|
Sperm Thermotaxis
Sperm thermotaxis is a form of sperm guidance, in which sperm cells (spermatozoa) actively change their swimming direction according to a temperature gradient, swimming up the gradient. Thus far this process has been discovered in mammals only. Background The discovery of mammalian sperm chemotaxis and the realization that it can guide spermatozoa for short distances only, estimated at the order of millimeters,Pérez-Cerezales, S., Boryshpolets, S. and Eisenbach, M. (2015) ''Behavioral mechanisms of mammalian sperm guidance''. Asian J. Androl. 17, 628-632. triggered a search for potential long-range guidance mechanisms. The findings that, at least in rabbits and pigs, a temperature difference exists within the oviduct, and that this temperature difference is established at ovulation in rabbits due to a temperature drop in the oviduct near the junction with the uterus, creating a temperature gradient between the sperm storage site and the fertilization site in the oviduct (Figure ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Figure 1
Figure 1 is a Toronto, Ontario-based online social networking service for healthcare professionals to post and comment on medical images. Figure 1 was founded in Toronto by Dr. Joshua Landy, Richard Penner and Gregory Levey. The platform launched in North America in May 2013 and is now available in more than 100 countries. The privately held company reports more than 1 million healthcare professionals use its app and website. Funding In 2013, Figure 1 launched with $2 million (CDN) in seed money, with Rho Canada Ventures and Version One Ventures led the investment. In 2015, the company added $5 million (USD) to its Series A financing round, which was led by Union Square Ventures, an early investor in Twitter, Tumblr, Etsy, and Kickstarter. This brings the total round to $9 million (USD). Reception Figure 1's content has been characterized as "gruesome". The app's founder said the "very colorful images" are what medics see every day. "It's a transparent view into a world y ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Hyperactivation
Hyperactivation is a type of sperm motility. Hyperactivated sperm motility is characterised by a high amplitude, asymmetrical beating pattern of the sperm tail (flagellum). This type of motility may aid in sperm penetration of the zona pellucida, which encloses the ovum. Hyperactivation could then be followed by the acrosome reaction where the cap-like structure on the head of the cell releases the enzymes it contains. This facilitates the penetration of the ovum and fertilisation. Some definitions consider sperm activation to consist of these two processes of hyperactivation and the acrosome reaction Hyperactivation is a term also used to express an X chromosome gene dosage compensation mechanism and is seen in Drosophila. Here, a complex of proteins bind to the X-linked genes to effectively double their genetic activity. This allows males (XY) to have equal genetic activity as females (XX), whose X's are not hyperactivated. Mechanisms Mammalian sperm cells become more act ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Phosphodiesterase
A phosphodiesterase (PDE) is an enzyme that breaks a phosphodiester bond. Usually, ''phosphodiesterase'' refers to cyclic nucleotide phosphodiesterases, which have great clinical significance and are described below. However, there are many other families of phosphodiesterases, including phospholipases C and D, autotaxin, sphingomyelin phosphodiesterase, DNases, RNases, and restriction endonucleases (which all break the phosphodiester backbone of DNA or RNA), as well as numerous less-well-characterized small-molecule phosphodiesterases. The cyclic nucleotide phosphodiesterases comprise a group of enzymes that degrade the phosphodiester bond in the second messenger molecules cAMP and cGMP. They regulate the localization, duration, and amplitude of cyclic nucleotide signaling within subcellular domains. PDEs are therefore important regulators of signal transduction mediated by these second messenger molecules. History These multiple forms (isoforms or subtypes) of phosphodies ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
TRPC3
Short transient receptor potential channel 3 (TrpC3) also known as transient receptor protein 3 (TRP-3) is a protein that in humans is encoded by the TRPC3 gene. The TRPC3/6/7 subfamily are implicated in the regulation of vascular tone, cell growth, proliferation and pathological hypertrophy. These are diacylgylcerol-sensitive cation channels known regulate intracellular calcium via activation of the phospholipase C (PLC) pathway and/or by sensing Ca2+ store depletion. Together, their role in calcium homeostasis has made them potential therapeutic targets for a variety of central and peripheral pathologies. Function Non-specific cation conductance elicited by the activation of TrkB by BDNF is TRPC3-dependent in the CNS. TRPC channels are almost always co-localized with mGluR1-expressing cells and likely play a role in mGluR-mediated EPSPs. The TRPC3 channel has been shown to be preferentially expressed in non-excitable cell types, such as oligodendrocytes. However, evidence ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Calcium In Biology
Calcium ions (Ca2+) contribute to the physiology and biochemistry of organisms' cell (biology), cells. They play an important role in signal transduction pathways, where they act as a second messenger, in neurotransmitter release from neurons, in contraction of all muscle cell types, and in fertilization. Many enzymes require calcium ions as a Cofactor (biochemistry), cofactor, including several of the coagulation factors. Extracellular calcium is also important for maintaining the potential difference across excitable cell cell membrane, membranes, as well as proper bone formation. Plasma calcium levels in mammals are tightly regulated, electronic-book electronic- with bone acting as the major mineral storage site. Calcium ions, Ca2+, are released from bone into the bloodstream under controlled conditions. Calcium is transported through the bloodstream as dissolved ions or bound to proteins such as serum albumin. Parathyroid hormone secreted by the parathyroid gland regulates ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
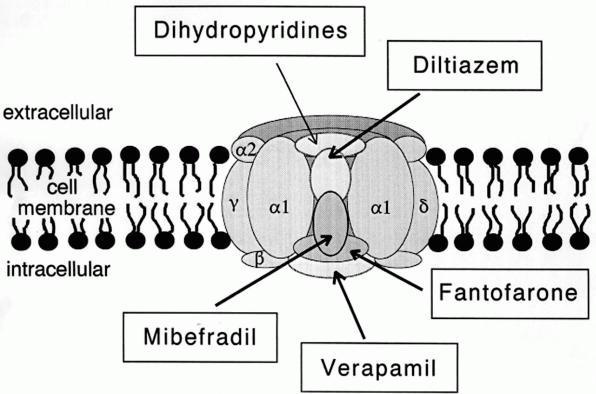
Calcium Channel
A calcium channel is an ion channel which shows selective permeability to calcium ions. It is sometimes synonymous with voltage-gated calcium channel, although there are also ligand-gated calcium channels. Comparison tables The following tables explain gating, gene, location and function of different types of calcium channels, both voltage and ligand-gated. Voltage-gated Ligand-gated *the ''receptor-operated calcium channels'' (in vasoconstriction) **P2X receptors Page 479 Pharmacology L-type calcium channel blockers are used to treat hypertension. In most areas of the body, depolarization is mediated by sodium influx into a cell; changing the calcium permeability has little effect on action potentials. However, in many smooth muscle tissues, depolarization is mediated primarily by calcium influx into the cell. L-type calcium channel blockers selectively inhibit these action potentials in smooth muscle which leads to dilation of blood vessels; this in turn corrects hypert ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Inositol Trisphosphate Receptor
Inositol trisphosphate receptor (InsP3R) is a membrane glycoprotein complex acting as a Ca2+ channel activated by inositol trisphosphate (InsP3). InsP3R is very diverse among organisms, and is necessary for the control of cellular and physiological processes including cell division, cell proliferation, apoptosis, fertilization, development, behavior, learning and memory. Inositol triphosphate receptor represents a dominant second messenger leading to the release of Ca2+ from intracellular store sites. There is strong evidence suggesting that the InsP3R plays an important role in the conversion of external stimuli to intracellular Ca2+ signals characterized by complex patterns relative to both space and time, such as Ca2+ waves and oscillations. Discovery The InsP3 receptor was first purified from rat cerebellum by neuroscientists Surachai Supattapone and Solomon Snyder at Johns Hopkins University School of Medicine. The cDNA of the InsP3 receptor was first cloned in the la ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
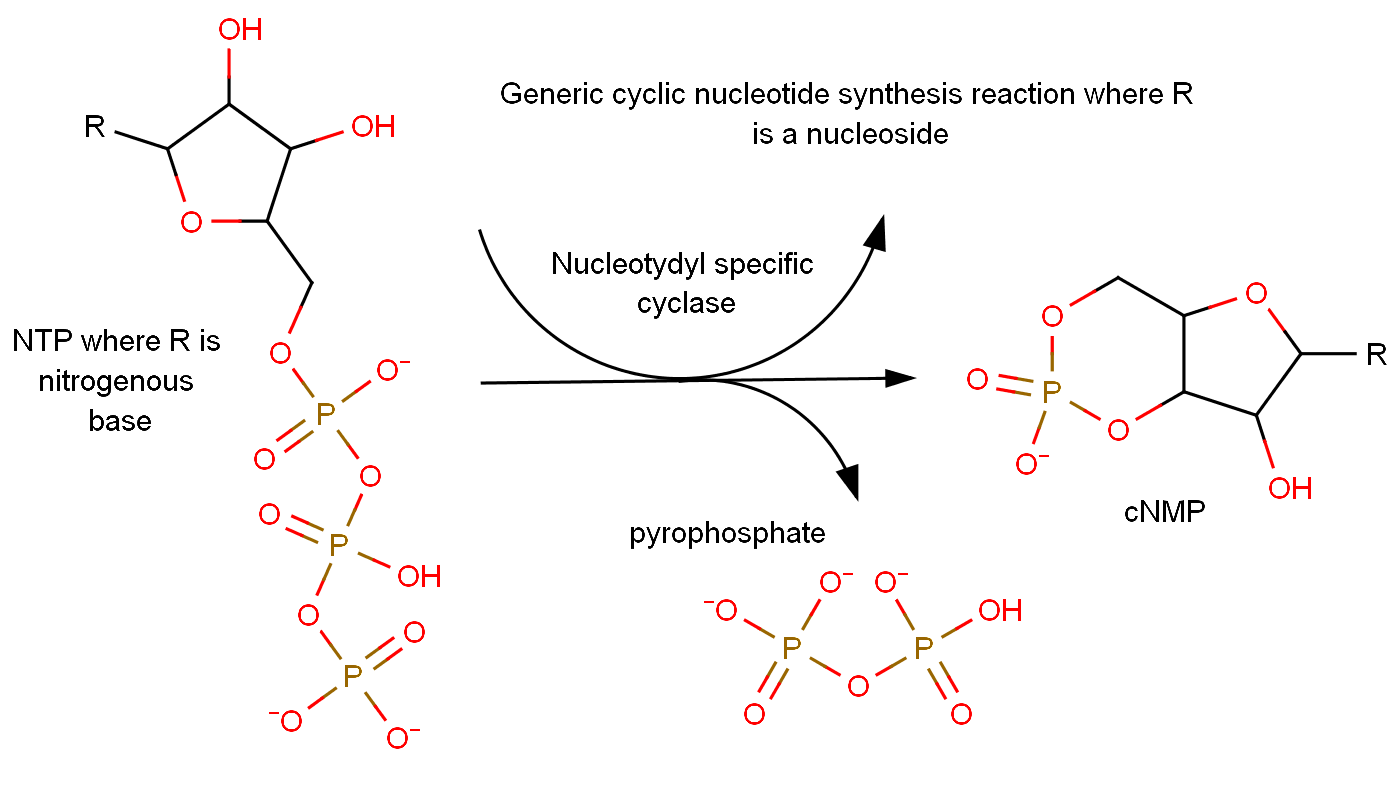
Cyclic Nucleotide
A cyclic nucleotide (cNMP) is a single-phosphate nucleotide with a cyclic bond arrangement between the sugar and phosphate groups. Like other nucleotides, cyclic nucleotides are composed of three functional groups: a sugar, a nitrogenous base, and a single phosphate group. As can be seen in the cyclic adenosine monophosphate (cAMP) and cyclic guanosine monophosphate (cGMP) images, the 'cyclic' portion consists of two bonds between the phosphate group and the 3' and 5' hydroxyl groups of the sugar, very often a ribose. Their biological significance includes a broad range of protein-ligand interactions. They have been identified as secondary messengers in both hormone and ion-channel signalling in eukaryotic cells, as well as allosteric effector compounds of DNA binding proteins in prokaryotic cells. cAMP and cGMP are currently the most well documented cyclic nucleotides, however there is evidence that cCMP (cytosine) is also involved in eukaryotic cellular messaging. The ro ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Phospholipase C
Phospholipase C (PLC) is a class of membrane-associated enzymes that cleave phospholipids just before the phosphate group (see figure). It is most commonly taken to be synonymous with the human forms of this enzyme, which play an important role in eukaryotic cell physiology, in particular signal transduction pathways. Phospholipase C's role in signal transduction is its cleavage of phosphatidylinositol 4,5-bisphosphate (PIP2) into diacyl glycerol (DAG) and inositol 1,4,5-trisphosphate (IP3), which serve as second messengers. Activators of each PLC vary, but typically include heterotrimeric G protein subunits, protein tyrosine kinases, small G proteins, Ca2+, and phospholipids. There are thirteen kinds of mammalian phospholipase C that are classified into six isotypes (β, γ, δ, ε, ζ, η) according to structure. Each PLC has unique and overlapping controls over expression and subcellular distribution. Variants Mammalian variants The extensive number of functions exerte ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Visual Perception
Visual perception is the ability to interpret the surrounding environment through photopic vision (daytime vision), color vision, scotopic vision (night vision), and mesopic vision (twilight vision), using light in the visible spectrum reflected by objects in the environment. This is different from visual acuity, which refers to how clearly a person sees (for example "20/20 vision"). A person can have problems with visual perceptual processing even if they have 20/20 vision. The resulting perception is also known as vision, sight, or eyesight (adjectives ''visual'', ''optical'', and ''ocular'', respectively). The various physiological components involved in vision are referred to collectively as the visual system, and are the focus of much research in linguistics, psychology, cognitive science, neuroscience, and molecular biology, collectively referred to as vision science. Visual system In humans and a number of other mammals, light enters the eye through the cornea and is ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
G-protein-coupled Receptor
G protein-coupled receptors (GPCRs), also known as seven-(pass)-transmembrane domain receptors, 7TM receptors, heptahelical receptors, serpentine receptors, and G protein-linked receptors (GPLR), form a large group of evolutionarily-related proteins that are cell surface receptors that detect molecules outside the cell and activate cellular responses. Coupling with G proteins, they are called seven-transmembrane receptors because they pass through the cell membrane seven times. Text was copied from this source, which is available under Attribution 2.5 Generic (CC BY 2.5) license. Ligands can bind either to extracellular N-terminus and loops (e.g. glutamate receptors) or to the binding site within transmembrane helices (Rhodopsin-like family). They are all activated by agonists although a spontaneous auto-activation of an empty receptor can also be observed. G protein-coupled receptors are found only in eukaryotes, including yeast, choanoflagellates, and a ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Opsin
Animal opsins are G-protein-coupled receptors and a group of proteins made light-sensitive via a chromophore, typically retinal. When bound to retinal, opsins become Retinylidene proteins, but are usually still called opsins regardless. Most prominently, they are found in photoreceptor cells of the retina. Five classical groups of opsins are involved in Visual perception, vision, mediating the conversion of a photon of light into an electrochemical signal, the first step in the Visual phototransduction, visual transduction cascade. Another opsin found in the mammalian retina, melanopsin, is involved in circadian rhythms and Pupillary light reflex, pupillary reflex but not in vision. Humans have in total nine opsins. Beside vision and light perception, opsins may also sense temperature, sound, or chemicals. Structure and function Animal opsins detect light and are the molecules that allow us to see. Opsins are G-protein-coupled receptors (GPCRs), which are chemoreceptors and hav ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |