|
Special No. 3 Flying Tank
The Special number 3 light tank Ku-Ro (特三号戦車 クロ) (also known as the "So-Ra") was an experimental Japanese winged light tank project, developed during World War II. History and development In the Fall of 1943, the Imperial Japanese Army's Teishin Shudan formed the 1st Glider Tank Troop. Before the 1st Glider Troop was established, the only heavy support available to Japan's airborne infantry was provided by the Kokusai Ku-8. This military glider was able to transport the Type 94 and Type 94 75 mm mountain guns, but these infantry support guns lacked the mobility and anti-tank capabilities required by Japan's paratroopers. The solution to this problem was to develop a glider-portable light tank, but the existing Ku-8 glider was not capable of supporting the weight of a vehicle as large as a tank. So in 1943 and into 1944 the Armoured Army Headquarters (army aviation headquarters) and the Fourth Army Institute of Technology collaborated on a new concept to fill ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Empire Of Japan
The also known as the Japanese Empire or Imperial Japan, was a historical nation-state and great power that existed from the Meiji Restoration in 1868 until the enactment of the post-World War II 1947 constitution and subsequent formation of modern Japan. It encompassed the Japanese archipelago and several colonies, protectorates, mandates, and other territories. Under the slogans of and following the Boshin War and restoration of power to the Emperor from the Shogun, Japan underwent a period of industrialization and militarization, the Meiji Restoration, which is often regarded as the fastest modernisation of any country to date. All of these aspects contributed to Japan's emergence as a great power and the establishment of a colonial empire following the First Sino-Japanese War, the Boxer Rebellion, the Russo-Japanese War, and World War I. Economic and political turmoil in the 1920s, including the Great Depression, led to the rise of militarism, nationa ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Type 98 Ke-Ni Light Tank
The or Type 98A Ke-Ni Ko (also known as Type 98 Chi-Ni light tank) was designed to replace the Imperial Japanese Army's Type 95 Ha-Go light tank, Japan's most numerous armored fighting vehicle during World War II. Although designed before World War II began, production did not start until 1942, with 104 being produced by the end of the war in the Pacific. History and development The Type 98 developed in 1938 was a light tank with the same weight as the earlier Type 95 Ha-Go, but with thicker armor. The first prototype was originally known as the "Chi-Ni Model A" and completed by Hino Motors. The second prototype was originally known as the "Chi-Ni Model B" (a/k/a the "Type 98B Ke-Ni Otsu") and completed by Mitsubishi. This second experimental model had a different suspension system with four larger road-wheels, similar to the US Christie suspension design. During field trials the "Model A" demonstrated superior performance, especially in off-road capabilities, so the Hino design ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
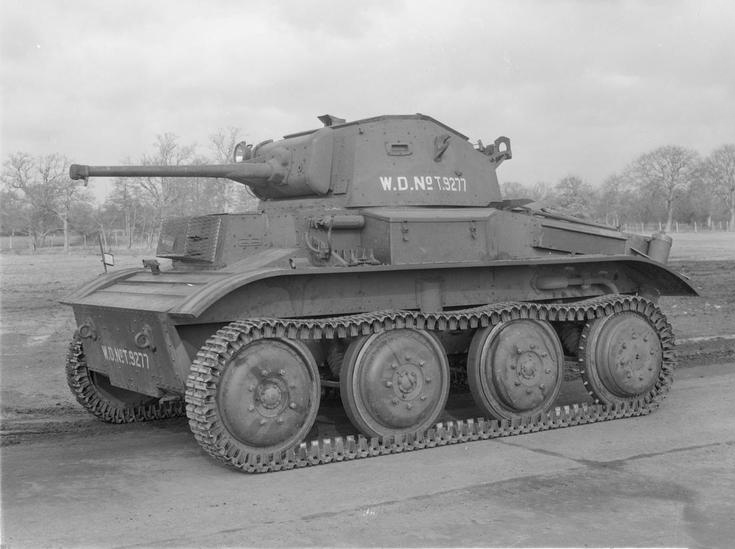
Light Tank Mk VII Tetrarch
The Light Tank Mk VII (A17), also known as the Tetrarch, was a British light tank produced by Vickers-Armstrongs in the late 1930s and used during the Second World War. The Tetrarch was the latest in the line of light tanks built by the company for the British Army. It improved upon its predecessor, the Light Tank Mk VIC, by introducing the extra firepower of a 2-pounder gun. The War Office ordered 70 tanks, an order that eventually increased to 220. Production was delayed by several factors and only 100 to 177 of the tanks were produced.Tucker (p. 90) states that 177 of the Mk VIIs were built during the war, but Flint (p. 12) states that whilst this figure is given in most published sources, surviving War Office documentation gives a lower figure of 100, putting the final tally somewhere between these two figures. The design flaws of the tank, combined with the decision by the War Office not to use light tanks in British armoured divisions, ruled out the use of Tetrarchs in ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
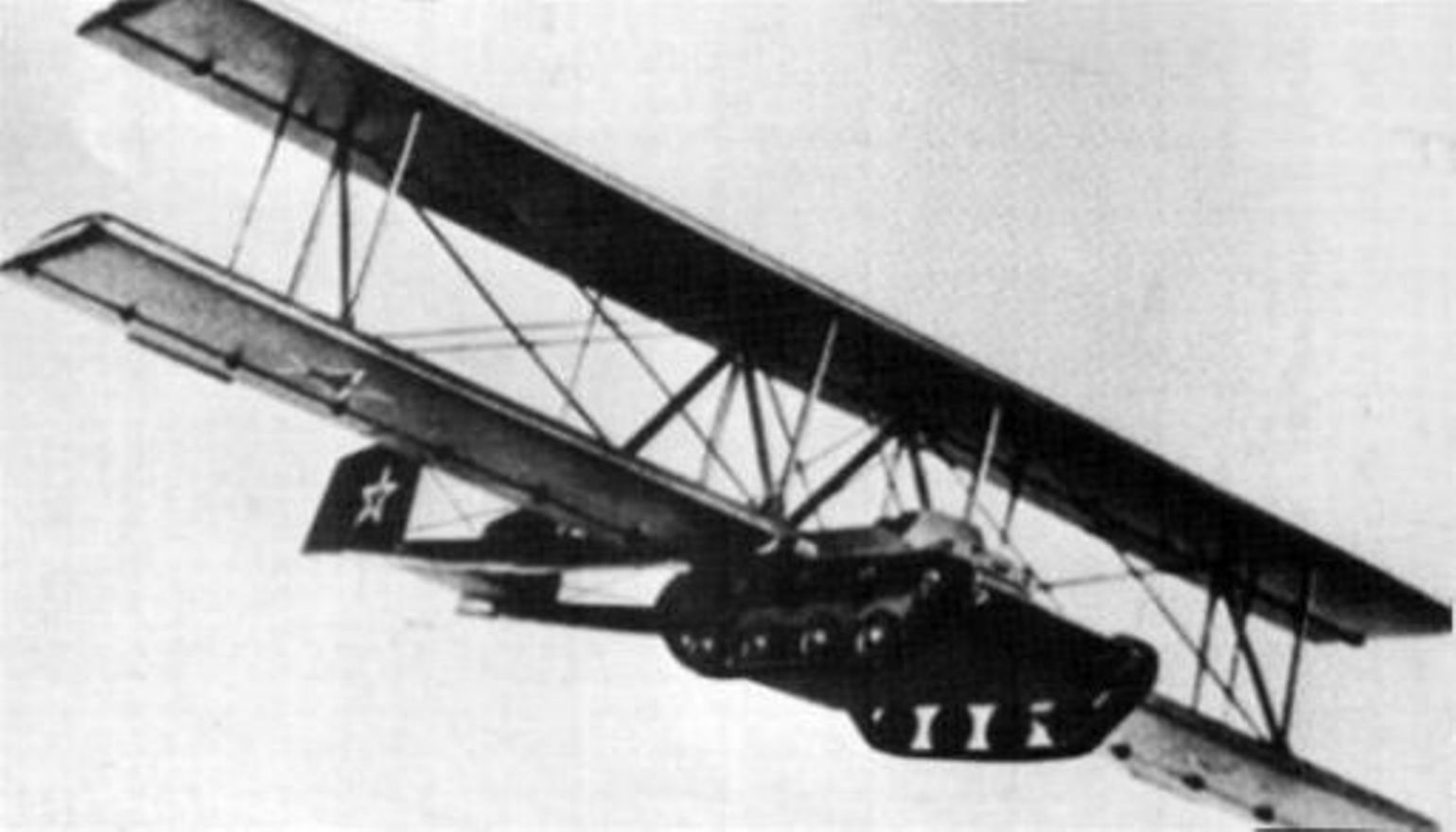
Antonov A-40
The Antonov A-40 ''Krylya Tanka'' (russian: крылья танка, meaning "tank wings") was a Soviet attempt to allow a tank to glide onto a battlefield after being towed aloft by an airplane, to support airborne forces or partisans.Winchester 2005, p. 62 A prototype was built and tested in 1942, but was found to be unworkable. This vehicle is sometimes called the ''A-40T'' or ''KT''. Design and development Instead of loading light tanks onto gliders, as other nations had done, Soviet airborne forces had strapped T-27 tankettes underneath heavy bombers and landed them on airfields. In the 1930s, there were experimental efforts to parachute tanks or simply drop them into water. During the 1940 occupation of Bessarabia, light tanks may have been dropped from a few meters up by TB-3 bombers, which, as long as the gearbox was in neutral, would allow them to roll to a stop. The biggest problem with air-dropping vehicles is if their crews are dropped separately, they may be ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Winged Tank
Tanks with glider wings were the subject of several unsuccessful experiments in the 20th century. It was intended that these could be towed behind, or carried under, an airplane, to glide into a battlefield, in support of infantry forces. In war, airborne forces use parachutes to drop soldiers behind enemy lines to capture and hold important objectives until more heavily equipped friendly troops can arrive. Military planners have always sought ways to provide airborne troops with combat support equipment in the form of light armored vehicles or artillery which can be dropped by parachute or military glider. The biggest problem with air-dropping vehicles is that their crews drop separately, and may be delayed or prevented from bringing them into action. Military gliders allow crews to arrive at the drop zone along with their vehicles. They also minimize exposure of the valuable towing aircraft, which need not appear over the battlefield. An improvement would be a tank which coul ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Strategic Bombing During World War II
World War II (1939–1945) involved sustained strategic bombing of railways, harbours, cities, workers' and civilian housing, and industrial districts in enemy territory. Strategic bombing as a military strategy is distinct both from close air support of ground forces and from tactical air power. During World War II, many military strategists of air power believed that air forces could win major victories by attacking industrial and political infrastructure, rather than purely military targets. Strategic bombing often involved bombing areas inhabited by civilians, and some campaigns were deliberately designed to target civilian populations in order to terrorize them and disrupt their usual activities. International law at the outset of World War II did not specifically forbid the aerial bombardment of cities – despite the prior occurrence of such bombing during World War I (1914–1918), the Spanish Civil War (1936–1939), and the Second Sino-Japanese War (1937–1945 ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
United States Air Force
The United States Air Force (USAF) is the air service branch of the United States Armed Forces, and is one of the eight uniformed services of the United States. Originally created on 1 August 1907, as a part of the United States Army Signal Corps, the USAF was established as a separate branch of the United States Armed Forces in 1947 with the enactment of the National Security Act of 1947. It is the second youngest branch of the United States Armed Forces and the fourth in order of precedence. The United States Air Force articulates its core missions as air supremacy, global integrated intelligence, surveillance and reconnaissance, rapid global mobility, global strike, and command and control. The United States Air Force is a military service branch organized within the Department of the Air Force, one of the three military departments of the Department of Defense. The Air Force through the Department of the Air Force is headed by the civilian Secretary of the Air Force ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Air Supremacy
Aerial supremacy (also air superiority) is the degree to which a side in a conflict holds control of air power over opposing forces. There are levels of control of the air in aerial warfare. Control of the air is the aerial equivalent of command of the sea. Air power has increasingly become a powerful element of military campaigns; military planners view having an environment of at least air superiority as a necessity. Air supremacy allows increased bombing efforts, tactical air support for ground forces, paratroop assaults, airdrops and simple cargo plane transfers, which can move ground forces and supplies. Air power is a function of the degree of air superiority and numbers or types of aircraft, but it represents a situation that defies black-and-white characterization. The degree of a force's air control is a zero-sum game with its opponent's; increasing control by one corresponds to decreasing control by the other. Air forces unable to contest for air superiority or a ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Pacific War
The Pacific War, sometimes called the Asia–Pacific War, was the theater of World War II that was fought in Asia, the Pacific Ocean, the Indian Ocean, and Oceania. It was geographically the largest theater of the war, including the vast Pacific Ocean theater, the South West Pacific theater, the Second Sino-Japanese War, and the Soviet–Japanese War. The Second Sino-Japanese War between the Empire of Japan and the Republic of China had been in progress since 7 July 1937, with hostilities dating back as far as 19 September 1931 with the Japanese invasion of Manchuria. However, it is more widely accepted that the Pacific War itself began on 7 December (8 December Japanese time) 1941, when the Japanese simultaneously invaded Thailand, attacked the British colonies of Malaya, Singapore, and Hong Kong as well as the United States military and naval bases in Hawaii, Wake Island, Guam, and the Philippines. The Pacific War saw the Allies pitted against Japan, the latter ai ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Continuous Track
Continuous track is a system of vehicle propulsion used in tracked vehicles, running on a continuous band of treads or track plates driven by two or more wheels. The large surface area of the tracks distributes the weight of the vehicle better than steel or rubber tires on an equivalent vehicle, enabling continuous tracked vehicles to traverse soft ground with less likelihood of becoming stuck due to sinking. Modern continuous tracks can be made with soft belts of synthetic rubber, reinforced with steel wires, in the case of lighter agricultural machinery. The more common classical type is a solid chain track made of steel plates (with or without rubber pads), also called caterpillar tread or tank tread, which is preferred for robust and heavy construction vehicles and military vehicles. The prominent treads of the metal plates are both hard-wearing and damage resistant, especially in comparison to rubber tyres. The aggressive treads of the tracks provide good trac ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Medium Bomber
A medium bomber is a military bomber Fixed-wing aircraft, aircraft designed to operate with medium-sized Aerial bomb, bombloads over medium Range (aeronautics), range distances; the name serves to distinguish this type from larger heavy bombers and smaller light bombers. Mediums generally carried about two tons of bombs, compared to light bombers that carried one ton, and heavies that carried four or more. The term was used prior to and during World War II, based on available parameters of Aircraft engine, engine and Aerospace engineering, aeronautical technology for bomber aircraft designs at that time. After the war, medium bombers were replaced in world air forces by more advanced and capable aircraft. History In the early 1930s many air forces were looking to modernize their existing bomber aircraft fleets, which frequently consisted of older biplanes. The new designs were typically twin-engined monoplanes, often of all-metal construction, and optimized for high enough pe ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
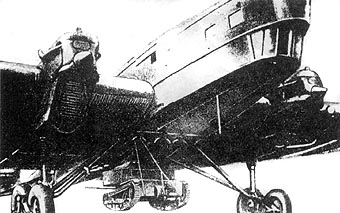
Mitsubishi Ki-21
The (Allied reporting name: "Sally" /"Gwen") was a Japanese heavy bomber during World War II. It began operations during the Second Sino-Japanese War participating in the Nomonhan Incident, and in the first stages of the Pacific War, including the Malayan, Burmese, Dutch East Indies and New Guinea Campaigns. It was also used to attack targets as far-flung as western China, India and northern Australia. Design and development In 1936, the Imperial Japanese Army Air Service issued a requirement for a new heavy bomber to replace both the Ki-20 (Army Type 92 Heavy Bomber) and the Ki-1 (Army Type 93 Heavy Bomber). The design called for a crew of at least four, top speed of , endurance of at least five hours, and a bombload of . The design parameters were very ambitious, and few twin-engine bombers anywhere in the world could exceed such performance at that time. Both Mitsubishi and Nakajima were asked to build two prototypes each, a further proposal from Kawasaki being rejecte ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |