|
Southerness Lighthouse
Southerness lighthouse is located at the village of Southerness in South West Scotland. It is at present the second oldest lighthouse in Scotland. The lighthouse was commissioned by the Town Council of Dumfries in 1748 to assist in the safe passage through the Solway Firth of ships heading to the Nith Estuary. At that time roads in South West Scotland were quite sparse so the bulk of trade even between local villages, was carried out by sea. Dumfries was a major port and there were regular connections with Liverpool and, especially, Ireland. Construction was completed in 1749. In 1805 the lighthouse was greatly improved under the guidance of the famous lighthouse engineer Robert Stevenson assisted by James Slight. The lighthouse was raised from its original structure twice, most notably between 1842 and 1844 to a design by Walter Newall. The lighthouse was first lit around 1800 and was decommissioned in 1936. The light was extinguished due to financial reasons between 1867 ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Walter Newall
Walter Newall (3 April 1780 – 25 December 1863) was a Scottish architect and civil engineer, born at Doubledyke in the parish of New Abbey in the historic county of Kirkcudbrightshire, Scotland. He was the leading architect in the Dumfries area, from the 1820s until his retirement.Colvin, Howard, (1978) ''A Biographical Dictionary of British Architects, 1600–1840'', John Murray, pp.697-699 He trained James Barbour who succeeded him as principal architect in the region. Career Newall began his design career in partnership with an upholsterer and a cabinet maker in the Dumfries firm of Newall, Hannah and Reid. Nothing is known of any architectural training, although Howard Colvin suggests that his knowledge of up-to-date styles points to time spent with an architect of standing. Throughout his working life he lived mainly in Dumfries, travelling around Dumfriesshire, Kirkcudbrightshire and Wigtownshire in the course of his work. His papers show him to have made tours of Ger ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Southerness
Southerness (; sco, Satterness) is a small, compact coastal village in Dumfries and Galloway, Scotland. Southerness is located approximately south of the A710 between Caulkerbush and Kirkbean. The town today is mainly a tourist village and has for many years had a large number of static caravans, some private and many rented to holiday makers. The local bus services to and from Dalbeattie and Dumfries are more frequent during the summer season. Southerness has a large, shallow, sandy beaches on both sides of the rocky next to the village and to the west extend out to the vast Mersehead Sands exposed at low tide. The only landmark is its Southerness lighthouse which was built in 1749 and is one of the oldest lighthouses in Scotland. The lighthouse stands approximately 56 feet (17 m) tall and was decommissioned in the 1930s. One of the two golf courses was redesigned in 1947 by course manager Mackenzie Ross. The village has to the north a magnificent backdrop of the "marilyn ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
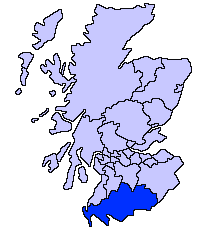
Dumfries And Galloway
Dumfries and Galloway ( sco, Dumfries an Gallowa; gd, Dùn Phrìs is Gall-Ghaidhealaibh) is one of 32 unitary council areas of Scotland and is located in the western Southern Uplands. It covers the counties of Scotland, historic counties of Dumfriesshire, Kirkcudbrightshire, and Wigtownshire, the latter two of which are collectively known as Galloway. The administrative centre and largest settlement is the town of Dumfries. The second largest town is Stranraer, on the North Channel (Great Britain and Ireland), North Channel coast, some to the west of Dumfries. Following the 1975 reorganisation of local government in Scotland, the three counties were joined to form a single regions and districts of Scotland, region of Dumfries and Galloway, with four districts within it. The districts were abolished in 1996, since when Dumfries and Galloway has been a unitary local authority. For lieutenancy areas of Scotland, lieutenancy purposes, the area is divided into three lieutenancy a ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Scotland
Scotland (, ) is a country that is part of the United Kingdom. Covering the northern third of the island of Great Britain, mainland Scotland has a border with England to the southeast and is otherwise surrounded by the Atlantic Ocean to the north and west, the North Sea to the northeast and east, and the Irish Sea to the south. It also contains more than 790 islands, principally in the archipelagos of the Hebrides and the Northern Isles. Most of the population, including the capital Edinburgh, is concentrated in the Central Belt—the plain between the Scottish Highlands and the Southern Uplands—in the Scottish Lowlands. Scotland is divided into 32 administrative subdivisions or local authorities, known as council areas. Glasgow City is the largest council area in terms of population, with Highland being the largest in terms of area. Limited self-governing power, covering matters such as education, social services and roads and transportation, is devolved from the Scott ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Solway Firth
The Solway Firth ( gd, Tràchd Romhra) is a firth that forms part of the border between England and Scotland, between Cumbria (including the Solway Plain) and Dumfries and Galloway. It stretches from St Bees Head, just south of Whitehaven in Cumbria, to the Mull of Galloway, on the western end of Dumfries and Galloway. The Isle of Man is also very near to the firth. The firth comprises part of the Irish Sea. The firth’s coastline is characterised by lowland hills and small mountains. It is a mainly rural area, with mostly small villages and settlements (such as Powfoot). Fishing, hill farming, and some arable farming play a large part in the local economy, although tourism is increasing. The northern part of the English coast of the Solway Firth was designated as an Area of Outstanding Natural Beauty, known as the Solway Coast, in 1964. Construction of the Robin Rigg Wind Farm in the firth began in 2007. Within the firth, there are some salt flats and mud flats that can b ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
River Nith
The River Nith ( gd, Abhainn Nid; Common Brittonic: ''Nowios'') is a river in south-west Scotland. The Nith rises in the Carsphairn hills of East Ayrshire, more precisely between Prickeny Hill and Enoch Hill, east of Dalmellington. For the majority of its course it flows in a south-easterly direction through Dumfries and Galloway and then into the Solway Firth at Airds Point. The territory through which the river flows is called Nithsdale (historically known as "Stranit" from gd, Strath Nid, "valley of the Nith"). Length For estuaries the principle followed is that the river should be visible at all times. The measurement therefore follows the centre of the river at low tide and the mouth of the river is assumed to be at the coastal high tide mark. In Scotland this does not generally make a significant difference, except for rivers draining into shallow sloping sands of the Irish Sea and Solway Firth, notably the Nith. At low tide, the sea recedes to such an extent that th ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Robert Stevenson (civil Engineer)
Robert Stevenson, FRSE, FGS, FRAS, FSA Scot, MWS (8 June 1772 – 12 July 1850) was a Scottish civil engineer, and designer and builder of lighthouses. His works include the Bell Rock Lighthouse. Early life Robert Stevenson was born in Glasgow. His father was Alan Stevenson, a partner in a West Indies sugar trading house in the city. Alan died of an epidemic fever on the island of St. Christopher in the West Indies on 26 May 1774, a few days before Robert's second birthday. Robert's uncle died of the same disease around the same time. Since this left Alan's widow, Jean Lillie Stevenson, in much-reduced financial circumstances, Robert was educated, as a young child, at a charity school. Robert's mother intended him to join the ministry, so when he was a bit older she enrolled him in the school of a locally famous Glasgow linguist, a Mr Macintyre. But when Robert was 15, she remarried and the family moved to 1 Blair Street, off the Royal Mile in Edinburgh. Robert's new stepfath ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
James Slight (engineer)
{{hndis, Slight, James ...
James Slight may refer to: * Jim Slight (1855–1930), Australian cricketer * James Slight, 19th century British agricultural writer, who wrote ''The Book of Farm Implements & Machines'' with Robert Scott Burn * James Slight (engineer) (1785–1854), lighthouse engineer, assistant to Robert Stevenson Robert Stevenson may refer to: * Robert Stevenson (actor and politician) (1915–1975), American actor and politician * Robert Stevenson (civil engineer) (1772–1850), Scottish lighthouse engineer * Robert Stevenson (director) (1905–1986), Engl ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
List Of Lighthouses In Scotland
This is a list of lighthouses in Scotland. The Northern Lighthouse Board, from which much of the information is derived, are responsible for most lighthouses in Scotland but have handed over responsibility in the major estuaries to the port authorities. Many of the more minor lights are not shown. A lighthouse that is no longer operating is indicated by the date of closure in the ''operated by'' column. Where two dates are shown, the lighthouse has been rebuilt. Nearly all the lighthouses in this list were designed by and most were built by four generations of one family, including Thomas Smith, who was both the stepfather and father-in-law of Robert Stevenson. Robert's sons and grandsons not only built most of the lights, often under the most appalling of conditions, but pioneered many of the improvements in lighting and signalling that cut down the enormous loss of life in shipping around the coasts of Scotland. The table may be sorted by any column by clicking on the headin ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
List Of Northern Lighthouse Board Lighthouses
This is a list of the currently operational lighthouses of the Northern Lighthouse Board (NLB). The list is divided by geographical location, and then by whether the lighthouses are classed by the NLB as a 'major lighthouse' or a 'minor light'. Former NLB lighthouses now disposed of are not included in the list. Scotland (except principal island groups) Major lighthouses Minor lights * Ardtornish * Bass Rock * Cailleach Head * Cairnbulg Briggs * Corran Narrows North East * Corran Point * Craigton Point * Dunollie * Elie Ness * Hestan Island * Holy Island (Inner) * Lady Isle * Little Ross * Little Ross Beacon * Loch Eriboll * Loch Ryan * Longman Point * Oban NLB Pier * Sandaig * Sgeir Bhuidhe * Sula Sgeir * Turnberry The Hebrides Major lighthouses * Barra Head * Butt of Lewis * Dubh Artach * Eilean Glas * Flannan Islands * * Hyskeir * Lismore * Monach * Neist Point * * Rinns of Islay * * Ruvaal * Scarinish * Skerryvore * Tiumpan Head * Ushenish Minor ligh ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
List Of Category A Listed Buildings In Dumfries And Galloway
This is a list of Category A listed buildings in Dumfries and Galloway, Scotland. In Scotland, the term listed building refers to a building or other structure officially designated as being of "special architectural or historic interest". Category A structures are those considered to be "buildings of national or international importance, either architectural or historic, or fine little-altered examples of some particular period, style or building type." Listing was begun by a provision in the Town and Country Planning (Scotland) Act 1947, and the current legislative basis for listing is the Planning (Listed Buildings and Conservation Areas) (Scotland) Act 1997. The authority for listing rests with Historic Scotland, an executive agency of the Scottish Government, which inherited this role from the Scottish Development Department in 1991. Once listed, severe restrictions are imposed on the modifications allowed to a building's structure or its fittings. Listed building cons ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Lighthouses Completed In 1800
A lighthouse is a tower, building, or other type of physical structure designed to emit light from a system of lamps and lenses and to serve as a beacon for navigational aid, for maritime pilots at sea or on inland waterways. Lighthouses mark dangerous coastlines, hazardous shoals, reefs, rocks, and safe entries to harbors; they also assist in aerial navigation. Once widely used, the number of operational lighthouses has declined due to the expense of maintenance and has become uneconomical since the advent of much cheaper, more sophisticated and effective electronic navigational systems. History Ancient lighthouses Before the development of clearly defined ports, mariners were guided by fires built on hilltops. Since elevating the fire would improve the visibility, placing the fire on a platform became a practice that led to the development of the lighthouse. In antiquity, the lighthouse functioned more as an entrance marker to ports than as a warning signal for ree ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |