|
Spirochete
A spirochaete () or spirochete is a member of the phylum Spirochaetota (), (synonym Spirochaetes) which contains distinctive diderm (double-membrane) gram-negative bacteria, most of which have long, helically coiled (corkscrew-shaped or spiraled, hence the name) cells. Spirochaetes are chemoheterotrophic in nature, with lengths between 3 and 500 μm and diameters around 0.09 to at least 3 μm. Spirochaetes are distinguished from other bacterial phyla by the location of their flagella, called endoflagella which are sometimes called ''axial filaments''. Endoflagella are anchored at each end (pole) of the bacterium within the periplasmic space (between the inner and outer membranes) where they project backwards to extend the length of the cell. These cause a twisting motion which allows the spirochaete to move about. When reproducing, a spirochaete will undergo asexual transverse binary fission. Most spirochaetes are free-living and anaerobic, but there are nume ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
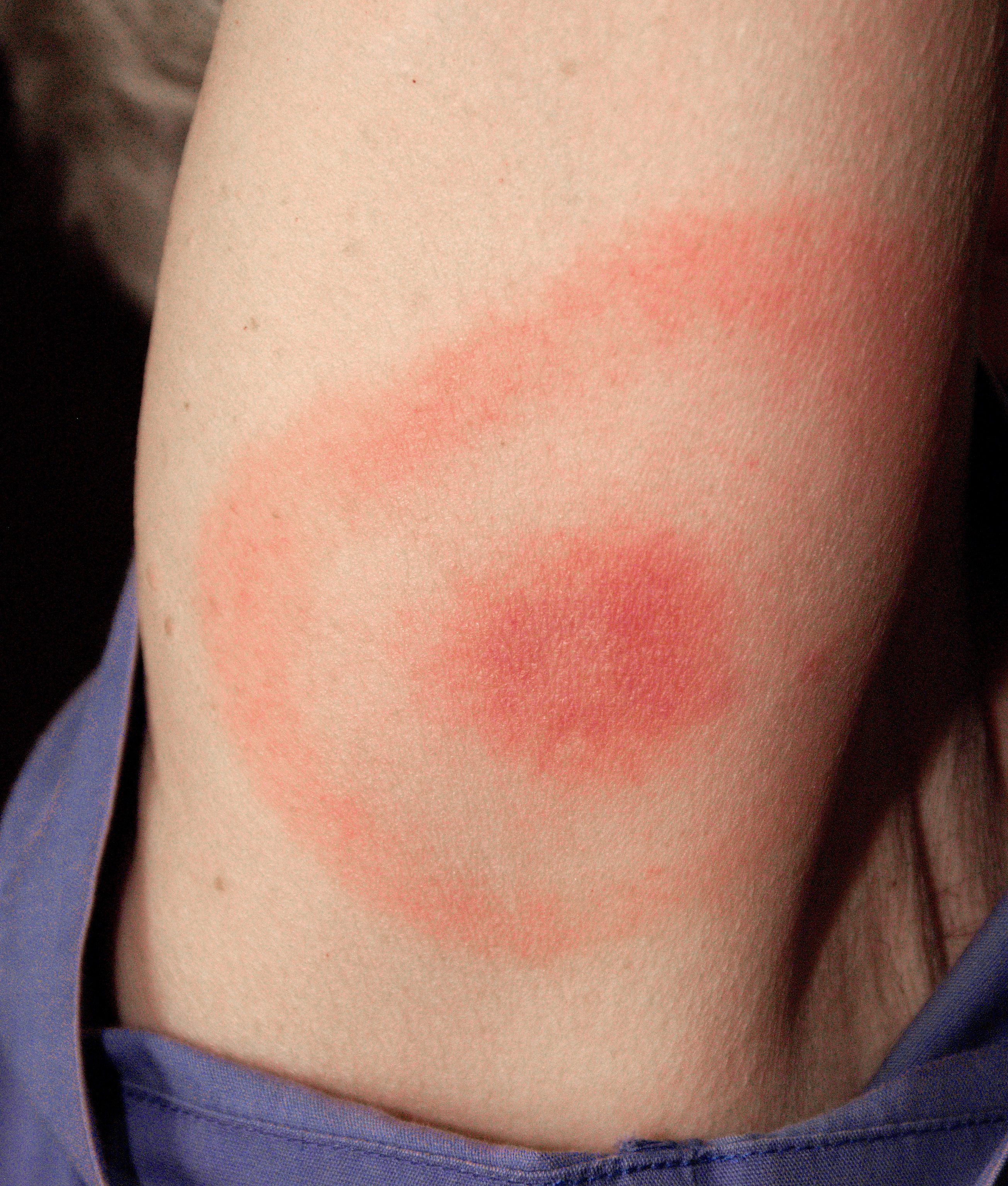
Borrelia Burgdorferi
''Borrelia burgdorferi'' is a bacterial species of the spirochete class in the genus '' Borrelia'', and is one of the causative agents of Lyme disease in humans. Along with a few similar genospecies, some of which also cause Lyme disease, it makes up the species complex of ''Borrelia burgdorferi'' sensu lato. The complex currently comprises 20 accepted and 3 proposed genospecies. ''B. burgdorferi'' sensu stricto exists in North America and Eurasia and until 2016 was the only known cause of Lyme disease in North America. ''Borrelia'' species are Gram-negative. Microbiology ''Borrelia burgdorferi'' is named after the researcher Willy Burgdorfer, who first isolated the bacterium in 1982. ''Borrelia burgdorferi'' is a microaerophile, requiring small amounts of oxygen in order to undergo glycolysis and survive. Like all other ''Borrelia'' sps., this bacterium is also gram-negative and a spirochete. Borrelia colonies are often smaller, rounded, and white with an elevated center ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Syphilis
Syphilis () is a sexually transmitted infection caused by the bacterium '' Treponema pallidum'' subspecies ''pallidum''. The signs and symptoms of syphilis vary depending in which of the four stages it presents (primary, secondary, latent, and tertiary). The primary stage classically presents with a single chancre (a firm, painless, non-itchy skin ulceration usually between 1 cm and 2 cm in diameter) though there may be multiple sores. In secondary syphilis, a diffuse rash occurs, which frequently involves the palms of the hands and soles of the feet. There may also be sores in the mouth or vagina. In latent syphilis, which can last for years, there are few or no symptoms. In tertiary syphilis, there are gummas (soft, non-cancerous growths), neurological problems, or heart symptoms. Syphilis has been known as " the great imitator" as it may cause symptoms similar to many other diseases. Syphilis is most commonly spread through sexual activity. It may also be tra ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Relapsing Fever
Relapsing fever is a vector-borne disease caused by infection with certain bacteria in the genus '' Borrelia'', which is transmitted through the bites of lice or soft-bodied ticks (genus '' Ornithodoros''). Signs and symptoms Most people who are infected develop sickness between 5 and 15 days after they are bitten. The symptoms may include a sudden fever, chills, headaches, muscle or joint aches, and nausea. A rash may also occur. These symptoms usually continue for 2 to 9 days, then disappear. This cycle may continue for several weeks if the person is not treated. Causes Louse-borne relapsing fever Along with '' Rickettsia prowazekii'' and '' Bartonella quintana'', '' Borrelia recurrentis'' is one of three pathogens of which the body louse ('' Pediculus humanus humanus'') is a vector. Louse-borne relapsing fever is more severe than the tick-borne variety. Louse-borne relapsing fever occurs in epidemics amid poor living conditions, famine and war in the developing world. ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Spirochete Cross Section
A spirochaete () or spirochete is a member of the phylum Spirochaetota (), (synonym Spirochaetes) which contains distinctive diderm (double-membrane) gram-negative bacteria, most of which have long, helically coiled (corkscrew-shaped or spiraled, hence the name) cells. Spirochaetes are chemoheterotrophic in nature, with lengths between 3 and 500 μm and diameters around 0.09 to at least 3 μm. Spirochaetes are distinguished from other bacterial phyla by the location of their flagella, called endoflagella which are sometimes called ''axial filaments''. Endoflagella are anchored at each end (pole) of the bacterium within the periplasmic space (between the inner and outer membranes) where they project backwards to extend the length of the cell. These cause a twisting motion which allows the spirochaete to move about. When reproducing, a spirochaete will undergo asexual transverse binary fission. Most spirochaetes are free-living and anaerobic, but there are nume ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Endoflagella Components
A spirochaete () or spirochete is a member of the phylum Spirochaetota (), (synonym Spirochaetes) which contains distinctive diderm (double-membrane) gram-negative bacteria, most of which have long, helically coiled (corkscrew-shaped or spiraled, hence the name) cells. Spirochaetes are chemoheterotrophic in nature, with lengths between 3 and 500 μm and diameters around 0.09 to at least 3 μm. Spirochaetes are distinguished from other bacterial phyla by the location of their flagella, called endoflagella which are sometimes called ''axial filaments''. Endoflagella are anchored at each end (pole) of the bacterium within the periplasmic space (between the inner and outer membranes) where they project backwards to extend the length of the cell. These cause a twisting motion which allows the spirochaete to move about. When reproducing, a spirochaete will undergo asexual transverse binary fission. Most spirochaetes are free-living and anaerobic, but there are nume ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Borrelia Mayonii
''Borrelia mayonii'' is a Gram-negative, host-associated spirochete that is capable of causing Lyme disease. This organism can infect various vertebrate and invertebrate hosts such as humans and ticks, primarily ''Ixodes scapularis''. Migratory songbirds play a role in the dispersal of the tick vector, ''Ixodes scapularis'', across long distances, indirectly dispersing ''Borrelia mayonii'' as well. Phylogenetic information ''Borrelia mayonii'' was identified as a ''sensu lato'' (broad sense), genospecies (Bbsl) of the known microbe, ''Borrelia burgdorferi''. A genospecies is a cluster of organisms with similar core genes that usually does not undergo genetic recombination with diverged organisms. Two isolates, gene strains, of ''B. mayonii'', named MN14-1420 and MN14-1539, were sequenced, process of arranging a chain of genetic information to match up to a specific organism's genetic code, and compared to the genome or genetic material of ''Borrelia burgdorferi''. With a ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Spiral Bacteria
Spiral bacteria, bacteria of spiral (helical) shape, form the third major morphological category of prokaryotes along with the rod-shaped bacilli and round cocci. Spiral bacteria can be subclassified by the number of twists per cell, cell thickness, cell flexibility, and motility. The two types of spiral cells are spirillum and spirochete, with spirillum being rigid with external flagella, and spirochetes being with internal flagella. Spirillum A spirillum (plural spirilla) is a rigid spiral bacterium that is Gram-negative and frequently has external amphitrichous or lophotrichous flagella. Examples include: * Members of the genus '' Spirillum'' * ''Campylobacter'' species, such as ''Campylobacter jejuni'', a foodborne pathogen that causes campylobacteriosis * '' Helicobacter'' species, such as ''Helicobacter pylori'', a cause of peptic ulcers Spirochetes A spirochete (plural spirochetes) is a very thin, elongate, flexible, spiral bacteria that is motile via internal p ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Treponema Pallidum
''Treponema pallidum'', formerly known as ''Spirochaeta pallida'', is a spirochaete bacterium with various subspecies that cause the diseases syphilis, bejel (also known as endemic syphilis), and yaws. It is transmitted only among humans. It is a helically coiled microorganism usually 6–15 μm long and 0.1–0.2 μm wide. ''T. pallidum'''s lack of either a tricarboxylic acid cycle or oxidative phosphorylation results in minimal metabolic activity. The treponemes have a cytoplasmic and an outer membrane. Using light microscopy, treponemes are visible only by using dark field illumination. ''Treponema pallidum'' consists of three subspecies, ''T. p. pallidum, T. p. endemicum,'' and ''T. p. pertenue,'' each of which has a distinct associated disease. Subspecies Three subspecies of ''T. pallidum'' are known: * ''Treponema pallidum pallidum'', which causes syphilis * ''T. p. endemicum'', which causes bejel or endemic syphilis * ''T. p. pertenue'', which causes yaw ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Brevinematales
''Brevinema andersonii'' (Brev. i. ne' ma. L. adj. brevis, short; Gr. n. nema, thread; N.L. neut. n. Brevinema, a short thread.) (an.derso'ni.i. N.L. gen. n. andersonii, of Anderson), named for John F. Anderson, who first described the organism. This organism is a Gram-negative, microaerophilic, helical shaped, chemoorganotrophic organism from the genus '' Brevinema''. ''Brevinema andersonii'' is host associated, strains have been isolated from blood and other tissues of short-tailed shrews ('' Blarina brevicauda'') and white-footed mice (''Peromyscus Zeucopus'') and are infectious for laboratory mice and Syrian hamsters.''B. andersonii'' is readily identified by restriction enzyme analysis, and SDS-PAGE, or fatty acid composition data. Another identifier for ''B. andersonii'' is the sheathed periplasmic flagella in the 1-2-1 configuration. While cells are visible by dark-field or phase-contrast microscopy, they cannot be seen when bright-field microscopy is used. History ''Bre ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Flagellum
A flagellum (; ) is a hairlike appendage that protrudes from certain plant and animal sperm cells, and from a wide range of microorganisms to provide motility. Many protists with flagella are termed as flagellates. A microorganism may have from one to many flagella. A gram-negative bacterium ''Helicobacter pylori'' for example uses its multiple flagella to propel itself through the mucus lining to reach the stomach epithelium, where it may cause a gastric ulcer to develop. In some bacteria the flagellum can also function as a sensory organelle, being sensitive to wetness outside the cell. Across the three domains of Bacteria, Archaea, and Eukaryota the flagellum has a different structure, protein composition, and mechanism of propulsion but shares the same function of providing motility. The Latin word means "whip" to describe its lash-like swimming motion. The flagellum in archaea is called the archaellum to note its difference from the bacterial flagellum. Eukary ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Leptospira
''Leptospira'' ( grc, leptos, italics=yes, 'fine, thin' and la, spira, links=no, 'coil') is a genus of spirochaete bacteria, including a small number of pathogenic and saprophytic species. ''Leptospira'' was first observed in 1907 in kidney tissue slices of a leptospirosis victim who was described as having died of "yellow fever". Taxonomy ''Leptospira'', together with the genera ''Leptonema'' and ''Turneria'', is a member of the family Leptospiraceae. The genus ''Leptospira'' is divided into 20 species based on DNA hybridization studies. Pathogenic ''Leptospira'' :''Leptospira alstonii'' Smythe et al. 2013 ''Leptospira alstoni''" Haake et al. 1993:''Leptospira interrogans'' (Stimson 1907) Wenyon 1926 emend. Faine and Stallman 1982 ["''Spirochaeta interrogans''" Stimson 1907; "''Spirochaeta nodosa''" Hubener & Reiter 1916; "''Spirochaeta icterohaemorrhagiae''" Inada et al. 1916; "''Spirochaeta icterogenes''" Uhlenhuth & Fromme 1916; "''Leptospira icteroides''" Noguchi 1919] ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Borrelia Lusitaniae
''Borrelia lusitaniae'' is a bacterium of the spirochete class of the genus'' Borrelia'', which has a diderm (double-membrane) envelope. It is a part of the ''Borrelia burgdorferi'' ''sensu lato'' genospecies and is a Gram-negative bacterium. ''B. lusitaniae'' is tick-borne; he type strain is PotiB2. It can be pathogenic, being involved in cases of Lyme borreliosis. A species of tick, ''Ixodes ricinus'', is the host of ''B. lusitaniae''. It is thought to have originated from Portugal and has since spread to parts of Europe and North Africa. Lizards of the family Lacertidae are now believed to be important reservoir hosts of this bacterium. Origin and distribution While ''B. lusitaniae'' is distributed throughout countries in Europe and North Africa, it is the sole species of the Lyme borreliosis group in southern Portugal. Lizards of the family Lacertidae are believed to be important reservoir hosts of ''B. lusitaniae''. They were first isolated in Portugal in 1993. These liza ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |