|
South American Pacific Mangroves
The South American Pacific mangroves, or Panama Bight mangroves, is an ecoregion along the Pacific coast of Panama, Colombia, Ecuador and Peru. Geography Location The South American Pacific mangroves ecoregion is found along the southern coast of Panama, extensive stretches of the Pacific coast of Colombia, sections of the Pacific coast of Ecuador, particularly around the estuary of the Guayas River, and in two small stretches along the northern coast of Peru. The Panama Bight Mangroves, a Global ecoregion, consists of the Gulf of Panama mangroves, Esmeraldas–Pacific Colombia mangroves, Manabí mangroves and Gulf of Guayaquil–Tumbes mangroves. The Gulf of Panama mangroves (NT1414) extend from the Gulf of Parita to the Bay of San Miguel. Mangroves are found along the coasts of Colombia and Ecuador from the Gulf of Tribugá in the north to Mompiche Bay in the south (NT1409). Mangroves are found along the coast of Manabí Province in Ecuador (NT1418). They are also found betwee ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Neotropical Realm
The Neotropical realm is one of the eight biogeographic realms constituting Earth's land surface. Physically, it includes the tropical terrestrial ecoregions of the Americas and the entire South American temperate zone. Definition In biogeography, the Neotropic or Neotropical realm is one of the eight terrestrial realms. This realm includes South America, Central America, the Caribbean islands, and southern North America. In Mexico, the Yucatán Peninsula and southern lowlands, and most of the east and west coastlines, including the southern tip of the Baja California Peninsula are Neotropical. In the United States southern Florida and coastal Central Florida are considered Neotropical. The realm also includes temperate southern South America. In contrast, the Neotropical Floristic Kingdom excludes southernmost South America, which instead is placed in the Antarctic kingdom. The Neotropic is delimited by similarities in fauna or flora. Its fauna and flora are distinct ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Panamanian Dry Forests
The Panamanian dry forests ecoregion (WWF ID: NT0224) covers low-lying dry forests around the coast of the Gulf of Panama on the Pacific Ocean side of Panama. It is one of the most heavily degraded ecoregions in Central America, having been heavily converted to agriculture. However, it is also important for its high biodiversity, high rates of endemic species, and its importance as a biological corridor between the moist forests inland and the mangroves on the coast. Location and description The Gulf of Panama has minor gulfs around its rim. The largest sector of this ecoregion is around the Gulf of Parita on the west. There are smaller sectors in the north on Panama Bay (around Panama City), and the Bay of San Miguel on the east. Most of the region is lowlands, with an average elevation of . The western sector is surrounded on the interior side by the Isthmian-Pacific moist forests ecoregion, the eastern sectors by the Isthmian-Atlantic moist forests ecoregion. There is ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
El Niño
El Niño (; ; ) is the warm phase of the El Niño–Southern Oscillation (ENSO) and is associated with a band of warm ocean water that develops in the central and east-central equatorial Pacific (approximately between the International Date Line and 120°W), including the area off the Pacific coast of South America. The ENSO is the cycle of warm and cold sea surface temperature (SST) of the tropical central and eastern Pacific Ocean. El Niño is accompanied by high air pressure in the western Pacific and low air pressure in the eastern Pacific. El Niño phases are known to last close to four years; however, records demonstrate that the cycles have lasted between two and seven years. During the development of El Niño, rainfall develops between September–November. The cool phase of ENSO is es, La Niña, translation=The Girl, with SSTs in the eastern Pacific below average, and air pressure high in the eastern Pacific and low in the western Pacific. The ENSO cycle, including bo ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Soil Salinity
Soil salinity is the salt content in the soil; the process of increasing the salt content is known as salinization. Salts occur naturally within soils and water. Salination can be caused by natural processes such as mineral weathering or by the gradual withdrawal of an ocean. It can also come about through artificial processes such as irrigation and road salt. Natural occurrence Salts are a natural component in soils and water. The ions responsible for salination are: Na+, K+, Ca2+, Mg2+ and Cl−. Over long periods of time, as soil minerals weather and release salts, these salts are flushed or leached out of the soil by drainage water in areas with sufficient precipitation. In addition to mineral weathering, salts are also deposited via dust and precipitation. Salts may accumulate in dry regions, leading to naturally saline soils. This is the case, for example, in large parts of Australia. Human practices can increase the salinity of soils by the addition of salts in i ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Humboldt Current
The Humboldt Current, also called the Peru Current, is a cold, low- salinity ocean current that flows north along the western coast of South America.Montecino, Vivian, and Carina B. Lange. "The Humboldt Current System: Ecosystem components and processes, fisheries, and sediment studies." ''Progress in Oceanography'' 83.1 (2009): 65-79. DOI10.1016/j.pocean.2009.07.041/ref> It is an eastern boundary current flowing in the direction of the equator, and extends offshore. The Humboldt Current is named after the German naturalist Alexander von Humboldt even though it was discovered by José de Acosta 250 years before Humboldt. In 1846, von Humboldt reported measurements of the cold-water current in his book ''Cosmos''. The current extends from southern Chile (~ 45th parallel south) to northern Peru (~ 4th parallel south) where cold, upwelled, waters intersect warm tropical waters to form the Equatorial Front. Sea surface temperatures off the coast of Peru, around 5th parallel sout ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Piura River
The Piura River is a river in northern Peru. The river flows westward from the Andes to the Pacific Ocean and is susceptible to major flooding. Piura is the largest city along the river's course. Course The Piura River has its source in eastern Piura Region near the Continental Divide of the Americas, continental divide of the Andes where the mountainous divide is relatively lower than elsewhere in Peru. The river flows in a northwesterly direction for approximately through a fertile valley that is a major agricultural region for northern Peru. At Tambo Grande District, Tambo Grande, the river course turns west. The Piura comes within of the Chira River before flowing southerly into the arid Sechura Desert. Through this desert the Piura River provides a rare source of fresh water and creates a strip of arable land in which the city of Piura is located. The Piura River has two mouths at Sechura Bay with its largest discharge at Laguna Ramon. Historically, the Piura River's ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Mangrove
A mangrove is a shrub or tree that grows in coastal saline water, saline or brackish water. The term is also used for tropical coastal vegetation consisting of such species. Mangroves are taxonomically diverse, as a result of convergent evolution in several plant families. They occur worldwide in the tropics and subtropics and even some temperate coastal areas, mainly between latitudes 30° N and 30° S, with the greatest mangrove area within 5° of the equator. Mangrove plant families first appeared during the Late Cretaceous to Paleocene epochs, and became widely distributed in part due to the plate tectonics, movement of tectonic plates. The oldest known fossils of Nypa fruticans, mangrove palm date to 75 million years ago. Mangroves are salt-tolerant trees, also called halophytes, and are adapted to live in harsh coastal conditions. They contain a complex salt filtration system and a complex root system to cope with saltwater immersion and wave action. They are ad ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Köppen Climate Classification
The Köppen climate classification is one of the most widely used climate classification systems. It was first published by German-Russian climatologist Wladimir Köppen (1846–1940) in 1884, with several later modifications by Köppen, notably in 1918 and 1936. Later, the climatologist Rudolf Geiger (1894–1981) introduced some changes to the classification system, which is thus sometimes called the Köppen–Geiger climate classification system. The Köppen climate classification divides climates into five main climate groups, with each group being divided based on seasonal precipitation and temperature patterns. The five main groups are ''A'' (tropical), ''B'' (arid), ''C'' (temperate), ''D'' (continental), and ''E'' (polar). Each group and subgroup is represented by a letter. All climates are assigned a main group (the first letter). All climates except for those in the ''E'' group are assigned a seasonal precipitation subgroup (the second letter). For example, ''Af'' indi ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
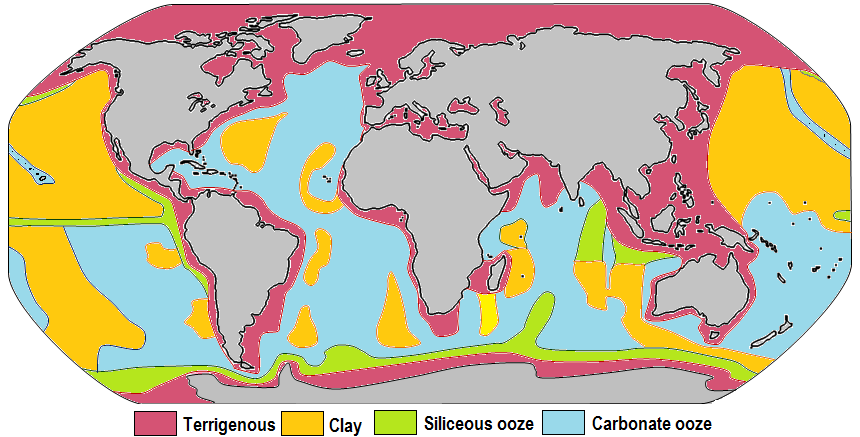
Marine Sediment
Marine sediment, or ocean sediment, or seafloor sediment, are deposits of insoluble particles that have accumulated on the seafloor. These particles have their origins in soil and rocks and have been transported from the land to the sea, mainly by rivers but also by dust carried by wind and by the flow of glaciers into the sea. Additional deposits come from marine organisms and chemical precipitation in seawater, as well as from underwater volcanoes and meteorite debris. Except within a few kilometres of a mid-ocean ridge, where the volcanic rock is still relatively young, most parts of the seafloor are covered in sediment. This material comes from several different sources and is highly variable in composition. Seafloor sediment can range in thickness from a few millimetres to several tens of kilometres. Near the surface seafloor sediment remains unconsolidated, but at depths of hundreds to thousands of metres the sediment becomes lithified (turned to rock). Rates of sediment ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Sechura Desert
The Sechura Desert is a coastal desert located south of the Piura Region of Peru along the Pacific Ocean coast and inland to the foothills of the Andes Mountains. Its extreme aridity is caused by the upwelling of cold coastal waters and subtropical atmospheric Subsidence (atmosphere), subsidence, but it is also subject to occasional flooding during El Niño years. In 1728, the town of Sechura was destroyed by a tsunami and was later rebuilt in its present location. In 1998, Surface runoff, runoff from flooding rivers caused the formation of a temporary lake some long filling the Bayóvar Depression. Short rivers flowing across the desert from the Andes support intensive irrigation-based agriculture. Location and extent Within Peru, the desert is described as the strip along the northern Pacific Ocean, Pacific coast of Peru in the southern Piura Region, Piura and western Lambayeque Region, Lambayeque regions, and extending from the coast inland to the secondary ridges of the A ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Tumbes–Piura Dry Forests
The Tumbes–Piura dry forests (NT0232) is an arid tropical ecoregion along the Pacific coasts of southern Ecuador and northern Peru. The ecoregion contains many endemic species of flora and birds adapted to the short wet season followed by a long dry season. Threats include extraction of wood for fuel or furniture, and capture of wild birds for sale. Location The Tumbes–Piura dry forests ecoregion has an area of . The northern tip is in the southern coastal plain of Ecuador, while most of the ecoregion is in the northwestern coastal plain of Peru. It covers all or part of the regions of Tumbes, Piura, Lambayeque and Cajamarca in northern Peru. Further north the similar Ecuadorian dry forests extend along the coast of central Ecuador. The Andes rise to the east. The northern tip of the ecoregion adjoins the Guayaquil flooded grasslands. In the north it is bounded to the west by a stretch of South American Pacific mangroves and to the east by Northwestern Andean montane fore ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Ecuadorian Dry Forests
The Ecuadorian dry forests (NT0214) is an ecoregion near the Pacific coast of the Ecuador. The habitat has been occupied by people for centuries and has been severely damaged by deforestation, overgrazing and hillside erosion due to unsustainable agriculture. Only 1% of the original forest remains. The patches of forest, mostly secondary growth, are fragmented. They are home to many endemic species at risk of extinction. Location The Ecuadorian dry forests have an area of . The ecoregion is mainly along the Pacific coast of central Ecuador to the north and west of Guayaquil, with a section to the east of Guayaquil. The western area is in the Cordillera de la Costa (Coastal Range) mountains. The western portion is bounded to the east by Western Ecuador moist forests. It adjoins South American Pacific mangroves along sections of the coast. The eastern portion is also bounded to the east by Western Ecuador moist forests, but to the west is bounded by Guayaquil flooded grasslands. ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |






.jpg)
