|
Spherical Symmetry
In geometry, circular symmetry is a type of continuous symmetry for a planar object that can be rotated by any arbitrary angle and map onto itself. Rotational circular symmetry is isomorphic with the circle group in the complex plane, or the special orthogonal group SO(2), and unitary group U(1). Reflective circular symmetry is isomorphic with the orthogonal group O(2). Two dimensions A 2-dimensional object with circular symmetry would consist of concentric circles and annular domains. Rotational circular symmetry has all cyclic symmetry, Z''n'' as subgroup symmetries. Reflective circular symmetry has all dihedral symmetry, Dih''n'' as subgroup symmetries. Three dimensions In 3-dimensions, a surface or solid of revolution has circular symmetry around an axis, also called cylindrical symmetry or axial symmetry. An example is a right circular cone. Circular symmetry in 3 dimensions has all pyramidal symmetry, C''n''v as subgroups. A double-cone, bicone, cylinder, toro ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Bilateral Symmetry
Symmetry in biology refers to the symmetry observed in organisms, including plants, animals, fungi, and bacteria. External symmetry can be easily seen by just looking at an organism. For example, take the face of a human being which has a plane of symmetry down its centre, or a pine cone with a clear symmetrical spiral pattern. Internal features can also show symmetry, for example the tubes in the human body (responsible for transporting gases, nutrients, and waste products) which are cylindrical and have several planes of symmetry. Biological symmetry can be thought of as a balanced distribution of duplicate body parts or shapes within the body of an organism. Importantly, unlike in mathematics, symmetry in biology is always approximate. For example, plant leaves – while considered symmetrical – rarely match up exactly when folded in half. Symmetry is one class of patterns in nature whereby there is near-repetition of the pattern element, either by reflection or rotation ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
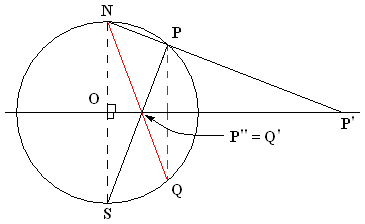
Stereographic Projection
In mathematics, a stereographic projection is a perspective projection of the sphere, through a specific point on the sphere (the ''pole'' or ''center of projection''), onto a plane (geometry), plane (the ''projection plane'') perpendicular to the diameter through the point. It is a smooth function, smooth, bijection, bijective function (mathematics), function from the entire sphere except the center of projection to the entire plane. It maps circle of a sphere, circles on the sphere to generalised circle, circles or lines on the plane, and is conformal map, conformal, meaning that it preserves angles at which curves meet and thus Local property, locally approximately preserves similarity (geometry), shapes. It is neither isometry, isometric (distance preserving) nor Equiareal map, equiareal (area preserving). The stereographic projection gives a way to representation (mathematics), represent a sphere by a plane. The metric tensor, metric induced metric, induced by the inverse s ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Clifford Torus
In geometric topology, the Clifford torus is the simplest and most symmetric flat embedding of the cartesian product of two circles ''S'' and ''S'' (in the same sense that the surface of a cylinder is "flat"). It is named after William Kingdon Clifford. It resides in R4, as opposed to in R3. To see why R4 is necessary, note that if ''S'' and ''S'' each exists in its own independent embedding space R and R, the resulting product space will be R4 rather than R3. The historically popular view that the cartesian product of two circles is an R3 torus in contrast requires the highly asymmetric application of a rotation operator to the second circle, since that circle will only have one independent axis ''z'' available to it after the first circle consumes ''x'' and ''y''. Stated another way, a torus embedded in R3 is an asymmetric reduced-dimension projection of the maximally symmetric Clifford torus embedded in R4. The relationship is similar to that of projecting the edges of ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Prismatic Symmetry
In geometry, dihedral symmetry in three dimensions is one of three infinite sequences of point groups in three dimensions which have a symmetry group that as an abstract group is a dihedral group Dih''n'' (for ''n'' ≥ 2). Types There are 3 types of dihedral symmetry in three dimensions, each shown below in 3 notations: Schönflies notation, Coxeter notation, and orbifold notation. ;Chiral: *''Dn'', 'n'',2sup>+, (22''n'') of order 2''n'' – dihedral symmetry or para-n-gonal group (abstract group: ''Dihn''). ;Achiral: *''Dnh'', 'n'',2 (*22''n'') of order 4''n'' – prismatic symmetry or full ortho-n-gonal group (abstract group: ''Dihn'' × ''Z''2). *''Dnd'' (or ''Dnv''), ''n'',2+ (2*''n'') of order 4''n'' – antiprismatic symmetry or full gyro-n-gonal group (abstract group: ''Dih''2''n''). For a given ''n'', all three have ''n''-fold rotational symmetry about one axis (rotation by an angle of 360°/''n'' does not change the object), and 2-fold rotational symmetr ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Spheroid
A spheroid, also known as an ellipsoid of revolution or rotational ellipsoid, is a quadric surface obtained by rotating an ellipse about one of its principal axes; in other words, an ellipsoid with two equal semi-diameters. A spheroid has circular symmetry. If the ellipse is rotated about its major axis, the result is a ''prolate spheroid'', elongated like a rugby ball. The American football is similar but has a pointier end than a spheroid could. If the ellipse is rotated about its minor axis, the result is an ''oblate spheroid'', flattened like a lentil or a plain M&M. If the generating ellipse is a circle, the result is a sphere. Due to the combined effects of gravity and rotation, the figure of the Earth (and of all planets) is not quite a sphere, but instead is slightly flattened in the direction of its axis of rotation. For that reason, in cartography and geodesy the Earth is often approximated by an oblate spheroid, known as the reference ellipsoid, instead of a sph ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Toroid
In mathematics, a toroid is a surface of revolution with a hole in the middle. The axis of revolution passes through the hole and so does not intersect the surface. For example, when a rectangle is rotated around an axis parallel to one of its edges, then a hollow rectangle-section ring is produced. If the revolved figure is a circle, then the object is called a torus. The term ''toroid'' is also used to describe a toroidal polyhedron. In this context a toroid need not be circular and may have any number of holes. A ''g''-holed ''toroid'' can be seen as approximating the surface of a torus having a topological genus, ''g'', of 1 or greater. The Euler characteristic χ of a ''g'' holed toroid is 2(1-''g'').Stewart, B.; "Adventures Among the Toroids:A Study of Orientable Polyhedra with Regular Faces", 2nd Edition, Stewart (1980). The torus is an example of a toroid, which is the surface of a doughnut. Doughnuts are an example of a solid torus created by rotating a disk, and s ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Cylinder (geometry)
A cylinder (from ) has traditionally been a three-dimensional solid, one of the most basic of curvilinear geometric shapes. In elementary geometry, it is considered a prism with a circle as its base. A cylinder may also be defined as an infinite curvilinear surface in various modern branches of geometry and topology. The shift in the basic meaning—solid versus surface (as in ball and sphere)—has created some ambiguity with terminology. The two concepts may be distinguished by referring to solid cylinders and cylindrical surfaces. In the literature the unadorned term cylinder could refer to either of these or to an even more specialized object, the ''right circular cylinder''. Types The definitions and results in this section are taken from the 1913 text ''Plane and Solid Geometry'' by George Wentworth and David Eugene Smith . A ' is a surface consisting of all the points on all the lines which are parallel to a given line and which pass through a fixed plane curve in a pla ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Bicone
In geometry, a bicone or dicone (from la, bi-, and Greek: ''di-'', both meaning "two") is the three-dimensional surface of revolution of a rhombus around one of its axes of symmetry. Equivalently, a bicone is the surface created by joining two congruent, right, circular cones at their bases. A bicone has circular symmetry and orthogonal bilateral symmetry. Geometry For a circular bicone with radius ''R'' and height center-to-top ''H'', the formula for volume becomes :V = \frac \pi R^2 H. For a right circular cone, the surface area is :SA =2\pi R S\, where S = \sqrt is the slant height. See also * Sphericon * Biconical antenna In radio systems, a biconical antenna is a broad-bandwidth antenna made of two roughly conical conductive objects, nearly touching at their points.Zhuohui Zhang,''Analysis and design of a broadband antenna for software defined radio'', ProQuest, 2 ... References External links * Elementary geometry Surfaces {{ ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Cone
A cone is a three-dimensional geometric shape that tapers smoothly from a flat base (frequently, though not necessarily, circular) to a point called the apex or vertex. A cone is formed by a set of line segments, half-lines, or lines connecting a common point, the apex, to all of the points on a base that is in a plane that does not contain the apex. Depending on the author, the base may be restricted to be a circle, any one-dimensional quadratic form in the plane, any closed one-dimensional figure, or any of the above plus all the enclosed points. If the enclosed points are included in the base, the cone is a solid object; otherwise it is a two-dimensional object in three-dimensional space. In the case of a solid object, the boundary formed by these lines or partial lines is called the ''lateral surface''; if the lateral surface is unbounded, it is a conical surface. In the case of line segments, the cone does not extend beyond the base, while in the case of half-lin ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |