|
Spectral Bands
Spectral bands are parts of the electromagnetic spectrum of specific wavelengths, which can be filtered by a standard filter. In nuclear physics, spectral bands are referred to the emission of polyatomic systems, including condensed materials, large molecules, etc. Each spectral line corresponds to one level in the atom splits in the molecules. When the number of atoms is large, one gets a continuum of energy levels, the so-called "spectral bands". They are often labeled in the same way as the monatomic lines. The bands may overlap. In general, the energy spectrum can be given by a density function, describing the number of energy levels of the quantum system for a given interval. Spectral bands have constant density, and when the bands overlap, the corresponding densities are added. Band spectra is the name given to a group of lines that are closely spaced and arranged in a regular sequence that appears to be a band. It is a colored band, separated by dark spaces on the two sides ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Electromagnetic Spectrum
The electromagnetic spectrum is the range of frequencies (the spectrum) of electromagnetic radiation and their respective wavelengths and photon energies. The electromagnetic spectrum covers electromagnetic waves with frequencies ranging from below one hertz to above 1025 hertz, corresponding to wavelengths from thousands of kilometers down to a fraction of the size of an atomic nucleus. This frequency range is divided into separate bands, and the electromagnetic waves within each frequency band are called by different names; beginning at the low frequency (long wavelength) end of the spectrum these are: radio waves, microwaves, infrared, visible light, ultraviolet, X-rays, and gamma rays at the high-frequency (short wavelength) end. The electromagnetic waves in each of these bands have different characteristics, such as how they are produced, how they interact with matter, and their practical applications. There is no known limit for long and short wavelengths. Extre ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Spectral Line
A spectral line is a dark or bright line in an otherwise uniform and continuous spectrum, resulting from emission or absorption of light in a narrow frequency range, compared with the nearby frequencies. Spectral lines are often used to identify atoms and molecules. These "fingerprints" can be compared to the previously collected ones of atoms and molecules, and are thus used to identify the atomic and molecular components of stars and planets, which would otherwise be impossible. Types of line spectra Spectral lines are the result of interaction between a quantum system (usually atoms, but sometimes molecules or atomic nuclei) and a single photon. When a photon has about the right amount of energy (which is connected to its frequency) to allow a change in the energy state of the system (in the case of an atom this is usually an electron changing orbitals), the photon is absorbed. Then the energy will be spontaneously re-emitted, either as one photon at the same frequ ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Molecular Spectra
The emission spectrum of a chemical element or chemical compound is the spectrum of frequencies of electromagnetic radiation emitted due to an electron making a transition from a high energy state to a lower energy state. The photon energy of the emitted photon is equal to the energy difference between the two states. There are many possible electron transitions for each atom, and each transition has a specific energy difference. This collection of different transitions, leading to different radiated wavelengths, make up an emission spectrum. Each element's emission spectrum is unique. Therefore, spectroscopy can be used to identify elements in matter of unknown composition. Similarly, the emission spectra of molecules can be used in chemical analysis of substances. Emission In physics, emission is the process by which a higher energy quantum mechanical state of a particle becomes converted to a lower one through the emission of a photon, resulting in the production of light. ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Vacuum Tube
A vacuum tube, electron tube, valve (British usage), or tube (North America), is a device that controls electric current flow in a high vacuum between electrodes to which an electric potential difference has been applied. The type known as a thermionic tube or thermionic valve utilizes thermionic emission of electrons from a hot cathode for fundamental electronic functions such as signal amplification and current rectification. Non-thermionic types such as a vacuum phototube, however, achieve electron emission through the photoelectric effect, and are used for such purposes as the detection of light intensities. In both types, the electrons are accelerated from the cathode to the anode by the electric field in the tube. The simplest vacuum tube, the diode (i.e. Fleming valve), invented in 1904 by John Ambrose Fleming, contains only a heated electron-emitting cathode and an anode. Electrons can only flow in one direction through the device—from the cathode to the ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
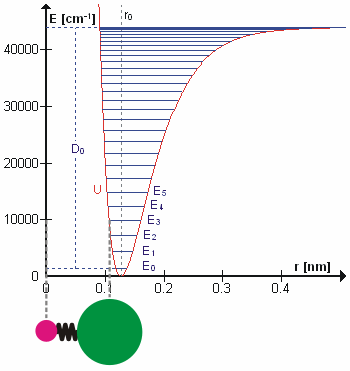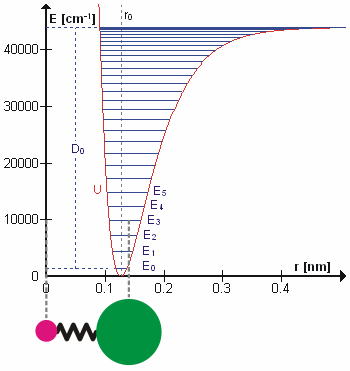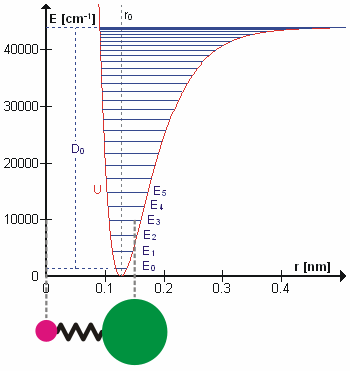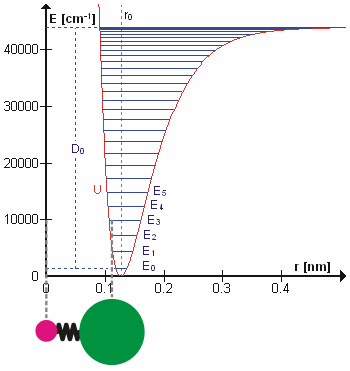
Molecular Vibration
A molecular vibration is a periodic motion of the atoms of a molecule relative to each other, such that the center of mass of the molecule remains unchanged. The typical vibrational frequencies range from less than 1013 Hz to approximately 1014 Hz, corresponding to wavenumbers of approximately 300 to 3000 cm−1 and wavelengths of approximately 30 to 3 µm. For a diatomic molecule A−B, the vibrational frequency in s−1 is given by \nu = \frac \sqrt , where k is the force constant in dyne/cm or erg/cm2 and μ is the reduced mass given by \frac = \frac+\frac. The vibrational wavenumber in cm−1 is \tilde \;= \frac \sqrt, where c is the speed of light in cm/s. Vibrations of polyatomic molecules are described in terms of normal modes, which are independent of each other, but each normal mode involves simultaneous vibrations of different parts of the molecule. In general, a non-linear molecule with ''N'' atoms has 3''N'' – 6 normal modes of vibration, but a ''linea ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Molecular Electronic Transition
Molecular electronic transitions take place when electrons in a molecule are excited from one energy level to a higher energy level. The energy change associated with this transition provides information on the structure of a molecule and determines many molecular properties such as colour. The relationship between the energy involved in the electronic transition and the frequency of radiation is given by Planck's relation. Organic molecules and other molecules The electronic transitions in organic compounds and some other compounds can be determined by ultraviolet–visible spectroscopy, provided that transitions in the ultraviolet (UV) or visible range of the electromagnetic spectrum exist for this compound. Electrons occupying a HOMO of a sigma bond can get excited to the LUMO of that bond. This process is denoted as a σ → σ* transition. Likewise promotion of an electron from a π-bonding orbital to an antibonding π orbital* is denoted as a π → π* transition ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Spectroscopy
Spectroscopy is the field of study that measures and interprets the electromagnetic spectra that result from the interaction between electromagnetic radiation and matter as a function of the wavelength or frequency of the radiation. Matter waves and acoustic waves can also be considered forms of radiative energy, and recently gravitational waves have been associated with a spectral signature in the context of the Laser Interferometer Gravitational-Wave Observatory (LIGO) In simpler terms, spectroscopy is the precise study of color as generalized from visible light to all bands of the electromagnetic spectrum. Historically, spectroscopy originated as the study of the wavelength dependence of the absorption by gas phase matter of visible light dispersed by a prism. Spectroscopy, primarily in the electromagnetic spectrum, is a fundamental exploratory tool in the fields of astronomy, chemistry, materials science, and physics, allowing the composition, physical structure an ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Astronomy
Astronomy () is a natural science that studies celestial objects and phenomena. It uses mathematics, physics, and chemistry in order to explain their origin and evolution. Objects of interest include planets, moons, stars, nebulae, galaxies, and comets. Relevant phenomena include supernova explosions, gamma ray bursts, quasars, blazars, pulsars, and cosmic microwave background radiation. More generally, astronomy studies everything that originates beyond Earth's atmosphere. Cosmology is a branch of astronomy that studies the universe as a whole. Astronomy is one of the oldest natural sciences. The early civilizations in recorded history made methodical observations of the night sky. These include the Babylonians, Greeks, Indians, Egyptians, Chinese, Maya, and many ancient indigenous peoples of the Americas. In the past, astronomy included disciplines as diverse as astrometry, celestial navigation, observational astronomy, and the making of calendars. ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Band Emission
Band emission, is the fraction of the total emission from a blackbody that is in a certain wavelength In physics, the wavelength is the spatial period of a periodic wave—the distance over which the wave's shape repeats. It is the distance between consecutive corresponding points of the same phase on the wave, such as two adjacent crests, t ... interval or band. For a prescribed temperature, T and the spectral interval from 0 to λ, is the ratio of the total emissive power of a black body from 0 to λ to the total emissive power over the entire spectrum. :F_ = \frac =\frac =\int_0^ \frac d(\lambda T) = f(\lambda T) See also * Spectral bands Spectroscopy {{spectroscopy-stub ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |