|
Spillover Infection
Spillover infection, also known as pathogen spillover and spillover event, occurs when a reservoir population with a high pathogen prevalence comes into contact with a novel host population. The pathogen is transmitted from the reservoir population and may or may not be transmitted within the host population. Due to climate change and land use expansion, the risk of viral spillover is predicted to significantly increase. Spillover zoonoses Spillover is a common event; in fact, more than two-thirds of human viruses are zoonotic. Most spillover events result in self-limited cases with no further human to human transmission, as occurs, for example, with rabies, anthrax, histoplasmosis or hidatidosis. Other zoonotic pathogens are able to be transmitted by humans to produce secondary cases and even to establish limited chains of transmission. Some examples are the Ebola and Marburg filoviruses, COVID-19, the MERS and SARS coronaviruses or some avian flu viruses. Finally, some few spil ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Natural Reservoir
In infectious disease ecology and epidemiology, a natural reservoir, also known as a disease reservoir or a reservoir of infection, is the population of organisms or the specific environment in which an infectious pathogen naturally lives and reproduces, or upon which the pathogen primarily depends for its survival. A reservoir is usually a living host of a certain species, such as an animal or a plant, inside of which a pathogen survives, often (though not always) without causing disease for the reservoir itself. By some definitions a reservoir may also be an environment external to an organism, such as a volume of contaminated air or water. Because of the enormous variety of infectious microorganisms capable of causing disease, precise definitions for what constitutes a natural reservoir are numerous, various, and often conflicting. The reservoir concept applies only for pathogens capable of infecting more than one host population and only with respect to a defined target popula ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Bumblebees
A bumblebee (or bumble bee, bumble-bee, or humble-bee) is any of over 250 species in the genus ''Bombus'', part of Apidae, one of the bee families. This genus is the only extant group in the tribe Bombini, though a few extinct related genera (e.g., ''Calyptapis'') are known from fossils. They are found primarily in higher altitudes or latitudes in the Northern Hemisphere, although they are also found in South America, where a few lowland tropical species have been identified. European bumblebees have also been introduced to New Zealand and Tasmania. Female bumblebees can sting repeatedly, but generally ignore humans and other animals. Most bumblebees are social insects that form colonies with a single queen. The colonies are smaller than those of honey bees, growing to as few as 50 individuals in a nest. Cuckoo bumblebees are brood parasitic and do not make nests or form colonies; their queens aggressively invade the nests of other bumblebee species, kill the resident queen ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
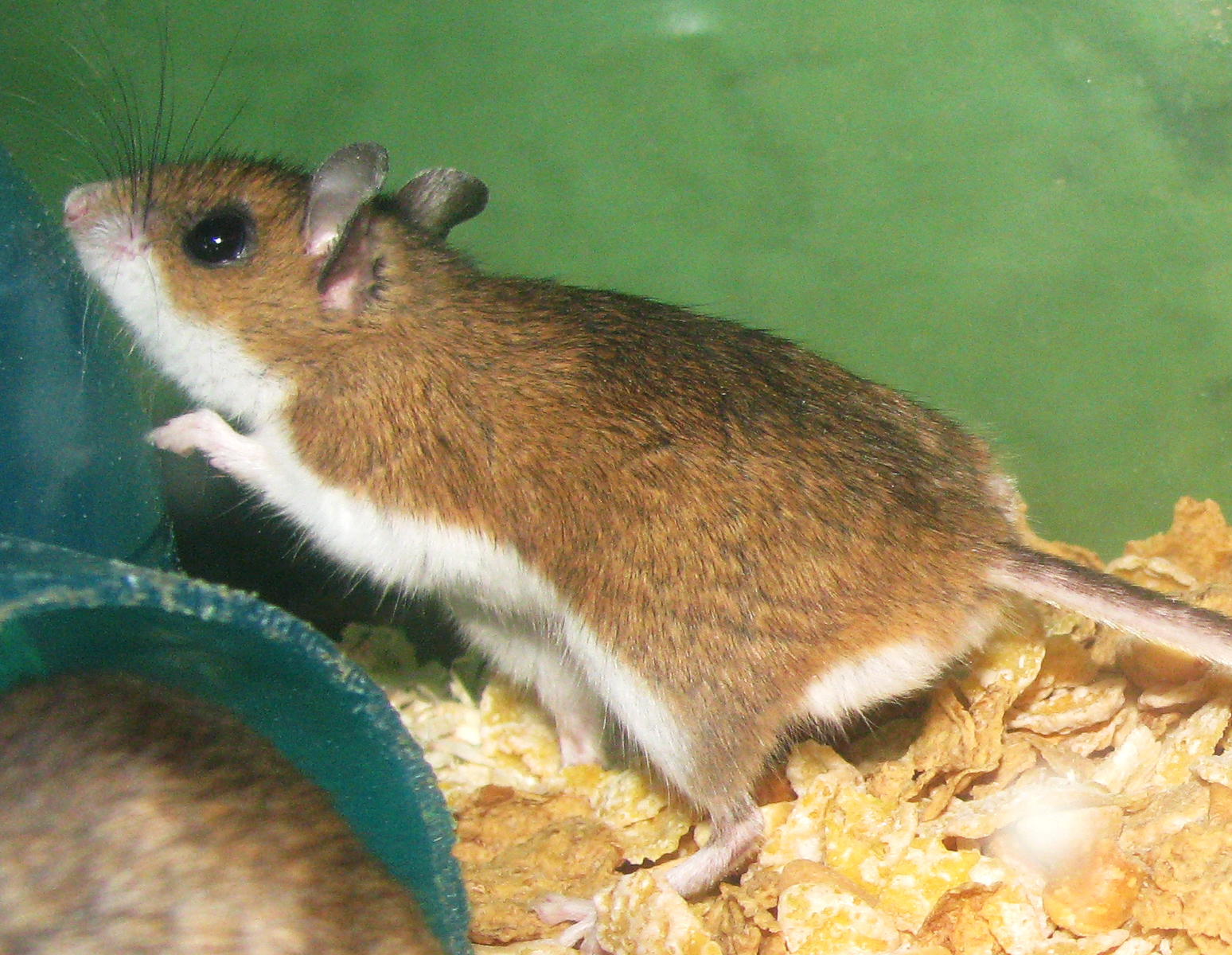
1993 Four Corners Hantavirus Outbreak
The 1993 Four Corners hantavirus outbreak was an outbreak of hantavirus that caused the first known human cases of hantavirus disease in the United States. It occurred within the Four Corners region – the geographic intersection of the U.S. states of Utah, Colorado, New Mexico, and Arizona – of the Southwestern United States in mid-1993. This region is largely occupied by Native American tribal lands, including the Hopi, Ute, Zuni, and Navajo reservations, from which many of the cases were reported. The virus killed 13 people — half of those it infected, for a mortality rate of 50%. The cause of the outbreak was found to be a previously unknown species of hantavirus, which was responsible for a new form of illness known as hantavirus pulmonary syndrome or HPS. The virus is carried by deer mice. Originally referred to as "Four Corners virus", "Muerto Canyon virus", and "Convict Creek virus", it was later named Sin Nombre virus. Transmission to humans was found to have ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
List Of Legionellosis Outbreaks
This is a list of Legionnaires' disease outbreaks; Legionnaire's is a potentially fatal infectious disease caused by gram negative, aerobic bacteria belonging to the genus ''Legionella''. The first reported outbreak was in Philadelphia, Pennsylvania in 1976 during a Legionnaires Convention at the Bellevue-Stratford Hotel. An outbreak is defined as two or more cases where the onset of illness is closely linked in time (weeks rather than months) ''and'' in space, where there is suspicion of, or evidence of, a common source of infection, with or without microbiological support (''i.e.'' common spatial location of cases from travel history). Worldwide listings by year 1960s 1970s 1980s 1990s 2000s 2010s 2020s Governmental controls to prevent outbreaks Regulations and ordinances The guidance issued by the UK government's Health and Safety Executive (HSE) now recommends that microbiological monitoring for wet cooling systems, using a dipslide, should be performed weekl ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Outbreak
In epidemiology, an outbreak is a sudden increase in occurrences of a disease when cases are in excess of normal expectancy for the location or season. It may affect a small and localized group or impact upon thousands of people across an entire continent. The number of cases varies according to the disease-causing agent, and the size and type of previous and existing exposure to the agent. Outbreaks include many epidemics, which term is normally only for infectious diseases, as well as diseases with an environmental origin, such as a water or foodborne disease. They may affect a region in a country or a group of countries. Pandemics are near-global disease outbreaks when multiple and various countries around the Earth are soon infected. Definition The terms "outbreak" and "epidemic" have often been used interchangeably. Researchers Manfred S. Green and colleagues propose that the latter term be restricted to larger events, pointing out that '' Chambers Concise Dictionary'' and ' ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Infection
An infection is the invasion of tissues by pathogens, their multiplication, and the reaction of host tissues to the infectious agent and the toxins they produce. An infectious disease, also known as a transmissible disease or communicable disease, is an illness resulting from an infection. Infections can be caused by a wide range of pathogens, most prominently bacteria and viruses. Hosts can fight infections using their immune system. Mammalian hosts react to infections with an innate response, often involving inflammation, followed by an adaptive response. Specific medications used to treat infections include antibiotics, antivirals, antifungals, antiprotozoals, and antihelminthics. Infectious diseases resulted in 9.2 million deaths in 2013 (about 17% of all deaths). The branch of medicine that focuses on infections is referred to as infectious disease. Types Infections are caused by infectious agents (pathogens) including: * Bacteria (e.g. ''Mycobacterium tuberculosis'', ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Epidemic
An epidemic (from Ancient Greek, Greek ἐπί ''epi'' "upon or above" and δῆμος ''demos'' "people") is the rapid spread of disease to a large number of patients among a given population within an area in a short period of time. Epidemics of infectious diseases are generally caused by several factors including a significant change in the ecology of the areal population (e.g., increased stress maybe additional reason or increase in the density of a vector species), the introduction of an emerging pathogen to an areal population (by movement of pathogen or host) or an unexpected genetic change that is in the pathogen reservoir. Generally, epidemics concerns with the patterns of infectious disease spread. An epidemic may occur when host immunity to either an established pathogen or newly emerging novel pathogen is suddenly reduced below that found in the endemic equilibrium and the transmission threshold is exceeded. For example, in meningococcal infections, an attack rate in ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Reverse Zoonosis
A reverse zoonosis, also known as a zooanthroponosis (Greek "animal", "man", ''"''disease") or anthroponosis, is a pathogen reservoired in humans that is capable of being transmitted to non-human animals. Terminology Anthroponosis refers to pathogens sourced from humans and can include human to non-human animal transmission but also human to human transmission. The term zoonosis technically refers to disease transferred between any animal and another animal, human or non-human, without discretion, and also been defined as disease transmitted from animals to humans ''and vice versa''. Yet because of human-centered medical biases, zoonosis tends to be used in the same manner as anthropozoonosis which specifically refers to pathogens reservoired in non-human animals that are transmissible to humans. Additional confusion due to frequency of scientists using "anthropozoonosis" and "zooanthroponosis" interchangeably was resolved during a 1967 Joint Food and Agriculture and World He ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Cross-species Transmission
Cross-species transmission (CST), also called interspecies transmission, host jump, or spillover, is the transmission of an infectious pathogen, such as a virus, between hosts belonging to different species. Once introduced into an individual of a new host species, the pathogen may cause disease for the new host and/or acquire the ability to infect other individuals of the same species, allowing it to spread through the new host population. The phenomenon is most commonly studied in virology, but cross-species transmission may also occur with bacterial pathogens or other types of microorganisms. Steps involved in the transfer of pathogens to new hosts include contact between the pathogen and the host; the successful infection of an initial individual host, which may lead to amplification and an outbreak; and the adaptation of the pathogen, within either the original or new host, which may render it capable of spreading efficiently between individuals in populations of the new host. ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Locustacarus Buchneri
''Locustacarus buchneri'' is a parasitic mite that lives in the respiratory air sacs of bumblebee A bumblebee (or bumble bee, bumble-bee, or humble-bee) is any of over 250 species in the genus ''Bombus'', part of Apidae, one of the bee families. This genus is the only extant group in the tribe Bombini, though a few extinct related gener ...s. They are relatively host-specific and are found primarily in the subgenus ''Bombus sensu stricto''. Bees infested with the mite have a reduced lifespan in laboratory conditions, and although in one study they foraged at a rate similar to uninfected bees, infected bees showed a greater preference for a single flower type. Prevalence varies, but infection appears to be more common among commercial colonies than wild populations. Among colonies commercially imported from the Netherlands and Belgium to Japan, infestation rates were 20%. In South America, prevalence is very low in native populations. In Canada, there was evidence that co ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Deformed Wing Virus
''Deformed wing virus'' (DWV) is an RNA virus, one of 22 known viruses affecting honey bees. While most commonly infecting the honey bee, ''Apis mellifera'', it has also been documented in other bee species, like '' Bombus terrestris'', thus, indicating it may have a wider host specificity than previously anticipated. The virus was first isolated from a sample of symptomatic honeybees from Japan in the early 1980s and is currently distributed worldwide. It is found also in pollen baskets and commercially reared bumblebees. Its main vector in ''A. mellifera'' is the '' Varroa'' mite. It is named after what is usually the most obvious deformity it induces in the development of a honeybee pupa, which is shrunken and deformed wings, but other developmental deformities are often present. Genomics The viral genome was published in 2006. The genome is 10140 nucleotides in length excluding the poly(A) tail and contains a single large open reading frame encoding a 328-kilo Dalton (kDA) p ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Nosema Ceranae
''Nosema ceranae'' is a microsporidian, a small, unicellular parasite that mainly affects '' Apis cerana'', the Asiatic honey bee. Along with ''Nosema apis'', it causes the disease nosemosis, the most widespread of the diseases of adult honey bees. ''N. ceranae'' can remain dormant as a long-lived spore which is resistant to temperature extremes and dehydration. This fungus has been shown to act in a synergistic fashion with diverse insecticides such as fipronil or neonicotinoids, by increasing the toxicity of pesticides for bees, leading to higher bee mortality. It may thus play an indirect role in colony collapse disorder. In addition, the interaction between fipronil and ''N. ceranae'' induces changes in male physiology leading to sterility. Range ''Nosema ceranae'' was first described in 1996 and was identified as a disease of ''Apis mellifera'' in 2004 in Taiwan. Since its emergence in honeybees, ''N. ceranae ''has been identified in bumblebee species in South America, ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
_(35908751483).jpg)