|
Squeak
Squeak is an object-oriented, class-based, and reflective programming language. It was derived from Smalltalk-80 by a group that included some of Smalltalk-80's original developers, initially at Apple Computer, then at Walt Disney Imagineering, where it was intended for use in internal Disney projects. The group would later go on to be supported by HP labs, SAP, and most recently, Y Combinator. Squeak runs on a virtual machine (VM), allowing for a high degree of portability. The Squeak system includes code for generating a new version of the VM on which it runs, along with a VM simulator written in Squeak. Developers Dan Ingalls, an important contributor to the Squeak project, wrote the paper upon which Squeak is built, and constructed the architecture for five generations of the Smalltalk language. Alan Kay is an important contributor to the Squeak project, and Squeak incorporates many elements of his proposed Dynabook concept. User interface frameworks Squeak includes fou ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Squeak 51 Morphic Interface Screenshot
Squeak is an object-oriented programming, object-oriented, class (computer science), class-based, and reflection (computer programming), reflective programming language. It was derived from Smalltalk, Smalltalk-80 by a group that included some of Smalltalk-80's original developers, initially at Apple Inc., Apple Computer, then at Walt Disney Imagineering, where it was intended for use in internal Disney projects. The group would later go on to be supported by HP Labs, HP labs, SAP, and most recently, Y Combinator (company), Y Combinator. Squeak runs on a virtual machine (VM), allowing for a high degree of portability. The Squeak system includes code for generating a new version of the VM on which it runs, along with a VM simulator written in Squeak. Developers Dan Ingalls, an important contributor to the Squeak project, wrote the paper upon which Squeak is built, and constructed the architecture for five generations of the Smalltalk language. Alan Kay is an important contributor ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Squeak
Squeak is an object-oriented, class-based, and reflective programming language. It was derived from Smalltalk-80 by a group that included some of Smalltalk-80's original developers, initially at Apple Computer, then at Walt Disney Imagineering, where it was intended for use in internal Disney projects. The group would later go on to be supported by HP labs, SAP, and most recently, Y Combinator. Squeak runs on a virtual machine (VM), allowing for a high degree of portability. The Squeak system includes code for generating a new version of the VM on which it runs, along with a VM simulator written in Squeak. Developers Dan Ingalls, an important contributor to the Squeak project, wrote the paper upon which Squeak is built, and constructed the architecture for five generations of the Smalltalk language. Alan Kay is an important contributor to the Squeak project, and Squeak incorporates many elements of his proposed Dynabook concept. User interface frameworks Squeak includes fou ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Etoys (programming Language)
Etoys is a child-friendly computer environment and object-oriented prototype-based programming language for use in education. Etoys is a media-rich authoring environment with a scripted object model for many different objects that runs on different platforms and is free and open source. History * Squeak was originally developed at Apple in 1996 by Dan Ingalls. * Squeak is a Smalltalk implementation, object-oriented, class-based, and reflective, derived from Smalltalk-80 at Apple Computer. It was developed by some of the original Smalltalk-80 developers, including Dan Ingalls, Ted Kaehler, and Alan Kay. The team also included Scott Wallace and John Maloney. * Squeak 4.0 is released under the MIT License, with some of the original Apple parts remaining under the Apache License. Contributions are required to be under MIT. * “Back to the Future: the story of Squeak, a practical Smalltalk written in itself” by Dan Ingalls, Ted Kaehler, John Maloney, Scott Wallace, Alan K ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Dan Ingalls
Daniel Henry Holmes Ingalls Jr. (born 1944) is a pioneer of object-oriented computer programming and the principal architect, designer and implementer of five generations of Smalltalk environments. He designed the bytecoded virtual machine that made Smalltalk practical in 1976. He also invented bit blit, the general-purpose graphical operation that underlies most bitmap computer graphics systems today, and pop-up menus. He designed the generalizations of BitBlt to arbitrary color depth, with built-in scaling, rotation, and anti-aliasing. He made major contributions to the Squeak version of Smalltalk, including the original concept of a Smalltalk written in itself and made portable and efficient by a Smalltalk-to- C translator. Education Ingalls received his Bachelor of Arts (B.A.) in physics from Harvard University, and his Master of Science (M.S.) in electrical engineering from Stanford University. While working toward a Doctor of Philosophy (Ph.D.) at Stanford, he started ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
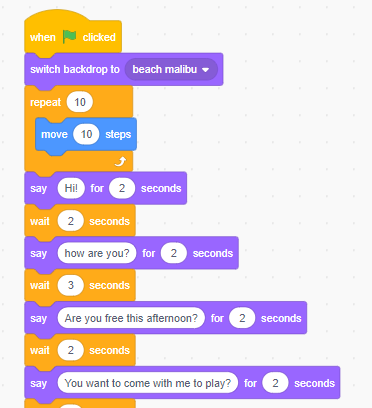
Scratch (programming Language)
Scratch is a high-level block-based visual programming language and website aimed primarily at children as an educational tool for programming, with a target audience of ages 8 to 16. Users on the site, called Scratchers, can create projects on the website using a block-like interface. Projects can be exported to HTML5, Android apps, Bundle (macOS) and EXE files using external tools. The service is developed by the MIT Media Lab, has been translated into 70+ languages, and is used in most parts of the world. Scratch is taught and used in after-school centers, schools, and colleges, as well as other public knowledge institutions. As of May 8, 2022, community statistics on the language's official website show more than 104 million projects shared by over 90 million users, over 686 million total projects ever created (including unshared projects), and more than 100 million monthly website visits. Scratch takes its name from a technique used by disk jockeys called "scratching", ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Pharo
Pharo is an open source, cross-platform implementation of the classic Smalltalk-80 programming language and runtime. It's based on the OpenSmalltalk virtual machine called Cog (VM), which evaluates a dynamic, reflective, and object-oriented programming language with a syntax closely resembling Smalltalk-80. Pharo is shipped with a source code compiled into a ''system image'' that contains all software necessary to run Pharo system. Like the original Smalltalk-80, Pharo provides several live programming features such as immediate object manipulation, live updates, and just-in-time compilation. The image includes an IDE-like software to modify its components. Pharo was forked from Squeak v3.9 in March of 2008. Overview Pharo is a pure object-oriented dynamically typed and reflective language. The stated goal of Pharo is to revisit Smalltalk design and enhance it. The name Pharo comes from the French word "phare" () which means lighthouse. This is why the Pharo log ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Alan Kay
Alan Curtis Kay (born May 17, 1940) published by the Association for Computing Machinery 2012 is an American computer scientist best known for his pioneering work on object-oriented programming and windowing graphical user interface (GUI) design. At Xerox PARC he led the design and development of the first modern windowed computer desktop interface. There he also led the development of the influential object-oriented programming language Smalltalk, both personally designing most of the early versions of the language and coining the term "object-oriented." He has been elected a Fellow of the American Academy of Arts and Sciences, the National Academy of Engineering, and the Royal Society of Arts. He received the Turing award in 2003. Kay is also a former professional jazz guitarist, composer, and theatrical designer. He also is an amateur classical pipe organist. Early life and work In an interview on education in America with the Davis Group Ltd., Kay said: O ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Croquet Project
Croquet OS is a web-based operating system for creating three-dimensional apps with multi-user functionalities that run simultaneously on any device. Croquet can be used for communication, online gaming environments such as massively multiplayer online role-playing games (MMORPGs), 3D wikis, virtual learning and problem solving environments, privately maintained or interconnected multi-user virtual environments, and more advanced functions such as highly scalable collaborative data visualization, resource sharing, and synchronous computation among multiple users. History The original authors of Croquet opened a commercial company named Qwaq which was later renamed to Teleplace. That technology was later sold back to a group of the original Croquet developers and became Immersive Terf. Croquet is the confluence of several independent lines of work that were being carried out by its six principal architects, Alan Kay, David A. Smith. David P. Reed, Andreas Raab, Julian L ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Self (programming Language)
is an object-oriented programming language based on the concept of ''prototypes''. Self began as a dialect of Smalltalk, being dynamically typed and using just-in-time compilation (JIT) as well as the prototype-based approach to objects: it was first used as an experimental test system for language design in the 1980s and 1990s. In 2006, Self was still being developed as part of the Klein project, which was a Self virtual machine written fully in Self. The latest version is 2017.1 released in May 2017. Several just-in-time compilation techniques were pioneered and improved in Self research as they were required to allow a very high level object oriented language to perform at up to half the speed of optimized C. Much of the development of Self took place at Sun Microsystems, and the techniques they developed were later deployed for Java's HotSpot virtual machine. At one point a version of Smalltalk was implemented in Self. Because it was able to use the JIT, this also gave ext ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Logo (programming Language)
Logo is an educational programming language, designed in 1967 by Wally Feurzeig, Seymour Papert, and Cynthia Solomon. ''Logo'' is not an acronym: the name was coined by Feurzeig while he was at Bolt, Beranek and Newman, and derives from the Greek ''logos'', meaning ''word'' or ''thought''. A general-purpose language, Logo is widely known for its use of turtle graphics, in which commands for movement and drawing produced line or vector graphics, either on screen or with a small robot termed a turtle. The language was conceived to teach concepts of programming related to Lisp and only later to enable what Papert called " body-syntonic reasoning", where students could understand, predict, and reason about the turtle's motion by imagining what they would do if they were the turtle. There are substantial differences among the many dialects of Logo, and the situation is confused by the regular appearance of turtle graphics programs that are named Logo. Logo is a multi-paradigm adaptati ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Newspeak (programming Language)
Newspeak is a programming language and Computing platform, platform in the tradition of Smalltalk and Self (programming language), Self being developed by a team led by Gilad Bracha. The platform includes an integrated development environment (IDE), a graphical user interface (GUI) Library (computing), library, and standard libraries. Starting in 2006, Cadence Design Systems funded its development and employed the main contributors, but ended funding in January 2009. Newspeak is a Class (computer programming), class-based language. Classes may be nested, as in BETA (programming language), BETA. This is one of the key differences between Newspeak and Smalltalk. All names in Newspeak are late-bound, and are interpreted as message passing, message sends, as in Self. Newspeak is distinguished by its unusual approach to modularity. The language has no global namespace. Top level classes act as module declarations. Module declarations are first class values (i.e., they may be stored in ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |