|
Stams
Stams is a municipality in Imst District, in the Austrian state of Tyrol. It is chiefly known for Cistercian Stams Abbey (''Stift Stams''), founded in 1273 by Count Meinhard II of Gorizia-Tyrol and his wife.Chizzali. ''Tyrol: Impressions of Tyrol.'' (Innsbruck: Alpina Printers and Publishers), p. 64 Geography Stams is located on the southern shore of the Inn River about east of Imst, west of Telfs and west of the state capital Innsbruck. The village contains Stams has 1300 inhabitants who are living in different parts of the village – called Thannrain, Windfang, Staudach, Haslach, Maehmoos und Hauland. History Archaeological findings indicate a church already existed at the site about 700 AD. The locality of ''Stammes'' in the Duchy of Bavaria was first mentioned in a 1063 deed, it became a possession of the Counts of Tyrol. The Meinhardiner count Meinhard II of Gorizia, sole ruler of Tyrol from 1271, established a proprietary monastery together with his wife Elisabeth of B ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Meinhard, Duke Of Carinthia
Meinhard II (c. 1238 – 1 November 1295), a member of the House of Gorizia (''Meinhardiner''), ruled the County of Gorizia (as Meinhard IV) and the County of Tyrol together with his younger brother Albert from 1258. In 1271 they divided their heritage and Meinhard became sole ruler of Tyrol. In 1286 he was enfeoffed with the Duchy of Carinthia and the adjacent March of Carniola. Life Meinhard II was the son of Count Meinhard III of Gorizia and his wife Adelheid (died 1275–79), daughter and heiress of Count Albert IV of Tyrol. His father had acquired the County of Tyrol (as Meinhard I) upon the death of his father-in-law in 1253 and already had attempted to gain control over neighbouring Carinthian lands against the forces of Duke Bernhard von Spanheim. However, he was defeated near Greifenburg and had to leave his minor sons Meinhard II and Albert held in hostage by Duke Bernhard's son, Archbishop-elect Philip of Salzburg. After their father's death in 1258, Meinhard II and ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Henry Of Bohemia
Henry of Gorizia (german: Heinrich, cs, Jindřich; – 2 April 1335), a member of the House of Gorizia, was Duke of Carinthia and Landgrave of Carniola (as Henry VI) and Count of Tyrol from 1295 until his death, as well as King of Bohemia, Margrave of Moravia and titular King of Poland in 1306 and again from 1307 until 1310. After his death, the Habsburgs took over Carinthia and Carniola and held them almost without interruption until 1918. Life Henry was a younger son of Count Meinhard II of Görz-Tyrol and Elizabeth of Bavaria, widow of King Conrad IV of Germany. Upon the partition of the Meinhardiner estates in 1271, his father maintained the Tyrolean lands, while Henry's uncle Albert received the County of Gorizia. In 1276 Count Meinhard married his eldest daughter, Henry's sister Elizabeth, to Albert, son of King Rudolph I of Germany, and in turn was enfeoffed with the Duchy of Carinthia in 1286. After his father's death in late October 1295, Henry inherited the Tyrolean ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Elisabeth Of Bavaria, Queen Of Germany
Elisabeth of Bavaria (, Trausnitz Castle, Landshut, Bavaria – 9 October 1273, Goyen Castle, Schenna, Tyrol), a member of the House of Wittelsbach, was Queen of Germany and Jerusalem from 1246 to 1254 by her marriage to King Conrad IV of Germany. Life She was born at Trausnitz Castle in Landshut, the eldest daughter of Otto II Wittelsbach and his wife Agnes of the Palatinate, herself a daughter of the Welf count palatine Henry V and Agnes of Hohenstaufen. Otto II succeeded his father Louis I as Bavarian duke and as Count palatine in 1231. In the conflict between the Hohenstaufen emperor Frederick II and the Roman Curia, he initially sided with the pope, but became a supporter of Frederick in 1241. Otto II had initially betrothed Elisabeth to Duke Frederick II of Austria, however, the new political alliance would lead to the marriage of the elder daughter of the Wittelsbach and the elder son of the Hohenstaufen, Conrad IV. The wedding ceremony took place on 1 September 12 ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Imst District
The Bezirk Imst is an administrative district (''Bezirk'') in Tyrol, Austria. It borders the district Reutte in the north, as well as sharing a small border with Bavaria (Germany). It borders the district Innsbruck-Land in the east, South Tyrol (Italy) in the south, and the district Landeck in the west. Area of the district is , which makes it by area rank 4 of the districts of Tyrol, with a population of 57,734 (as of January 1, 2012) (Number 6 in Tyrol), and a population density of 33 persons per km². The administrative center of the district is Imst. Geography The district comprises a part of the upper Inn valley, with its tributary valleys Ötztal, Pitztal, and Gurgltal, and the Mieming Plateau. The area is dominated by high alpine mountains. Mountain ranges include the Stubai Alps, Ötztal Alps, and Mieminger Mountains. The District is around 35 km from west to east and 80 km from north to south. The Highest mountain is the Wildspitze (3.768 meters), the secon ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Austria
Austria, , bar, Östareich officially the Republic of Austria, is a country in the southern part of Central Europe, lying in the Eastern Alps. It is a federation of nine states, one of which is the capital, Vienna, the most populous city and state. A landlocked country, Austria is bordered by Germany to the northwest, the Czech Republic to the north, Slovakia to the northeast, Hungary to the east, Slovenia and Italy to the south, and Switzerland and Liechtenstein to the west. The country occupies an area of and has a population of 9 million. Austria emerged from the remnants of the Eastern and Hungarian March at the end of the first millennium. Originally a margraviate of Bavaria, it developed into a duchy of the Holy Roman Empire in 1156 and was later made an archduchy in 1453. In the 16th century, Vienna began serving as the empire's administrative capital and Austria thus became the heartland of the Habsburg monarchy. After the dissolution of the H ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Duchy Of Bavaria
The Duchy of Bavaria (German: ''Herzogtum Bayern'') was a frontier region in the southeastern part of the Merovingian kingdom from the sixth through the eighth century. It was settled by Bavarian tribes and ruled by dukes (''duces'') under Frankish overlordship. A new duchy was created from this area during the decline of the Carolingian Empire in the late ninth century. It became one of the stem duchies of the East Frankish realm which evolved as the Kingdom of Germany and the Holy Roman Empire. During internal struggles of the ruling Ottonian dynasty, the Bavarian territory was considerably diminished by the separation of the newly established Duchy of Carinthia in 976. Between 1070 and 1180 the Holy Roman Emperors were again strongly opposed by Bavaria, especially by the ducal House of Welf. In the final conflict between the Welf and Hohenstaufen dynasties, Duke Henry the Lion was banned and deprived of his Bavarian and Saxon fiefs by Emperor Frederick Barbarossa. Fr ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Mals
Mals (; it, Malles Venosta ) is a ''comune'' (municipality) in South Tyrol in northern Italy, located about northwest of Bolzano, on the border with Switzerland and Austria. History Coat-of-arms The emblem is party per fess: the upper of gules a fess argent, at the bottom or three gules circles arranged in a triangle upside-down. It is the combination of coats of arms of the House of Austria and Medici. The emblem was adopted in 1928. Geography As of 30 November 2010, it had a population of 5,092 and an area of .All demographics and other statistics: Italian statistical institute Istat. The Zerzer Tal, a side valley of the Vinschgau, is in Mals. Mals borders the following municipalities: Graun im Vinschgau, Glurns, Laas, Scuol (Switzerland), Schnals, Sent (Switzerland), Schlanders, Schluderns, Sölden (Austria), and Taufers im Münstertal. Frazioni The municipality of Mals contains the ''frazioni'' (subdivisions, mainly villages and hamlets): Burgeis (Burgusio), Laatsch ( ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
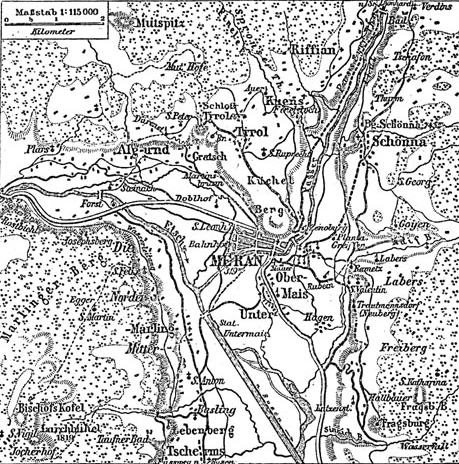
Meran
Merano (, , ) or Meran () is a city and ''comune'' in South Tyrol, northern Italy. Generally best known for its spa resorts, it is located within a basin, surrounded by mountains standing up to above sea level, at the entrance to the Passeier Valley and the Vinschgau. In the past, the city has been a popular place of residence for several scientists, literary people, and artists, including Franz Kafka, Ezra Pound, Paul Lazarsfeld, and also Empress Elisabeth of Austria, who appreciated its mild climate. Name Both the Italian () and the German () names for the city are used in English. The Ladin form of the name is . The official name of the municipality (''comune'') is ''Comune di Merano'' in Italian and ''Stadtgemeinde Meran'' in German (both are in official use). History In 17th-century Latin, the city was called ''Meranum''. Other archaic names are ''Mairania'' (from 857 AD) and ''an der Meran'' (from the 15th century). Origin The area has been inhabited since the thir ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Silz, Tyrol
Silz is a municipality in the Imst district and is located east of Imst and west of Telfs. The ski resort Kühtai administratively belongs to the village area. Besides winter tourism also summer tourism, especially rafting Rafting and whitewater rafting are recreational outdoor activities which use an inflatable raft to navigate a river or other body of water. This is often done on whitewater or different degrees of rough water. Dealing with risk is often a ... on the Inn River, is an important source of income for Silz. Population Notable people * Helmuth Orthner (1941–2009), American scientist References External links Official web presence of the municipality of Silz Cities and towns in Imst District {{Tyrol-geo-stub ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Morimond Abbey
Morimond Abbey is a religious complex in Parnoy-en-Bassigny, Haute-Marne department, in the Champagne-Ardenne region of France. It was the fourth of the four great daughter abbeys of Cîteaux Abbey, of primary importance in the spread of the Cistercian Order, along with La Ferté to the south, Pontigny to the west and Clairvaux to the north. History Situated in the diocese of Langres, Morimond was founded in 1115 by Count Odelric of Aigremont and his wife Adeline of Choiseul and settled from Citeaux. The first abbot, known as a "pillar of the Cistercians", was Arnold the German. Thanks to his energy and influence, Morimond grew very rapidly, and established numerous colonies in France, Germany, Poland, Bohemia, Spain, and Cyprus. The only daughter-house in England and Wales was Dore Abbey, founded in 1147. Amongst the best-known were Ebrach Abbey in Germany (1126); Heiligenkreuz Abbey in Austria (1134); and Aiguebelle Abbey in France (1137), which was later restored by the Refo ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Duchy Of Swabia
The Duchy of Swabia (German: ''Herzogtum Schwaben'') was one of the five stem duchies of the medieval German Kingdom. It arose in the 10th century in the southwestern area that had been settled by Alemanni tribes in Late Antiquity. While the historic region of Swabia takes its name from the ancient Suebi, dwelling in the angle formed by the Rhine and the Danube, the stem duchy comprised a much larger territory, stretching from the Alsatian Vosges mountain range in the west to the right bank of the river Lech in the east and up to Chiavenna (''Kleven'') and Gotthard Pass in the south. The name of the larger stem duchy was often used interchangeably with '' Alamannia'' during the High Middle Ages, until about the 11th century, when the form Swabia began to prevail. The Duchy of Swabia was proclaimed by the Ahalolfing count palatine Erchanger in 915. He had allied himself with his Hunfriding rival Burchard II and defeated King Conrad I of Germany in a battle at Wahlwies. Th ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Kaisheim Abbey
The Imperial Abbey of Kaisersheim (German:''Reichsstift Kaisersheim'' or ''Kloster Kaisersheim''), was a Cistercian monastery in Kaisersheim (now Kaisheim), Bavaria, Germany. As one of the 40-odd self-ruling imperial abbeys of the Holy Roman Empire, Kaisersheim was a virtually independent state. Its abbot had seat and voice at the Imperial Diet where he sat on the Bench of the Prelates of Swabia. At the time of its secularisation in 1802, the Abbey covered 136 square kilometers and has 9,500-10,000 subjects. History The monastery was founded by Henry II, Count of Lechsgemünd (d. 1142) and his wife Liutgard, and was a daughter house of Lucelle Abbey in Alsace. Count Henry's initial gift of the land was made in 1133; the foundation charter was dated 21 September 1135. The first church was dedicated in 1183 by the Bishop of Augsburg, but was damaged in a fire in 1286, and re-built in its entirety between 1352 and 1387, when the new building was dedicated. The foundation chart ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |