|
South Asian River Dolphin
South Asian river dolphins are toothed whales in the genus ''Platanista'', which inhabit fresh water habitats in the northern Indian subcontinent. They were historically considered to be one species (''P. gangetica'') with the Ganges river dolphin and the Indus river dolphin being subspecies (''P. g. gangetica'' and ''P. g. minor'' respectively). Genetic and morphological evidence in 2021 has shown them to be separate species. The Ganges and Indus river dolphins are estimated to have diverged 550,000 years ago. They are the only living members of the family Platanistidae and the superfamily Platanistoidea. Fossils of ancient relatives date to the late Oligocene. South Asian river dolphins are small but stocky cetaceans with long snouts or rostra, broad flippers, and small dorsal fins. They have several unusual features. Living in murky river waters, their eyes are tiny and lensless, relying instead on echolocation for navigation. The skull has large crests over the melon, w ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
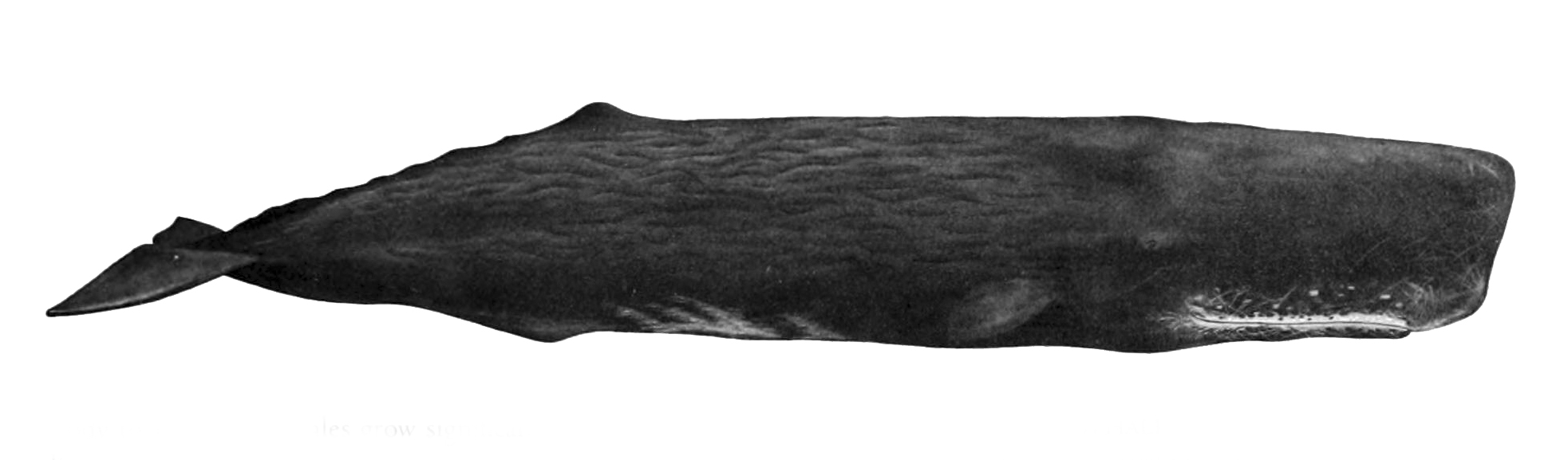
Ganges River Dolphin
The Ganges river dolphin (''Platanista gangetica'') is a species of toothed whale classified in the family Platanistidae. It lives in the Ganges and related rivers of South Asia, namely in the countries of India, Nepal, and Bangladesh. It is related to the much smaller Indus river dolphin which lives in the Indus River in Pakistan and the Beas River of northwestern India. It is also known by the name ''susu'' (popular name) or "Sisu" (Assamese language) and ''shushuk'' (Bengali)., page 451 etter Aand page 568 etter S The Ganges river dolphin has been recognized by the government of India as its National Aquatic Animal and is the official animal of the Indian city of Guwahati. Its first occurrence, within the Hooghly River, was documented bWilliam Roxburgh Taxonomy The Ganges river dolphin split from the Indus river dolphin during the Pleistocene, around 550,000 years ago. This species and the Indus river dolphin, were initially classified as a single species, ''Platanista ga ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Quaternary
The Quaternary ( ) is the current and most recent of the three periods of the Cenozoic Era in the geologic time scale of the International Commission on Stratigraphy (ICS). It follows the Neogene Period and spans from 2.58 million years ago to the present. The Quaternary Period is divided into two epochs: the Pleistocene (2.58 million years ago to 11.7 thousand years ago) and the Holocene (11.7 thousand years ago to today, although a third epoch, the Anthropocene, has been proposed but is not yet officially recognised by the ICS). The Quaternary Period is typically defined by the cyclic growth and decay of continental ice sheets related to the Milankovitch cycles and the associated climate and environmental changes that they caused. Research history In 1759 Giovanni Arduino proposed that the geological strata of northern Italy could be divided into four successive formations or "orders" ( it, quattro ordini). The term "quaternary" was introduced by Jules Desnoye ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
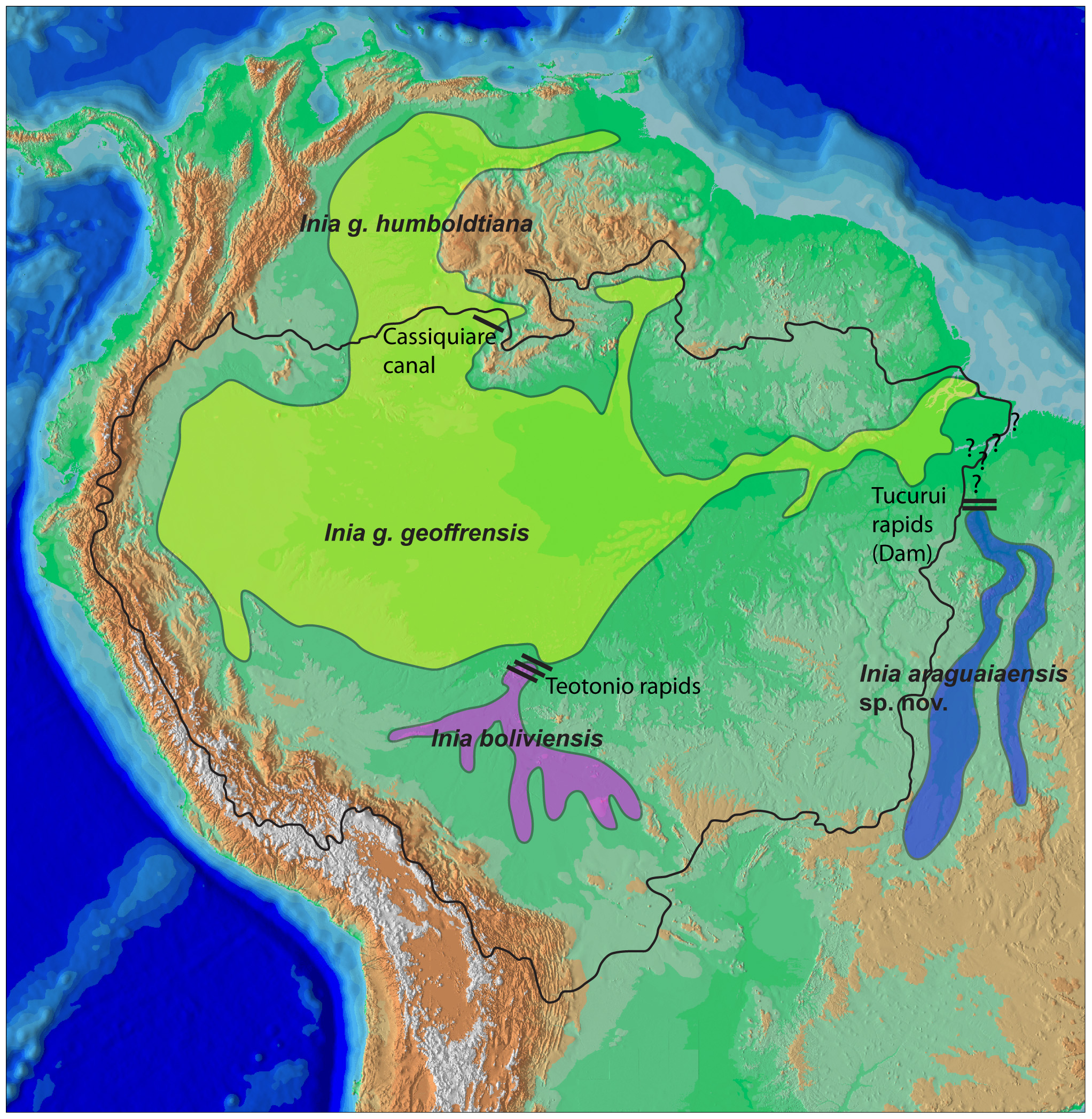
Iniidae
Iniidae is a family of river dolphins containing one living genus, ''Inia'', and four extinct genera. The extant genus inhabits the river basins of South America, but the family formerly had a wider presence across the Atlantic Ocean. Iniidae are highly morphologically different from marine dolphins by way of adaptations suited to their freshwater riverine habitat. They also display a high amount of sexual dimorphism in the form of color and size. Seasonal movement between flooded plains and rivers is common, due to the variation of seasonal rain. There has been little research done on the family, in particular the species aside from the Amazon river dolphin. Evolution The South American river basins were flooded by marine waters, creating a new brackish habitat that allowed marine mammals to move into them. During the Miocene era, the sea level began to recede, trapping the mammals within the continent. Morphology Their their necks are flexible, since their cervical vertebr ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Lipotidae
Lipotidae is a family of river dolphins containing the possibly extinct baiji of China and the fossil genus ''Parapontoporia'' from the Late Miocene and Pliocene of the Pacific coast of North America. The genus '' Prolipotes'', which is based on a mandible fragment from Neogene coastal deposits in Guangxi, China, has been classified as an extinct relative of the baiji, but is dubious. The putative kentriodontid '' "Lophocetus" pappus'' is a possible relative of Lipotidae.Olivier Lambert, Giovanni Bianucci, Mario Urbina, Jonathan H. Geisler; A new inioid (Cetacea, Odontoceti, Delphinida) from the Miocene of Peru and the origin of modern dolphin and porpoise families. Zool J Linn Soc 2017; 179 (4): 919-946. doi: 10.1111/zoj.12479. https://academic.oup.com/zoolinnean/article/179/4/919/3076080/A-new-inioid-Cetacea-Odontoceti-Delphinida-from?guestAccessKey=3b956b95-d215-488a-8d90-1cff59554290#63703008 Genera and Species * †(?) '' Lipotes'' ** †(?) ''Lipotes vexillifer'' * ''Par ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
River Dolphin
River dolphins are a polyphyletic group of fully aquatic mammals that reside exclusively in freshwater or brackish water. They are an informal grouping of dolphins, which itself is a paraphyletic group within the infraorder Cetacea. Extant river dolphins are placed in two superfamilies, Platanistoidea and Inioidea. They comprise the families Platanistidae (the South Asian dolphins), the recently extinct Lipotidae (Yangtze river dolphin), Iniidae (the Amazonian dolphins) and Pontoporiidae. There are five extant species of river dolphins. River dolphins, alongside other cetaceans, belong to the clade Artiodactyla, with even-toed ungulates, and their closest living relatives the hippopotamuses, from which they diverged about 40 million years ago. Specific types of Dolphins can be pink. River dolphins are relatively small compared to other dolphins, having evolved to survive in warm, shallow water and strong river currents. They range in size from the long South Asian river dolp ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Mitochondrial DNA
Mitochondrial DNA (mtDNA or mDNA) is the DNA located in mitochondria, cellular organelles within eukaryotic cells that convert chemical energy from food into a form that cells can use, such as adenosine triphosphate (ATP). Mitochondrial DNA is only a small portion of the DNA in a eukaryotic cell; most of the DNA can be found in the cell nucleus and, in plants and algae, also in plastids such as chloroplasts. Human mitochondrial DNA was the first significant part of the human genome to be sequenced. This sequencing revealed that the human mtDNA includes 16,569 base pairs and encodes 13 proteins. Since animal mtDNA evolves faster than nuclear genetic markers, it represents a mainstay of phylogenetics and evolutionary biology. It also permits an examination of the relatedness of populations, and so has become important in anthropology and biogeography. Origin Nuclear and mitochondrial DNA are thought to be of separate evolutionary origin, with the mtDNA being derived ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Lipid
Lipids are a broad group of naturally-occurring molecules which includes fats, waxes, sterols, fat-soluble vitamins (such as vitamins A, D, E and K), monoglycerides, diglycerides, phospholipids, and others. The functions of lipids include storing energy, signaling, and acting as structural components of cell membranes. Lipids have applications in the cosmetic and food industries, and in nanotechnology. Lipids may be broadly defined as hydrophobic or amphiphilic small molecules; the amphiphilic nature of some lipids allows them to form structures such as vesicles, multilamellar/unilamellar liposomes, or membranes in an aqueous environment. Biological lipids originate entirely or in part from two distinct types of biochemical subunits or "building-blocks": ketoacyl and isoprene groups. Using this approach, lipids may be divided into eight categories: fatty acyls, glycerolipids, glycerophospholipids, sphingolipids, saccharolipids, and polyketides (derived from condensati ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Richard Owen
Sir Richard Owen (20 July 1804 – 18 December 1892) was an English biologist, comparative anatomist and paleontologist. Owen is generally considered to have been an outstanding naturalist with a remarkable gift for interpreting fossils. Owen produced a vast array of scientific work, but is probably best remembered today for coining the word '' Dinosauria'' (meaning "Terrible Reptile" or "Fearfully Great Reptile"). An outspoken critic of Charles Darwin's theory of evolution by natural selection, Owen agreed with Darwin that evolution occurred, but thought it was more complex than outlined in Darwin's ''On the Origin of Species''. Owen's approach to evolution can be considered to have anticipated the issues that have gained greater attention with the recent emergence of evolutionary developmental biology. Owen was the first president of the Microscopical Society of London in 1839 and edited many issues of its journal – then known as ''The Microscopic Journal''. Owen also c ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Ancient Greek
Ancient Greek includes the forms of the Greek language used in ancient Greece and the ancient world from around 1500 BC to 300 BC. It is often roughly divided into the following periods: Mycenaean Greek (), Dark Ages (), the Archaic period (), and the Classical period (). Ancient Greek was the language of Homer and of fifth-century Athenian historians, playwrights, and philosophers. It has contributed many words to English vocabulary and has been a standard subject of study in educational institutions of the Western world since the Renaissance. This article primarily contains information about the Epic and Classical periods of the language. From the Hellenistic period (), Ancient Greek was followed by Koine Greek, which is regarded as a separate historical stage, although its earliest form closely resembles Attic Greek and its latest form approaches Medieval Greek. There were several regional dialects of Ancient Greek, of which Attic Greek developed into Koine. Dia ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Latin
Latin (, or , ) is a classical language belonging to the Italic branch of the Indo-European languages. Latin was originally a dialect spoken in the lower Tiber area (then known as Latium) around present-day Rome, but through the power of the Roman Republic it became the dominant language in the Italian region and subsequently throughout the Roman Empire. Even after the fall of Western Rome, Latin remained the common language of international communication, science, scholarship and academia in Europe until well into the 18th century, when other regional vernaculars (including its own descendants, the Romance languages) supplanted it in common academic and political usage, and it eventually became a dead language in the modern linguistic definition. Latin is a highly inflected language, with three distinct genders (masculine, feminine, and neuter), six or seven noun cases (nominative, accusative, genitive, dative, ablative, and vocative), five declensions, four verb conjuga ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Heinrich Julius Lebeck
Heinrich may refer to: People * Heinrich (given name), a given name (including a list of people with the name) * Heinrich (surname), a surname (including a list of people with the name) *Hetty (given name), a given name (including a list of people with the name) Places * Heinrich (crater), a lunar crater * Heinrich-Hertz-Turm, a telecommunication tower and landmark of Hamburg, Germany Other uses * Heinrich event, a climatic event during the last ice age * Heinrich (card game), a north German card game * Heinrich (farmer), participant in the German TV show a ''Farmer Wants a Wife'' * Heinrich Greif Prize, an award of the former East German government * Heinrich Heine Prize, the name of two different awards * Heinrich Mann Prize, a literary award given by the Berlin Academy of Art * Heinrich Tessenow Medal, an architecture prize established in 1963 * Heinrich Wieland Prize, an annual award in the fields of chemistry, biochemistry and physiology * Heinrich, known as Haida ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |