|
Stanford Hall, Leicestershire
Stanford Hall is a stately home in Leicestershire, England, near the village of Stanford on Avon (which is in Northamptonshire) and the town of Lutterworth, Leicestershire. The population of any residents in the area is included in the civil parish of Misterton with Walcote. History Ancestral home of the Cave family from c. 1430, the hall was built in the 1690s for Sir Roger Cave, 2nd Baronet. Described by Simon Jenkins as the "perfect William and Mary house", the architect was William Smith of Warwick. In 1792 Sarah, daughter of Sir Thomas Cave Bt, inherited the Cave estate on the death of her nephew Sir Thomas Cave, 7th Baronet. She had married Henry Otway in 1790 and was created Baroness Braye in 1839. Her descendants remain in residence. (Henry Otway was High Sheriff of Leicestershire in 1804). The River Avon flows through the grounds, with a weir downstream, so a small lake is formed. The aviation pioneer Percy Pilcher built some of his early gliders here in the ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Stanford Hall, Lutterworth
Stanford University, officially Leland Stanford Junior University, is a private research university in Stanford, California. The campus occupies , among the largest in the United States, and enrolls over 17,000 students. Stanford is considered among the most prestigious universities in the world. Stanford was founded in 1885 by Leland and Jane Stanford in memory of their only child, Leland Stanford Jr., who had died of typhoid fever at age 15 the previous year. Leland Stanford was a U.S. senator and former governor of California who made his fortune as a railroad tycoon. The school admitted its first students on October 1, 1891, as a coeducational and non-denominational institution. Stanford University struggled financially after the death of Leland Stanford in 1893 and again after much of the campus was damaged by the 1906 San Francisco earthquake. Following World War II, provost of Stanford Frederick Terman inspired and supported faculty and graduates' entrepreneurialism t ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
River Avon, Warwickshire
The River Avon () in central England flows generally southwestwards and is a major left-bank tributary of the River Severn, of which it is the easternmost. It is also known as the Warwickshire Avon or Shakespeare's Avon, to distinguish it from several other rivers of the same name in the United Kingdom. Beginning in Northamptonshire, the river flows through or adjoining the counties of Leicestershire, Northamptonshire, Warwickshire, Worcestershire and Gloucestershire, near the Cotswold Hills area. Notable towns it flows through include Rugby, Warwick, Stratford-upon-Avon, Evesham, Pershore and Tewkesbury, where it joins the Severn. It has traditionally been divided since 1719 into the Lower Avon, below Evesham, and the Upper Avon, from Evesham to above Stratford-upon-Avon. Improvements to aid navigation began in 1635, and a series of locks and weirs made it possible to reach Stratford, and to within of Warwick. The Upper Avon was tortuous and prone to flooding, and was ab ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Trabant
Trabant () is a series of small cars produced from 1957 until 1991 by former East German car manufacturer VEB Sachsenring Automobilwerke Zwickau. In total, four different models were made, the Trabant 500, Trabant 600, Trabant 601, and the Trabant 1.1. The first Trabant model, the Trabant 500, was a modern car when it was introduced in 1957. It featured a duroplast body mounted on a one-piece steel chassis (a so-called unibody), front-wheel drive, a transverse two-stroke engine, and independent suspension. Because this 1950s design remained largely unchanged until the introduction of the last Trabant model, the Trabant 1.1 in 1990, the Trabant became symbolic of the former East Germany's stagnant economy and the collapse of the Eastern Bloc in general. Called "a spark plug with a roof", 3,096,999 Trabants were produced. Older models have been sought by collectors in the United States due to their low cost and fewer restrictions on the importation of antique cars. The Trabant al ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
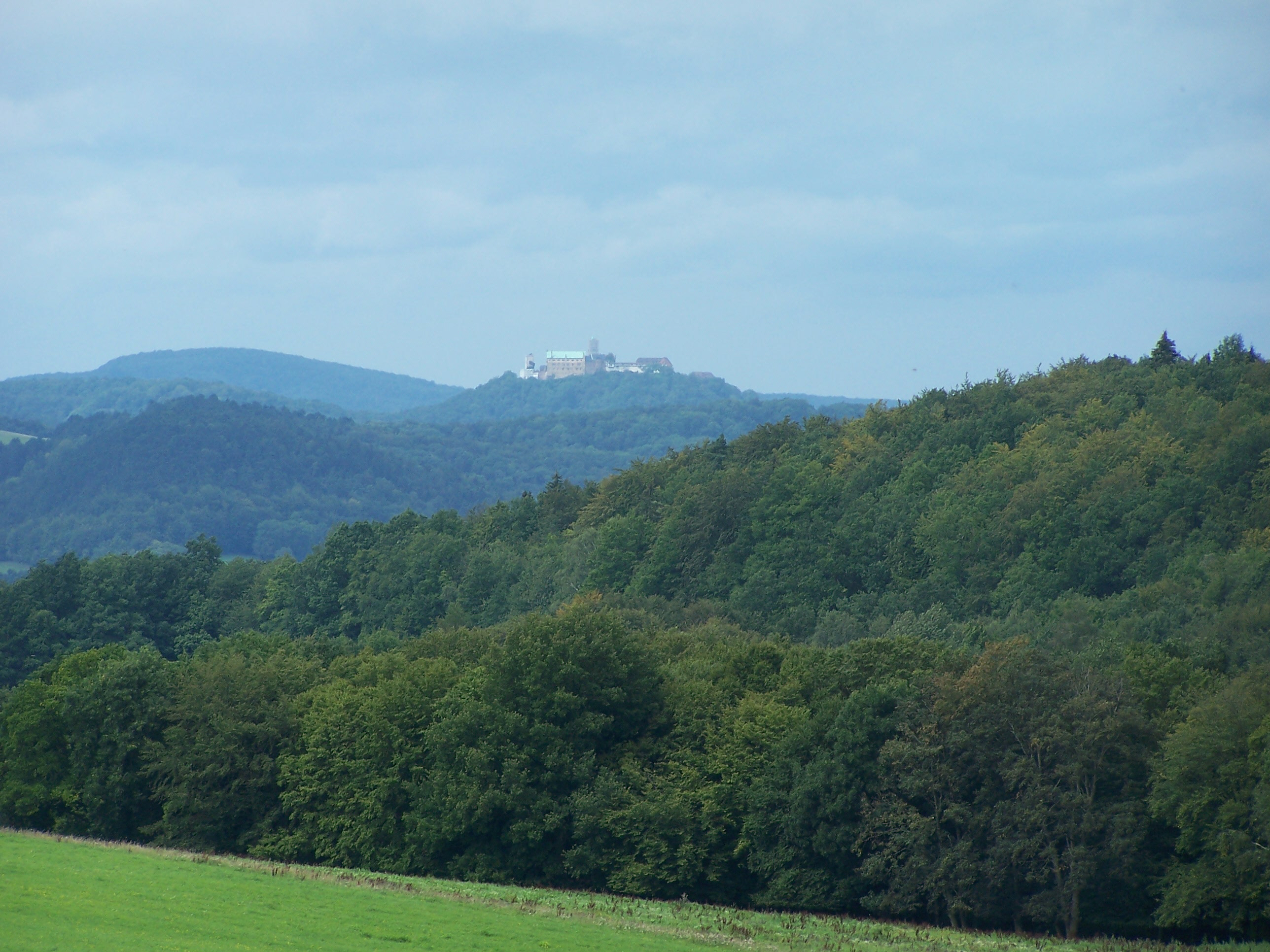
Wartburg
The Wartburg () is a castle originally built in the Middle Ages. It is situated on a precipice of to the southwest of and overlooking the town of Eisenach, in the state of Thuringia, Germany. It was the home of St. Elisabeth of Hungary, the place where Martin Luther translated the New Testament of the Bible into German, the site of the Wartburg festival of 1817 and the supposed setting for the possibly legendary ''Sängerkrieg''. It was an important inspiration for Ludwig II when he decided to build Neuschwanstein Castle. Wartburg is the most-visited tourist attraction in Thuringia after Weimar. Although the castle today still contains substantial original structures from the 12th through 15th centuries, much of the interior dates back only to the 19th century. In 1999, Wartburg Castle was inscribed on the UNESCO World Heritage List because of its quintessential medieval architecture and its historical and religious significance. Etymology The name of the castle is probably d ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Classic Car
A classic car is an older car, typically 25 years or older, though definitions vary.While other languages, such as German and Dutch, may refer to classic cars as "oldtimers", this usage is unknown in English, where "old-timer" refers to an elderly person. The common theme is of an older car of historical interest to be collectible and tend to be restored rather than scrapped. Classic cars are a subset of a broader category of "collector cars" (which includes both restored classic cars vehicles and newer exotic vehicles). A subset of what is considered classic cars are known as antique cars (manufactured before 1980) or vintage cars (manufactured pre-World War II). Organizations such as the Classic Car Club of America (CCCA) maintain lists of eligible unmodified cars that are called "classic". These are described as "fine" or "distinctive" automobile, either American or foreign built, produced between 1915 and 1948. Post-World War II "classic cars" are not precisely defined an ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
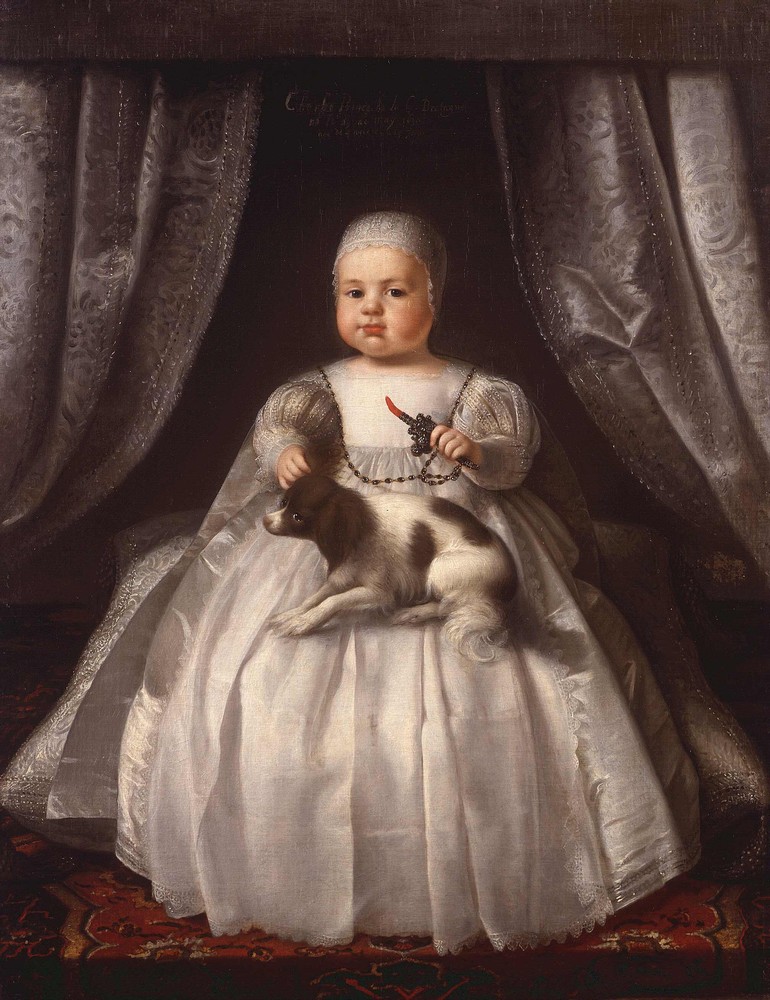
Charles II Of England
Charles II (29 May 1630 – 6 February 1685) was King of Scotland from 1649 until 1651, and King of England, Scotland and Ireland from the 1660 Restoration of the monarchy until his death in 1685. Charles II was the eldest surviving child of Charles I of England, Scotland and Ireland and Henrietta Maria of France. After Charles I's execution at Whitehall on 30 January 1649, at the climax of the English Civil War, the Parliament of Scotland proclaimed Charles II king on 5 February 1649. But England entered the period known as the English Interregnum or the English Commonwealth, and the country was a de facto republic led by Oliver Cromwell. Cromwell defeated Charles II at the Battle of Worcester on 3 September 1651, and Charles fled to mainland Europe. Cromwell became virtual dictator of England, Scotland and Ireland. Charles spent the next nine years in exile in France, the Dutch Republic and the Spanish Netherlands. The political crisis that followed Cromwell's death in 1 ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Refectory Table
A refectory table is a highly elongated table used originally for dining in monasteries during Medieval times. In the Late Middle Ages, the table gradually became a banqueting or feasting table in castles and other noble residences. The original table manufacture was by hand and created of oak or walnut; the design is based on a trestle style. Typically, the table legs are supported by circumferential stretchers positioned very low to the floor. History In its original use, one or more refectory tables were placed within the monks' dining hall or refectory. The larger refectories would have a number of refectory tables where monks would take their meals, often while one of the monks read sacred texts from an elevated pulpit, frequently reached from a stone staircase to one side of the refectory. Secular use of the refectory table is thought to have originated in the Mediterranean regions of Europe, where increasingly ornate designs were adopted by Italian and other crafts ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Tourist Attraction
A tourist attraction is a place of interest that tourists visit, typically for its inherent or an exhibited natural or cultural value, historical significance, natural or built beauty, offering leisure and amusement. Types Places of natural beauty such as beaches, tropical island resorts, national parks, mountains, deserts and forests, are examples of traditional tourist attractions which people may visit. Cultural tourist attractions can include historical places, sites of significant historic event, monuments, ancient temples, zoos, aquaria, museums and art galleries, botanical gardens, buildings and structures (such as forts, castles, libraries, former prisons, skyscrapers, bridges), theme parks and carnivals, living history museums, public art (sculptures, statues, murals), ethnic enclave communities, historic trains and cultural events. Factory tours, industrial heritage, creative art and crafts workshops are the object of cultural niches like industrial tourism and ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Historic Buildings Council
Three separate historic buildings councils were created by the Historic Buildings and Ancient Monuments Act 1953, one for each of England, Scotland, and Wales. Each Historic Buildings Council advised the relevant government minister on the exercise of powers under the 1953 Act relating to the preservation of listed buildings and other buildings of special architectural or historic interest, including applications for grants. Responsibilities for advice in relation to the Planning (Listed Buildings and Conservation Areas) Act 1990 were added latter. All three have now been abolished and replaced by other bodies. *The Historic Buildings Council for England was abolished by section 39 of the National Heritage Act 1983; its functions, and those of the Ancient Monuments Board for England, were taken up by Historic Buildings and Monuments Commission for England (better known as English Heritage). *The Historic Buildings Council for Scotland was abolished, along with various other public ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Woldingham School
Woldingham School is an independent school for girls, located in the former Marden Park of outside the village of Woldingham, Surrey, in South East England. It is a Roman Catholic school and a member of the global Network of Sacred Heart Schools. History The school was founded as the Convent of the Sacred Heart in 1842 in Berrymead, London by the Society of the Sacred Heart; the first Convent of the Sacred Heart in England. The Society had been founded in France in 1800 by Madeleine Sophie Barat (canonized in 1925) immediately after the French Revolution (1789–1799). The first Sacred Heart school had opened in 1801 at Amiens, France; others were soon established in France and across Europe. The Convent of the Sacred Heart moved to Roehampton, London, in 1850. Shortly after the 1939 outbreak of World War II, the school was evacuated, first to Newquay and later to Stanford Hall, near Rugby. Because the house at the Roehampton site was badly damaged during a 1941 air raid and l ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
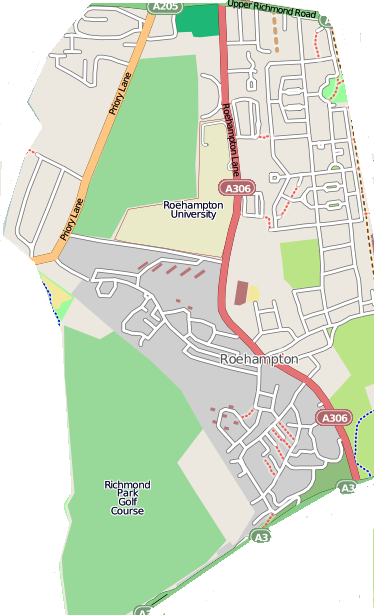
Roehampton
Roehampton is an area in southwest London, in the Putney SW15 postal district, and takes up a far western strip running north to south of the London Borough of Wandsworth. It contains a number of large council house estates and is home to the University of Roehampton. Etymology The ''Roe'' in Roehampton's name is thought to refer to the large number of rooks that still inhabit the area. Location Roehampton is centred about 6.3 miles (roughly 10 km) south-west of Charing Cross. It occupies high land, with Barnes to the north, Putney and Putney Heath to the east, and Richmond Park and Richmond Park Golf Course to the west. To the south is Roehampton Vale, that straddles the A3, with Wimbledon Common and Putney Vale beyond. History Roehampton was originally a small village – with only 14 houses during the reign of Henry VII – with the area largely forest and heath. The population gradually increased in the 18th and 19th centuries as it became a favoured residential ou ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
World War II
World War II or the Second World War, often abbreviated as WWII or WW2, was a world war that lasted from 1939 to 1945. It involved the vast majority of the world's countries—including all of the great powers—forming two opposing military alliances: the Allies and the Axis powers. World War II was a total war that directly involved more than 100 million personnel from more than 30 countries. The major participants in the war threw their entire economic, industrial, and scientific capabilities behind the war effort, blurring the distinction between civilian and military resources. Aircraft played a major role in the conflict, enabling the strategic bombing of population centres and deploying the only two nuclear weapons ever used in war. World War II was by far the deadliest conflict in human history; it resulted in 70 to 85 million fatalities, mostly among civilians. Tens of millions died due to genocides (including the Holocaust), starvation, ma ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |