|
St. George's Abbey In The Black Forest
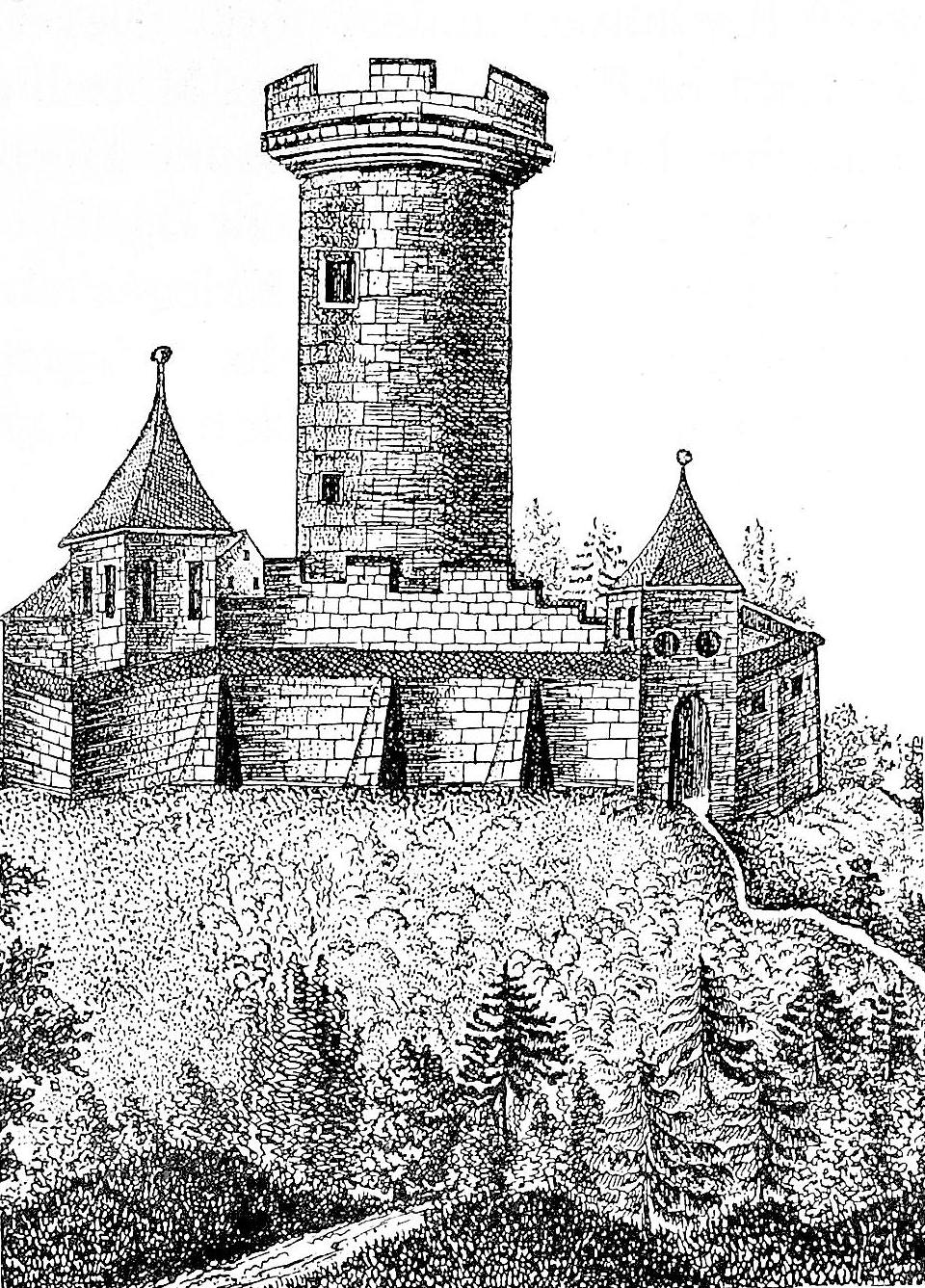
St. George's Abbey in the Black Forest (Kloster Sankt Georgen im Schwarzwald) was a Benedictine monastery in St. Georgen im Schwarzwald in the southern Black Forest in Baden-Württemberg, Germany. History Foundation to Reformation The monastery was founded in 1084– 85 in the Black Forest, by the source of the Brigach, against the background of the Investiture Controversy, as a result of the community of interests of the Swabian aristocracy and the church reform party, the founders being Hezelo and Hesso of the family of the ''Vögte'' of Reichenau, and the politically influential Abbot William of Hirsau. The intended site was initially to be at Königseggwald in Upper Swabia, but at William's behest St. Georgen was chosen instead. The settlement, by monks from Hirsau Abbey, took place in the spring and summer of 1084; the chapel was dedicated on 24 June 1085. At first a priory of Hirsau, the new foundation was declared an independent abbey in 1086, and under Abbot Theoger ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Kloster St
Kloster is the German and Scandinavian word for monastery. It may also refer to: Places * Kloster, Styria * Kloster, Denmark * Kloster, Sweden * Klošter, settlement in Slovenia People * Asbjørn Kloster (1823–1876), Norwegian social reformer * Chuck Klosterman (b. 1972), American author and essayist * Knut Kloster (b. 1929), Norwegian shipping magnate, grandson of Lauritz * Lauritz Kloster (1870–1952), Norwegian shipping magnate, grandfather of Knut * Robert Kloster (1905–1979), Norwegian museum director and art historian Other * ''Das Kloster'', a collection of magical and occult texts compiled by Johann Scheible See also * Klosters Klosters is a Swiss village in the Prättigau, politically part of the municipality of Klosters-Serneus, which belongs to the political district Prättigau/Davos in the canton of Graubünden. In 2021, the municipality shortened its name to Kl ... * Closter (other) {{Disambiguation, geo, surname Norwegian-language surname ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
House Of Zähringen
The House of Zähringen (german: Zähringer) was a dynasty of Swabian nobility. The family's name derived from Zähringen Castle near Freiburg im Breisgau. The Zähringer in the 12th century used the title of Duke of Zähringen, in compensation for having conceded the title of Duke of Swabia to the Staufer in 1098. The Zähringer were granted the special title of Rector of Burgundy in 1127, and they continued to use both titles until the extinction of the ducal line in 1218. The territories and fiefs held by the Zähringer were known as the 'Duchy of Zähringen' (), but it was not seen as a duchy in equal standing with the old stem duchies. The Zähringer attempted to expand their territories in Swabia and Burgundy into a fully recognized duchy, but their expansion was halted in the 1130s due to their feud with the Welfs. Pursuing their territorial ambitions, the Zähringer founded numerous cities and monasteries on either side of the Black Forest, as well as in the western S ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Cluniac Reform
The Cluniac Reforms (also called the Benedictine Reform) were a series of changes within medieval monasticism of the Western Church focused on restoring the traditional monastic life, encouraging art, and caring for the poor. The movement began within the Benedictine order at Cluny Abbey, founded in 910 by William I, Duke of Aquitaine (875–918). The reforms were largely carried out by Saint Odo (c. 878 – 942) and spread throughout France (Burgundy, Provence, Auvergne, Poitou), into England (the English Benedictine Reform), and through much of Italy and Spain. Background In the early 10th century, Western monasticism, which had flourished several centuries earlier with St Benedict of Nursia, was experiencing a severe decline due to unstable political and social conditions resulting from the nearly continuous Viking raids, widespread poverty and, especially, the dependence of abbeys on the local nobles who controlled all that belonged to the territories under their jurisdiction. ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Hirsau Reform
William of Hirsau (or Wilhelm von Hirschau) ( 1030 – 5 July 1091) was a Benedictine abbot and monastic reformer. He was abbot of Hirsau Abbey, for whom he created the ''Constitutiones Hirsaugienses'', based on the uses of Cluny, and was the father of the Hirsau Reforms, which influenced many Benedictine monasteries in Germany. He supported the papacy in the Investiture Controversy. In the Roman Catholic Church, he is a Blessed, the second of three steps toward recognition as a saint. Early life William was born in Bavaria, possibly in about 1030; nothing more is known of his origins. As a ''puer oblatus'' entrusted to the Benedictines he received his education as a monk in St. Emmeram's Abbey,Ott, Michael. "Bl. William." The Catholic Encyclopedia Vol. 15. New York: Robert Appleton Company, 1912. 17 December ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Prüfening Abbey
Prüfening Abbey (german: Kloster Prüfening) was a Benedictine monastery on the outskirts of Regensburg in Bavaria, Germany. Since the beginning of the 19th century it has also been known as Prüfening Castle (''Schloss Prüfening''). Notably, its extant dedicatory inscription, commemorating the founding of the abbey in 1119, was created by printing and is a unique document of medieval typography.; History Monastery The monastery is situated on the western edge of the town of Regensburg and was founded in 1119 by Bishop Otto I of Bamberg as a Benedictine abbey. The abbey church, dedicated to Saint George, completed in 1125, is the first major church building of the so-called "School of Hirsau" in Bavaria. It is a Romanesque basilica with a transept . The Romanesque wall-paintings are well-preserved. The first abbot, Erminold, is supposed to have been killed by the monks because of his strictness. The tomb built in his honour by Bishop Heinrich II of Regensburg in 1283 wa ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Augsburg
Augsburg (; bar , Augschburg , links=https://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Swabian_German , label=Swabian German, , ) is a city in Swabia, Bavaria, Germany, around west of Bavarian capital Munich. It is a university town and regional seat of the ''Regierungsbezirk'' Schwaben with an impressive Altstadt (historical city centre). Augsburg is an urban district and home to the institutions of the Landkreis Augsburg. It is the third-largest city in Bavaria (after Munich and Nuremberg) with a population of 300,000 inhabitants, with 885,000 in its metropolitan area. After Neuss, Trier, Cologne and Xanten, Augsburg is one of Germany's oldest cities, founded in 15 BC by the Romans as Augsburg#Early history, Augusta Vindelicorum, named after the Roman emperor Augustus. It was a Free Imperial City from 1276 to 1803 and the home of the patrician (post-Roman Europe), patrician Fugger and Welser families that dominated European banking in the 16th century. According to Behringer, in the sixteen ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Admont Abbey
Admont Abbey (german: Stift Admont) is a Order of St. Benedict, Benedictine monastery located on the Enns River in the town of Admont, Austria. The oldest remaining monastery in Styria, Admont Abbey contains the largest monastic library in the world as well as a long-established scientific collection. It is known for its Baroque architecture, Baroque architecture, art, and manuscripts. The abbey's location on the borders of the mountainous Gesäuse National Park (the name Admont derives from the Latin expression "ad montes", which means "at the mountains") is of unusual scenic beauty. History Dedicated to Saint Blaise, Admont Abbey was founded in 1074 by Archbishop Gebhard of Salzburg with the legacy of the late Saint Hemma of Gurk, and settled by monks from St. Peter's Archabbey, Salzburg, St. Peter's Abbey in Salzburg under abbot Isingrin. The second abbot, Giselbert, is said to have introduced the Cluniac reforms here. Another of the early abbots, Wolfhold, established a co ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Ottobeuren Abbey
Ottobeuren is a Benedictine abbey, located in Ottobeuren, near Memmingen in the Bavarian Allgäu, Germany. For part of its history Ottobeuren Abbey was one of the 40-odd self-ruling imperial abbeys of the Holy Roman Empire and, as such, was a virtually independent state. At the time of its dissolution in 1802, the imperial abbey covered 266 square kilometers and had about 10,000 subjects. First foundation It was founded in 764 by Blessed Toto, and dedicated to Alexander of Bergamo, St. Alexander, the martyr. Of its early history little is known beyond the fact that Toto, its first abbot, died about 815 and that Ulrich of Augsburg, Saint Ulrich was its abbot in 972. In the 11th century its discipline was on the decline, until Abbot Adalhalm (1082–94) introduced the Hirsau Reform. The same abbot began a restoration of the decaying buildings, which was completed along with the addition of a convent for noble ladies, by his successor, Abbot Rupert I (1102–45). Under the rule of ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Bavaria
Bavaria ( ; ), officially the Free State of Bavaria (german: Freistaat Bayern, link=no ), is a state in the south-east of Germany. With an area of , Bavaria is the largest German state by land area, comprising roughly a fifth of the total land area of Germany. With over 13 million inhabitants, it is second in population only to North Rhine-Westphalia, but due to its large size its population density is below the German average. Bavaria's main cities are Munich (its capital and largest city and also the third largest city in Germany), Nuremberg, and Augsburg. The history of Bavaria includes its earliest settlement by Iron Age Celtic tribes, followed by the conquests of the Roman Empire in the 1st century BC, when the territory was incorporated into the provinces of Raetia and Noricum. It became the Duchy of Bavaria (a stem duchy) in the 6th century AD following the collapse of the Western Roman Empire. It was later incorporated into the Holy Roman Empire, became an ind ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Lotharingia
Lotharingia ( la, regnum Lotharii regnum Lothariense Lotharingia; french: Lotharingie; german: Reich des Lothar Lotharingien Mittelreich; nl, Lotharingen) was a short-lived medieval successor kingdom of the Carolingian Empire. As a more durable later duchy of the Ottonian Empire, it comprised present-day Lorraine (France), Luxembourg, Saarland (Germany), Netherlands, and the eastern half of Belgium, along with parts of today's North Rhine-Westphalia (Germany), Rhineland-Palatinate (Germany) and Nord (France). It was named after King Lothair II, who received this territory after his father Lothair I's kingdom of Middle Francia was divided among his three sons in 855. Lotharingia resulted from the tripartite division in 855 of the kingdom of Middle Francia, which itself was formed after the threefold division of the Carolingian Empire by the Treaty of Verdun of 843. Conflict between East and West Francia over Lotharingia was based on the fact that these were the old Frankish hom ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Alsace
Alsace (, ; ; Low Alemannic German/ gsw-FR, Elsàss ; german: Elsass ; la, Alsatia) is a cultural region and a territorial collectivity in eastern France, on the west bank of the upper Rhine next to Germany and Switzerland. In 2020, it had a population of 1,898,533. Alsatian culture is characterized by a blend of Germanic and French influences. Until 1871, Alsace included the area now known as the Territoire de Belfort, which formed its southernmost part. From 1982 to 2016, Alsace was the smallest administrative ''région'' in metropolitan France, consisting of the Bas-Rhin and Haut-Rhin departments. Territorial reform passed by the French Parliament in 2014 resulted in the merger of the Alsace administrative region with Champagne-Ardenne and Lorraine to form Grand Est. On 1 January 2021, the departments of Bas-Rhin and Haut-Rhin merged into the new European Collectivity of Alsace but remained part of the region Grand Est. Alsatian is an Alemannic dialect closely related ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Pope Alexander III
Pope Alexander III (c. 1100/1105 – 30 August 1181), born Roland ( it, Rolando), was head of the Catholic Church and ruler of the Papal States from 7 September 1159 until his death in 1181. A native of Siena, Alexander became pope after a contested election, but had to spend much of his pontificate outside Rome while several rivals, supported by Holy Roman Emperor Frederick I Barbarossa, claimed the papacy. Alexander rejected Byzantine Emperor Manuel I Komnenos' offer to end the East–West Schism, sanctioned the Northern Crusades, and held the Third Council of the Lateran. The city of Alessandria in Piedmont is named after him. Early life and career Rolando was born in Siena. From the 14th century, he was referred to as a member of the aristocratic family of Bandinelli, although this has not been proven. He was long thought to be the 12th-century canon lawyer and theologian Master Roland of Bologna, who composed the "Stroma" or "Summa Rolandi"—one of the earliest comment ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |





.jpg)