|
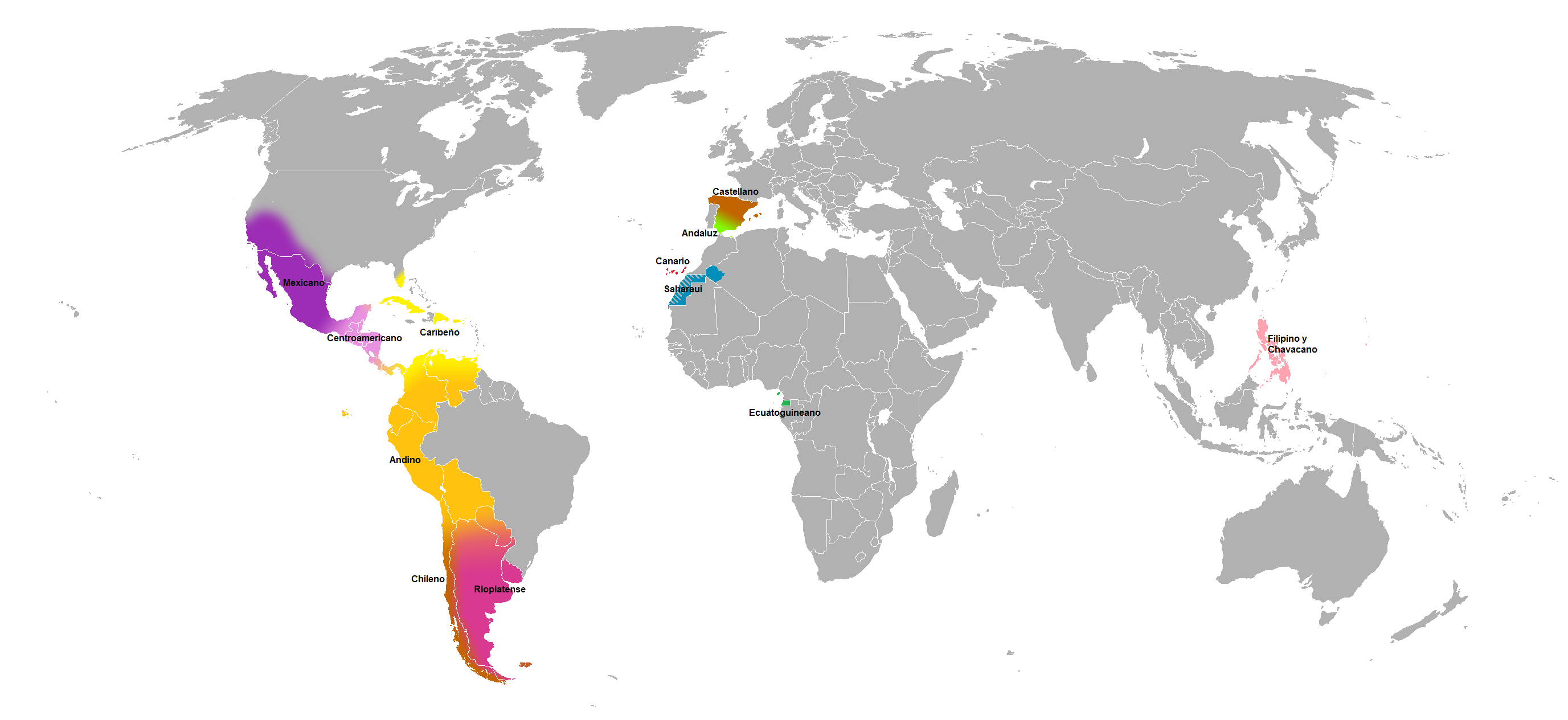
Spanish-speaking Countries
The following is a list of countries where Spanish is an official language, plus a number of countries where Spanish or any language closely related to it, is an important or significant language. Official or national language Spanish is the official language (either by law or ''de facto'') in 20 sovereign states and one dependent territory, totaling around 442 million people. This includes Equatorial Guinea, where it is official but not a native language. In these countries and territories, Spanish is the main or mostly used language of communication of the vast majority of the population; official documents are written chiefly or solely in that language; and it is taught in schools and utilized as the primary medium of instruction as part of the official curriculum. Sovereign states Territory Notes: Significant language Though not an official language at the national level, Spanish is regularly spoken by significant populations throughout these countries. Public service ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Countries With Spanish As An Official Language
A country is a distinct part of the world, such as a state, nation, or other political entity. It may be a sovereign state or make up one part of a larger state. For example, the country of Japan is an independent, sovereign state, while the country of Wales is a component of a multi-part sovereign state, the United Kingdom. A country may be a historically sovereign area (such as Korea), a currently sovereign territory with a unified government (such as Senegal), or a non-sovereign geographic region associated with certain distinct political, ethnic, or cultural characteristics (such as the Basque Country). The definition and usage of the word "country" is flexible and has changed over time. ''The Economist'' wrote in 2010 that "any attempt to find a clear definition of a country soon runs into a thicket of exceptions and anomalies." Most sovereign states, but not all countries, are members of the United Nations. The largest country by area is Russia, while the smallest is ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Peruvian Academy Of Language
The Peruvian Academy of Language ( es, Academia Peruana de la Lengua) is an association of academics and experts on the use of the Spanish language in Peru. It was founded in Lima on May 5, 1887. Its first elected president was Francisco García Calderón. The second president was Ricardo Palma. It is a member of the Association of Spanish Language Academies. Current members * Sr. D. Estuardo Núñez * Sr. D. Francisco Miró Quesada Cantuarias * Sra. D.ª Martha Hildebrandt * Sr. D. Mario Vargas Llosa * Sr. D. Carlos Germán Belli * Sr. D. José A. de la Puente Candamo * Sr. D. Enrique Carrión Ordóñez * Sr. D. José Luis Rivarola * Sr. D. Manuel Pantigoso Pecero * Sr. D. Rodolfo Cerrón Palomino * Sr. D. Jorge Puccinelli Converso * Sr. D. Gustavo Gutiérrez * Sr. D. Fernando de Trazegnies Granda * Sr. D. Fernando de Szyszlo * Sr. D. José León Herrera * Sr. D. Marco Martos Carrera - President of the Academy from 2006 to 2014 and since 2018. * Sr. D. Ricardo Gonzále ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Ecuadorian Spanish
Spanish is the most-widely spoken language in Ecuador, though great variations are present depending on several factors, the most important one being the geographical region where it is spoken. The three main regional variants are: * Equatorial Pacific Spanish or Equatorial Coastal Spanish * Andean Spanish * Amazonic Spanish Additionally to the characteristics described below, Ecuadorian Spanish shares many characteristics that are widespread in Spanish in the Americas. Other sociolinguistic factors that influence in the way of speaking are the ethnic or social class of the speaker, and whether the speaker lives in an urban or rural area. Since the Coast and the Highlands are the most populous areas, these are the country's most widely used dialects, despite being quite different from each other. For instance, there are many idioms specific to each region or province, and others that are used and understood nationwide. Pacific Coast This Spanish variant is classified wi ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Academia Ecuatoriana De La Lengua
The Academia Ecuatoriana de la Lengua (''Ecuadorian Academy of Language'') is an association of academics and experts on the use of the Spanish language in Ecuador. The Academia was founded on March 4, 1875, in Quito, following the Real Academia Española The Royal Spanish Academy ( es, Real Academia Española, generally abbreviated as RAE) is Spain's official royal institution with a mission to ensure the stability of the Spanish language. It is based in Madrid, Spain, and is affiliated with ... giving permission for the creation of national academies in 1870. It aimed to bring together regional intellectual and literary groups. The Academia is the highest cultural institution in Ecuador. References Spanish language academies Ecuadorian culture 1875 establishments in South America Organizations established in 1875 {{Spanish-lang-stub ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Ecuador
Ecuador ( ; ; Quechua: ''Ikwayur''; Shuar: ''Ecuador'' or ''Ekuatur''), officially the Republic of Ecuador ( es, República del Ecuador, which literally translates as "Republic of the Equator"; Quechua: ''Ikwadur Ripuwlika''; Shuar: ''Ekuatur Nunka''), is a country in northwestern South America, bordered by Colombia on the north, Peru on the east and south, and the Pacific Ocean on the west. Ecuador also includes the Galápagos Islands in the Pacific, about west of the mainland. The country's capital and largest city is Quito. The territories of modern-day Ecuador were once home to a variety of Indigenous groups that were gradually incorporated into the Inca Empire during the 15th century. The territory was colonized by Spain during the 16th century, achieving independence in 1820 as part of Gran Colombia, from which it emerged as its own sovereign state in 1830. The legacy of both empires is reflected in Ecuador's ethnically diverse population, with most of its mill ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Guatemalan Spanish
Guatemalan Spanish ( es, Español guatemalteco) is the national variant of Spanish spoken in the Central American country of Guatemala. About 13.7 million of the 17 million population speak Spanish. It includes the use of the second-person singular personal pronoun alongside the standard Spanish second-person singular pronouns and to form a three-level system of second-person singular address. Phonetics and phonology *The presence of Seseo wherein there is no distinction between and . Seseo is common to all of Latin American Spanish, and the Andalusian and Canarian Spanish varieties within Spain. * is realized as glottal . * Syllable-final is only occasionally aspirated, and only when before consonants or a pause. It's weakened less often than in any other Central American dialect. * Word-final is pronounced velar . *As Guatemala was part of First Mexican Empire, Guatemalan dialect adopted the voiceless alveolar affricate and the cluster (originally ) represented by t ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Academia Guatemalteca De La Lengua
The Academia Guatemalteca de la Lengua (Spanish for ''Guatemalan Academy of the Language'') is an association of academics and experts on the use of the Spanish language in Guatemala. It was founded on June 30, 1887. It is a member of the Association of Spanish Language Academies. Current members * Margarita Carrera Molina * Gustavo Adolfo Wyld Ferraté * Mario Alberto Carrera Galindo * Julia Guillermina Herrera Peña * Francisco Pérez de Antón * Rigoberto Juárez-Paz * Ana M.ª Urruela de Quezada * Mario Antonio Sandoval Samayoa * Carmen Matute * Lucrecia Méndez Lucrecia Méndez de Penedo (born 21 July 1943) is a Guatemalan university professor, essayist, researcher, and literary and art critic. She has been instrumental in rescuing some of Guatemala's literary heritage from obscurity. Biography Marta Lu ... de Penedo * Francisco Morales Santos * Delia Quiñónez Castillo * Gonzalo de Villa y Vásquez * Dieter Hasso Lehnhoff Temme * Mario Roberto Morales Álvarez * María ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Guatemala
Guatemala ( ; ), officially the Republic of Guatemala ( es, República de Guatemala, links=no), is a country in Central America. It is bordered to the north and west by Mexico; to the northeast by Belize and the Caribbean; to the east by Honduras; to the southeast by El Salvador and to the south by the Pacific Ocean. With an estimated population of around million, Guatemala is the most populous country in Central America and the 11th most populous country in the Americas. It is a representative democracy with its capital and largest city being Nueva Guatemala de la Asunción, also known as Guatemala City, the most populous city in Central America. The territory of modern Guatemala hosted the core of the Maya civilization, which extended across Mesoamerica. In the 16th century, most of this area was conquered by the Spanish and claimed as part of the viceroyalty of New Spain. Guatemala attained independence in 1821 from Spain and Mexico. In 1823, it became part of the Fe ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Chilean Spanish
Chilean Spanish ( es, español chileno) is any of several varieties of the Spanish language spoken in most of Chile. Chilean Spanish dialects have distinctive pronunciation, grammar, vocabulary, and slang usages that differ from those of Standard Spanish. Formal Spanish in Chile has recently incorporated an increasing number of colloquial elements. The Royal Spanish Academy recognizes 2,214 words and idioms exclusively or mainly produced in Chilean Spanish, in addition to many still unrecognized slang expressions. Alongside Honduran Spanish, Chilean Spanish has been identified by various linguists as one of the two most divergent varieties. Variation and accents In Chile, there are not many differences between the Spanish spoken in the northern, central and southern areas of the country, although there are notable differences in zones of the far south—such as Aysén, Magallanes (mainly along the border with Argentina), and Chiloé—and in Arica in the extreme north. ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Academia Chilena De La Lengua
The Academia Chilena de la Lengua (Spanish for ''Chilean Language Academy'') is an association of academics and experts on the use of the Spanish language in Chile. It is a member of the Association of Academies of the Spanish Language and is a part of the Instituto de Chile. History and purpose The academy was founded in Santiago de Chile on June 5, 1885. It started out with 18 members designated by the Royal Spanish Academy. Its stated aims, according to its bylaws, are: to ensure the purity and splendor of the Spanish language, to contribute to the work of the Royal Spanish Academy and the Association of Academies of the Spanish Language, and to collaborate with other institutions on matters related to the language and its literature, particularly Chilean literature. Today, its members are chosen by co-option. The academy currently has 36 members, as well as a variable number of correspondent members in various Chilean regions and abroad. It has several honorary members, includ ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Chile
Chile, officially the Republic of Chile, is a country in the western part of South America. It is the southernmost country in the world, and the closest to Antarctica, occupying a long and narrow strip of land between the Andes to the east and the Pacific Ocean to the west. Chile covers an area of , with a population of 17.5 million as of 2017. It shares land borders with Peru to the north, Bolivia to the north-east, Argentina to the east, and the Drake Passage in the far south. Chile also controls the Pacific islands of Juan Fernández, Isla Salas y Gómez, Desventuradas, and Easter Island in Oceania. It also claims about of Antarctica under the Chilean Antarctic Territory. The country's capital and largest city is Santiago, and its national language is Spanish. Spain conquered and colonized the region in the mid-16th century, replacing Inca rule, but failing to conquer the independent Mapuche who inhabited what is now south-central Chile. In 1818, after declaring in ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Venezuelan Spanish
Venezuelan Spanish ( or ) refers to the Spanish spoken in Venezuela. Spanish was introduced in Venezuela by colonists. Most of them were from Galicia, Basque Country, Andalusia, or the Canary Islands. The last has been the most fundamental influence on modern Venezuelan Spanish, and Canarian and Venezuelan accents may even be indistinguishable to other Spanish-speakers. Italian and Portuguese immigrants from the late 19th and the early 20th century have also had an influence; they influenced vocabulary and its accent, given its slight sing-songy intonation, like Rioplatense Spanish. German settlers also left an influence when Venezuela was contracted as a concession by the King of Spain to the German Welser banking family (Klein-Venedig, 1528–1546). The Spaniards additionally brought African slaves, which is the origin of expressions such as ("excellent"), which comes from Yoruba . Other non-Romance words came from indigenous languages, such as (a type of coffee) and ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |