|
Spark (cellular Automaton)
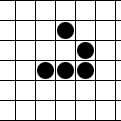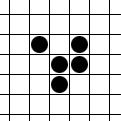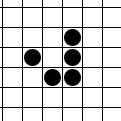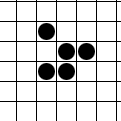
In Conway's Game of Life and similar cellular automaton rules, a spark is a small collection of live cells that appears at the edge of some larger pattern such as a spaceship or oscillator Oscillation is the repetitive or periodic variation, typically in time, of some measure about a central value (often a point of equilibrium) or between two or more different states. Familiar examples of oscillation include a swinging pendulum ..., then quickly dies off. Sparks are commonly separated by some distance from the main body of the pattern -- the analogy is to an object "throwing off sparks" -- but the minimum requirement is a set of cells on the pattern boundary that are alive in one phase but dead in a later phase, and that are unaffected by other parts of the pattern (they would die in the same way if the rest of the pattern were removed). The converse is not necessarily true: for example, removing the spark in the accompanying illustration would destabilize the fumarole ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Conway's Game Of Life
The Game of Life, also known simply as Life, is a cellular automaton devised by the British mathematician John Horton Conway in 1970. It is a zero-player game, meaning that its evolution is determined by its initial state, requiring no further input. One interacts with the Game of Life by creating an initial configuration and observing how it evolves. It is Turing complete and can simulate a universal constructor or any other Turing machine. Rules The universe of the Game of Life is an infinite, two-dimensional orthogonal grid of square ''cells'', each of which is in one of two possible states, ''live'' or ''dead'' (or ''populated'' and ''unpopulated'', respectively). Every cell interacts with its eight '' neighbours'', which are the cells that are horizontally, vertically, or diagonally adjacent. At each step in time, the following transitions occur: # Any live cell with fewer than two live neighbours dies, as if by underpopulation. # Any live cell with two or three live neig ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Life-like Cellular Automaton
Life-Like was a manufacturer of model trains and accessories. In 1960, the company purchased the assets of the defunct Varney Scale Models and began manufacturing model trains and accessories under the name Life-Like in 1970. In 2005 the parent company, Lifoam Industries, LLC, chose to concentrate on their core products and sold their model railroad operations to hobby distributor Wm. K. Walthers. Today, the Life-Like trademark is used by Walthers for HO Scale Buildings. History Life-Like Products was founded by brothers Lou and Sol Kramer, whose parents were Lithuanian immigrants residing in Baltimore, Maryland. Their experience in the hobby industry began in the 1930s when they became interested in constructing model airplanes. With money borrowed from their mother, the brothers formed the Burd Model Airplane Manufacturing Co. and sold their own model airplane kits using balsa wood they would salvage from discarded banana crates. As the business grew, their line had expanded to ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Spaceship (cellular Automaton)
In a cellular automaton, a finite pattern is called a spaceship if it reappears after a certain number of generations in the same orientation but in a different position. The smallest such number of generations is called the period of the spaceship. Description The speed of a spaceship is often expressed in terms of ''c'', the metaphorical speed of light (one cell per generation) which in many cellular automata is the fastest that an effect can spread. For example, a glider in Conway's Game of Life is said to have a speed of c/4, as it takes four generations for a given state to be translated by one cell. Similarly, the ''lightweight spaceship'' is said to have a speed of c/2, as it takes four generations for a given state to be translated by two cells. More generally, if a spaceship in a 2D automaton with the Moore neighborhood is translated by (x, y) after n generations, then the speed v is defined as: This notation can be readily generalised to cellular automata with di ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Oscillator (cellular Automaton)
In a cellular automaton, an oscillator is a pattern that returns to its original state, in the same orientation and position, after a finite number of generations. Thus the evolution of such a pattern repeats itself indefinitely. Depending on context, the term may also include spaceships as well. The smallest number of generations it takes before the pattern returns to its initial condition is called the ''period'' of the oscillator. An oscillator with a period of 1 is usually called a still life, as such a pattern never changes. Sometimes, still lifes are not taken to be oscillators. Another common stipulation is that an oscillator must be finite. Examples In Conway's Game of Life, finite oscillators are known to exist for all periods except 19 and 41. Additionally, until July 2022, the only known examples for period 34 were considered trivial because they consisted of essentially separate components that oscillate at smaller periods. For instance, one can create a period 34 osc ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Fumarole
A fumarole (or fumerole) is a vent in the surface of the Earth or other rocky planet from which hot volcanic gases and vapors are emitted, without any accompanying liquids or solids. Fumaroles are characteristic of the late stages of volcanic activity, but fumarole activity can also precede a volcanic eruption and has been used for eruption prediction. Most fumaroles die down within a few days or weeks of the end of an eruption, but a few are persistent, lasting for decades or longer. An area containing fumaroles is known as a fumarole field. The predominant vapor emitted by fumaroles is steam, formed by the circulation of groundwater through heated rock. This is typically accompanied by volcanic gases given off by magma cooling deep below the surface. These volcanic gases include sulfur compounds, such as various sulfur oxides and hydrogen sulfide, and sometimes hydrogen chloride, hydrogen fluoride, and other gases. A fumarole that emits significant sulfur compounds is some ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Glider (Conway's Life)
The glider is a pattern that travels across the board in Conway's Game of Life. It was first discovered by Richard K. Guy in 1969, while John Conway's group was attempting to track the evolution of the R-pentomino. Gliders are the smallest spaceships, and they travel diagonally at a speed of one cell every four generations, or c/4. The glider is often produced from randomly generated starting configurations. The name comes from the fact that, after two steps, the glider pattern repeats its configuration with a glide reflection symmetry. After four steps and two glide reflections, it returns to its original orientation. John Conway remarked that he wished he hadn't called it the glider. The game was developed before the widespread use of interactive computers, and after seeing it animated, he feels the glider looks more like an ant walking across the plane. Importance Gliders are important to the Game of Life because they are easily produced, can be collided with each other ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Puffer Train (cellular Automaton)
In a cellular automaton, a puffer train, or simply puffer, is a finite pattern that moves itself across the "universe", leaving debris behind. Thus a pattern consisting of only a puffer will grow arbitrarily large over time. While both puffers and spaceships have periods and speeds, unlike puffers, spaceships do not leave debris behind. The period of a puffer can be considered as the combination of ''two'' periods; the first is the period of the puffer itself, while the second is the apparent period of the pattern of debris produced. This is often the same as the period of the puffer, but sometimes is a factor of the period. A puffer for which the apparent period deduced from the debris is smaller than the period of the engine is a pseudoperiod puffer. Such puffers are typically produced by artificial means. A true period puffer is one in which the period of the debris matches that of the puffer. Puffers are divided into two classes, dirty puffers and clean puffers. While there i ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |

.jpg)