|
Southern Schleswig Danish
Southern Schleswig Danish ( da, Sydslesvigdansk, german: Südschleswigdänisch) is a variety of the Danish language spoken in Southern Schleswig in Northern Germany. It is a variety of Standard Danish () influenced by the surrounding German language in relation to prosody, syntax and morphology, used by the Danish minority in Southern Schleswig. Originally Southern Jutlandic was spoken in most parts of the area (in the variants of Angel Danish and Mellemslesvigsk). On the western coast, North Frisian was also spoken. After the language shift in the 18th, 19th and 20th centuries, most of the Danish and North Frisian dialects were replaced by Low and Standard German Standard High German (SHG), less precisely Standard German or High German (not to be confused with High German dialects, more precisely Upper German dialects) (german: Standardhochdeutsch, , or, in Switzerland, ), is the standardized variety .... Accordingly, there is a Northern Schleswig variety of Germa ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Southern Schleswig
Southern Schleswig (german: Südschleswig or ', da, Sydslesvig; frr, Söödslaswik) is the southern half of the former Duchy of Schleswig in Germany on the Jutland Peninsula. The geographical area today covers the large area between the Eider (river), Eider river in the south and the Flensburg Fjord in the north, where it borders Denmark. Northern Schleswig, congruent with the former South Jutland County, forms the southernmost part of Denmark. The area belonged to the Denmark, Crown of Denmark until Prussia and Austria declared war on Denmark in 1864. Denmark wanted to give away the German-speaking Holstein, Holsten and set the new border at the small river Ejderen. Prussian chancellor Otto von Bismarck concluded that this justified a war, and even proclaimed it a "holy war". He also turned to the Emperor of Austria, Franz Joseph I of Austria for help. A similar war in 1848 had gone poorly for the Prussians. With Prussia's modern weapons and the help from both the Austrians an ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Morphology (linguistics)
In linguistics, morphology () is the study of words, how they are formed, and their relationship to other words in the same language. It analyzes the structure of words and parts of words such as stems, root words, prefixes, and suffixes. Morphology also looks at parts of speech, intonation and stress, and the ways context can change a word's pronunciation and meaning. Morphology differs from morphological typology, which is the classification of languages based on their use of words, and lexicology, which is the study of words and how they make up a language's vocabulary. While words, along with clitics, are generally accepted as being the smallest units of syntax, in most languages, if not all, many words can be related to other words by rules that collectively describe the grammar for that language. For example, English speakers recognize that the words ''dog'' and ''dogs'' are closely related, differentiated only by the plurality morpheme "-s", only found bound to noun ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Languages Of Denmark
The Kingdom of Denmark has only one official language, Danish, the national language of the Danish people, but there are several minority languages spoken, namely Faroese, German, and Greenlandic. A large majority (about 86%) of Danes also speak English as a second language; it is mandatory for Danish students to learn from first grade in the public elementary schools ( da, folkeskole), by far the most popular option in the country. In the 1st (or 3rd, depends on the school) grade of folkeskole, a third language option is given, usually German or French. The vast majority pick German (about 47% of Danes report being able to speak conversational German). The third most widely understood foreign language is Swedish, with about 13% of Danes reporting to be able to speak it. Officially recognized minority languages Faroese Faroese, a North Germanic language like Danish, is the primary language of the Faroe Islands, a self-governing territory of the Kingdom. It is also spoken ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Danish Dialects
The Danish language has a number of regional and local dialect varieties. These can be divided into the traditional dialects, which differ from modern Standard Danish in both phonology and grammar, and the Danish accents, which are local varieties of the standard language distinguished mostly by pronunciation and local vocabulary colored by traditional dialects. Traditional dialects are now mostly extinct in Denmark, with only the oldest generations still speaking them. The traditional dialects are generally divided into three main dialectal areas: Jutlandic dialect, Insular Danish, and Bornholmish. Bornholmish is the only Eastern Danish dialect spoken in Denmark, since the other Eastern Danish dialects (, , and ) were spoken in areas ceded to Sweden and subsequently assimilated to Standard Swedish. Jutlandic is further divided into Southern Jutlandic and Northern Jutlandic, with Northern Jutlandic subdivided into North Jutlandic and West Jutlandic. Insular Danish is divided into ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Faroe Islands
The Faroe Islands ( ), or simply the Faroes ( fo, Føroyar ; da, Færøerne ), are a North Atlantic island group and an autonomous territory of the Kingdom of Denmark. They are located north-northwest of Scotland, and about halfway between Norway ( away) and Iceland ( away). The islands form part of the Kingdom of Denmark, along with mainland Denmark and Greenland. The islands have a total area of about with a population of 54,000 as of June 2022. The terrain is rugged, and the subpolar oceanic climate (Cfc) is windy, wet, cloudy, and cool. Temperatures for such a northerly climate are moderated by the Gulf Stream, averaging above freezing throughout the year, and hovering around in summer and 5 °C (41 °F) in winter. The northerly latitude also results in perpetual civil twilight during summer nights and very short winter days. Between 1035 and 1814, the Faroe Islands were part of the Kingdom of Norway, which was in a personal union with Denmark from 1 ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Gøtudanskt Accent
Gøtudanskt/Dano-Faroese (pronounced , Faroese for " (Norðra)gøta Danish" or alternatively "street Danish") is a name for a variant of Danish language spoken in the Faroe Islands. Its intonation and pronunciation are influenced by Faroese. Etymology Poulsen (1993) attributes the term to a teacher (1850–1930) from the small village of Gøta on Eysturoy who spoke Danish with a pronounced accent, his idiolect forming the basis of many of the common features of Gøtudanskt. Definition of ''Gøtudanskt'' Gøtudanskt is highly proficient (L2) Danish spoken mainly as the written Danish standard by Faroe Islanders with Faroese interference at all levels of language processing. It is characteristic for the elder generation. The younger generation usually (but not always) uses standard Danish pronunciation. An example of Gøtudanskt is the jingle "" ‘Away from the road! The king is sledding’, where comes from the Faroese verb ‘to sled’. Another is from Poulsen (199 ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Northern Schleswig
South Jutland County (Danish: ''Sønderjyllands Amt'') is a former county (Danish: ''amt'') on the south-central portion of the Jutland Peninsula in southern Denmark. The county was formed on 1 April 1970, comprising the former counties of Aabenraa (E), Haderslev (N), Sønderborg (SE), and Tønder (SW). The county was abolished effective 1 January 2007, when the Region of Southern Denmark was formed. Following the reunification of the region with Denmark, the Church of Denmark elevated Haderslev to a diocese in 1923 and divided the region between the dioceses of Ribe (W) and Haderslev (E). This arrangement remains in effect. Description South Jutland county is also known as Northern Schleswig (Danish: ''Nordslesvig'', German: ''Nordschleswig''). The name refers specifically to the southernmost of the Danish part of the Jutland Peninsula that formerly belonged to the former Duchy of Schleswig (Danish: ''Slesvig'' or ''Sønderjylland''), a Danish fief under the Kings of Denmark. ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Standard German
Standard High German (SHG), less precisely Standard German or High German (not to be confused with High German dialects, more precisely Upper German dialects) (german: Standardhochdeutsch, , or, in Switzerland, ), is the standardized variety of the German language used in formal contexts and for communication between different dialect areas. It is a pluricentric Dachsprache with three codified (or standardised) specific regional variants: German Standard German, Austrian Standard German and Swiss Standard German. Regarding the spelling and punctuation, a recommended standard is published by the Council for German Orthography which represents the governments of all majority and minority German-speaking countries and dependencies. Adherence is obligatory for government institutions, including schools. Regarding the pronunciation, although there is no official standards body, there is a long-standing ''de facto'' standard pronunciation (Bühnendeutsch), most commonly used in fo ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Low German
: : : : : (70,000) (30,000) (8,000) , familycolor = Indo-European , fam2 = Germanic , fam3 = West Germanic , fam4 = North Sea Germanic , ancestor = Old Saxon , ancestor2 = Middle Low German , dia1 = West Low German , dia2 = East Low German , iso2 = nds , iso3 = nds , iso3comment = (Dutch varieties and Westphalian have separate codes) , lingua = 52-ACB , map = Nds Spraakrebeet na1945.svg , mapcaption = Present day Low German language area in Europe. , glotto = lowg1239 , glottoname = Low German , notice = IPA Low German or Low Saxon (in the language itself: , and other names; german: Plattdeutsch, ) is a West Germanic language variety spoken mainly in Northern Germany and the northeastern part of the Netherlands. The dialect of Plautdietsch is also spoken in the Russian Mennonite diaspora worldwi ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Language Shift
Language shift, also known as language transfer or language replacement or language assimilation, is the process whereby a speech community shifts to a different language, usually over an extended period of time. Often, languages that are perceived to be higher status stabilise or spread at the expense of other languages that are perceived by their own speakers to be lower-status. An example is the shift from Gaulish to Latin during the time of the Roman Empire. Mechanisms Prehistory For prehistory, Forster et al. (2004) and Forster and Renfrew (2011) observe that there is a correlation of language shift with intrusive male Y chromosomes but not necessarily with intrusive female mtDNA. They conclude that technological innovation (the transition from hunting-gathering to farming, or from stone to metal tools) or military prowess (as in the abduction of British women by Vikings to Iceland) causes immigration of at least some men, who are perceived to be of higher status than loca ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
North Frisian Language
North Frisian (''nordfriisk'') is a minority language of Germany, spoken by about 10,000 people in North Frisia. The language is part of the larger group of the West Germanic Frisian languages. The language comprises 10 dialects which are themselves divided into an insular and a mainland group. North Frisian is closely related to the Saterland Frisian language of Northwest Germany and West Frisian which is spoken in the Netherlands. All of these are also closely related to the English language forming the Anglo-Frisian group. The phonological system of the North Frisian dialects is strongly being influenced by Standard German and is slowly adapting to that of the German language. With a number of native speakers probably even less than 10,000 and decreasing use in mainland North Frisia, the North Frisian language is endangered. It is protected as a minority language and has become an official language in the Nordfriesland district and on Heligoland island. Classification The ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
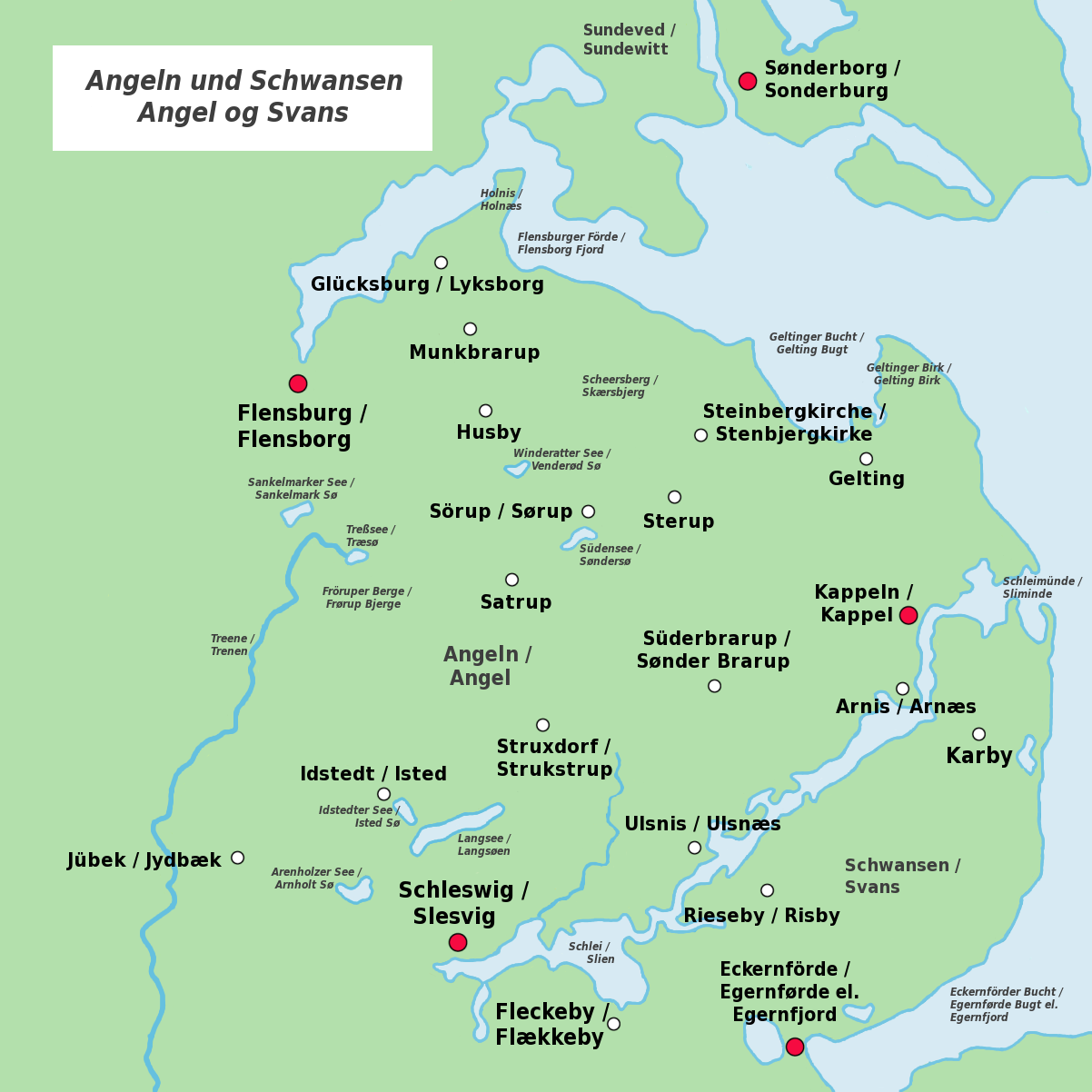
Angel Danish
Angel Danish (German: ''Angeldänisch'', Danish: ''Angeldansk'' or ''Angelbomål'') was a variant of South Jutlandic spoken in the area of Angelia (German: ''Angeln;'', Danish: ''Angel'') and Swania (German: ''Schwansen'', Danish: ''Svansø'') in Southern Schleswig partly until the 20th century. Both landscapes belonged to the Danish Duchy of Schleswig until 1864, since then to Germany. Characteristic of Angel Danish was among other the tonal pitch accent (like in the Danish dialects of Als and Langeland as well as in Swedish and Norwegian) and the fricative for the hard ''G'' (like today in the Angel Low German). There were also elevations from ''O'' to ''U'' (instead of Danish ''honning'' it was ''hunne'' in Angel Danish, cf. Icelandic ''hunang''). There were also older Nordic forms such as ''hvénner'' (German ''wenn'', Danish ''hvornår'', Old Norse ''hvenær''), ''mjølk'' (German ''Milch'', Danish ''mælk'', Old Norse ''mjólk'') or ''gut'' (German ''Junge'', Danish ''dren ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |