Taphii (or Teleboae), the Leleges, and the Curete ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Aetolia
Aetolia ( el, Αἰτωλία, Aἰtōlía) is a mountainous region of Greece on the north coast of the Gulf of Corinth, forming the eastern part of the modern regional unit of Aetolia-Acarnania. Geography The Achelous River separates Aetolia from Acarnania to the west; on the north it had boundaries with Epirus and Thessaly; on the east with the Ozolian Locrians; and on the south the entrance to the Corinthian Gulf defined the limits of Aetolia. In classical times Aetolia comprised two parts: "Old Aetolia" ( el, Παλιά Αιτωλία, Paliá Aitolía) in the west, from the Achelous to the Evenus and Calydon; and "New Aetolia" ( el, Νέα Αιτωλία, Néa Aitolía) or "Acquired Aetolia" ( el, Αἰτωλία Ἐπίκτητος, Aitolía Epíktitos) in the east, from the Evenus and Calydon to the Ozolian Locrians. The country has a level and fruitful coastal region, but an unproductive and mountainous interior. The mountains contained many wild beasts, and acqui ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
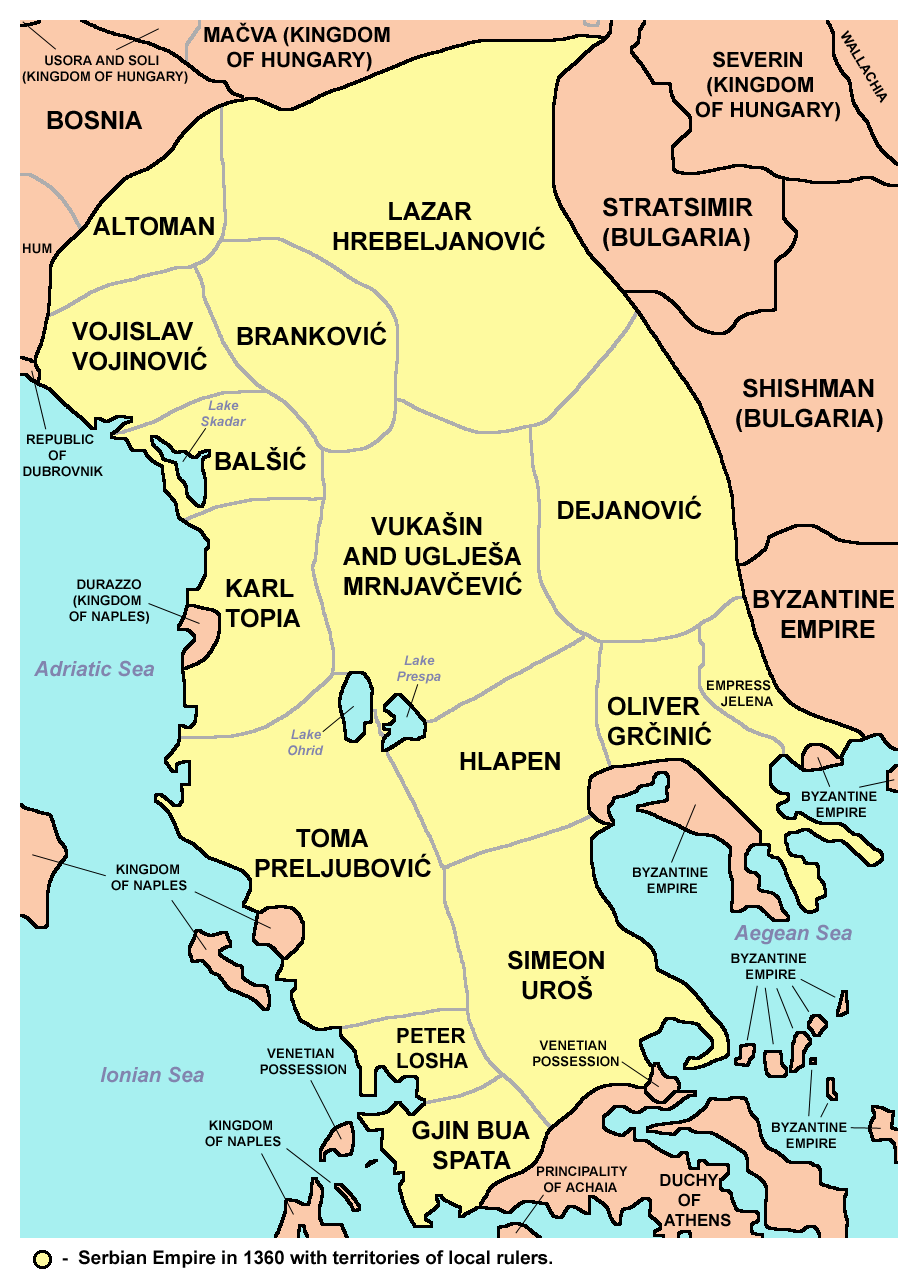
Simeon Uroš
Simeon Uroš ( sr-cyr, Симеон Урош, gr, Συμεών Ούρεσης; 1326–1370), nicknamed Siniša (Синиша), was a self-proclaimed Emperor of Serbs and Greeks, from 1356 to 1370. He was son of Serbian King Stephen Uroš III and Byzantine Princess Maria Palaiologina. Initially, he was awarded the title of despot in 1346, and appointed governor of southern Epirus and Acarnania in 1347 by his half-brother, Serbian Emperor Stephen Dušan. After Dušan's death in 1355, the Serbian throne passed to Dušan's son Stephen Uroš V, but despot Simeon decided to seize the opportunity in order to impose himself as co-ruler and lord of all southern provinces of the Serbian Empire. That led him to conflict with his nephew in 1356, when Simeon started to expand his control in southern regions of the Empire, trying to take Thessaly and Macedonia. He proclaimed himself '' Emperor of the Serbs and Greeks'', creating a separate state, centered in regions of Thessaly and Epiru ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Nikephoros II Orsini
Nikephoros II Orsini - Doukas (Greek: Νικηφόρος Β΄ Δούκας, ''Nikēphoros II Doukas''), was the ruler of Epirus from 1335 to 1338 and from 1356 until his death in 1359. Life Nikephoros was the son of John Orsini of Epirus and Anna Palaiologina. When his mother allegedly poisoned his father in 1335, Nikephoros II succeeded as a 7-year-old child. His mother Anna assumed the regency for her young son but failed to allay the enmity of the Byzantine Emperor Andronikos III Palaiologos, who invaded and annexed the Epirote part of Thessaly in 1336 and advanced on Ioannina. The Albanians took advantage of conflict to the south to raid the Byzantine possessions in the north, but were defeated by the emperor in 1337. Andronikos summoned Anna to negotiate in 1338 but refused to accept her son as Byzantine vassal and installed his governors in Epirus. Keeping Anna as hostage, Andronikos arranged for the marriage between Nikephoros and Maria Kantakouzene, the daughter of hi ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Thessaly
Thessaly ( el, Θεσσαλία, translit=Thessalía, ; ancient Thessalian: , ) is a traditional geographic and modern administrative region of Greece, comprising most of the ancient region of the same name. Before the Greek Dark Ages, Thessaly was known as Aeolia (, ), and appears thus in Homer's '' Odyssey''. Thessaly became part of the modern Greek state in 1881, after four and a half centuries of Ottoman rule. Since 1987 it has formed one of the country's 13 regions and is further (since the Kallikratis reform of 2011) sub-divided into five regional units and 25 municipalities. The capital of the region is Larissa. Thessaly lies in northern Greece and borders the regions of Macedonia on the north, Epirus on the west, Central Greece on the south, and the Aegean Sea on the east. The Thessaly region also includes the Sporades islands. Name and etymology Thessaly is named after the ''Thessaloi'', an ancient Greek tribe. The meaning of the name of this tribe is ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |