|
Sophie Eliott-Lynn
Mary, Lady Heath (17 November 1896 – 9 May 1939) was an Irish aviator and began life as Sophie Catherine Theresa Mary Peirce-Evans in Knockaderry, County Limerick, near the town of Newcastle West. She was one of the best known women in the world for a five-year period from the mid-1920s. Early life When the young Sophie Peirce-Evans was one year old, her father John Peirce-Evans, bludgeoned her mother Kate Theresa Dooling to death with a heavy stick. He was found guilty of murder and declared insane. His daughter was taken to the home of her grandfather in Newcastle West where she was brought up by two maiden aunts, who discouraged her passion for sports. After schooldays in Rochelle School, Cork; Princess Garden Belfast and St Margaret's Hall on Mespil Road in Dublin, where she played hockey and tennis, Sophie enrolled in the Royal College of Science for Ireland on Merrion Street (now Government Buildings). The college was designed to produce the educated farmers which ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Knockaderry
Knockaderry () is a village in County Limerick, Ireland. The population of the Knockaderry electoral division (including the village and surrounding rural catchment) is approximately 500 people. Name and location The name Knockaderry derives from the Irish ''Cnoc an Doire'', meaning 'hill of the oak-wood'. There is still an oak grove evident near the village. It is a long single-street village. The other village in the parish is Cloncagh, originally spelt 'Clouncagh', which comes from the Irish: Cluain Cath, meaning 'the meadow of the battle'. During the ministry of Canon Lyons as parish priest, the "u" in Clouncagh was dropped, although it can still be seen on some of the signs entering the parish. History Not far from the village is Knockaderry House, the ancient seat of the D'Arcy family. Reportedly a patent was granted to John Jephson in 1711 for the holding of fairs in Knockaderry. The village of Knockaderry was burned to the ground in 1789 when, according to Begley ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
John Lavery
Sir John Lavery (20 March 1856 – 10 January 1941) was a Northern Irish painter best known for his portraits and wartime depictions. Life and career John Lavery was born in inner North Belfast, baptised at St Patrick's Church, Belfast and, while still a child, moved to Scotland where he attended Haldane Academy in Glasgow in the 1870s. In 1878 he set up his own studio which was razed in a fire in the following year. With a £300 insurance pay-out he spent a year studying at Heatherley's School in London. Lavery continued his studies at the Académie Julian in Paris in the early 1880s. He returned to Glasgow and was associated with the Glasgow School. William Burrell, a wealthy shipowner, was a faithful patron of Scottish artists including Joseph Crawhall II, with whom Lavery studied. In 1888 he was commissioned to paint the state visit of Queen Victoria to the Glasgow International Exhibition. This launched his career as a society painter and he moved to London soon aft ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Sport Of Athletics
Athletics is a group of sporting events that involves competitive running, jumping, throwing sports, throwing, and walking. The most common types of athletics competitions are track and field, road running, cross country running, and racewalking. The results of racing events are decided by finishing position (or time, where measured), while the jumps and throws are won by the athlete that achieves the highest or furthest measurement from a series of attempts. The simplicity of the competitions, and the lack of a need for expensive equipment, makes athletics one of the most common types of sports in the world. Athletics is mostly an individual sport, with the exception of relay (athletics), relay races and competitions which combine athletes' performances for a team score, such as cross country. Organized athletics are traced back to the Ancient Olympic Games from 776 BC. The rules and format of the modern athletics events, events in athletics were defined in Western Europe and N ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
1928 Summer Olympics
The 1928 Summer Olympics ( nl, Olympische Zomerspelen 1928), officially known as the Games of the IX Olympiad ( nl, Spelen van de IXe Olympiade) and commonly known as Amsterdam 1928, was an international multi-sport event that was celebrated from 28 July to 12 August 1928 in Amsterdam, Netherlands. The city of Amsterdam had previously bid for the 1920 and 1924 Olympic Games, but was obliged to give way to war-torn Antwerp in Belgium for the 1920 Games and Pierre de Coubertin's Paris for the 1924 Games. The only other candidate city for the 1928 Olympics was Los Angeles, which would eventually be selected to host the Olympics four years later. In preparation for the 1932 Summer Olympics, the United States Olympic Committee reviewed the costs and revenue of the 1928 Games. The committee reported a total cost of US$1.183 million with receipts of US$1.165 million, giving a negligible loss of US$18,000, which was a considerable improvement over the 1924 Games. The United S ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
1926 Women's World Games
The 1926 Women's World Games (Swedish II. Internationella kvinnliga idrottsspelen, French 2èmes jeux féminins mondiaux ) were the second regular international Women's World Games, the tournament was held between 27''Jeux Mondiaux Féminins'' Commission documentation et histoire, cdm.athle.com (accessdate = 15 August 2016) – 29 August at the Slottsskogsvallen Stadium in . [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
1924 Women's Olympiad
The 1924 Women's Olympiad (formally called ''Women's International and British Games'', French ''Grand meeting international féminin'') was the first international competition for women in track and field in the United Kingdom. The tournament was held on 4 August 1924 in London, United Kingdom. Events After the successful first 1922 Women's World Games in Paris and the three Women's Olympiads ( 1921 Women's Olympiad, 1922 Women's Olympiad and 1923 Women's Olympiad) in Monaco the interest for women's sports also grew internationally. In 1922 the "Women's Amateur Athletic Association" (WAAA) was founded in the UK: the WAAA organised the first official British women championships in track and field ( WAAA Championships) on 18 August 1923 at the Oxo Sports Ground in Downham outside London. In the US the "Amateur Athletic Union" (AAU) organised the first official American women championships in track and field on 29 September 1923 at Weequahic Park in Newark, New Jersey. Th ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
1923 WAAA Championships
The 1923 WAAA Championships were the first national track and field championships for women in the UK. The tournament was held on 18 August 1923 at the Oxo Sport Grounds in London, United Kingdom. Background After the successful first 1922 Women's World Games in Paris and the three Women's Olympiads (1921 Women's Olympiad, 1922 Women's Olympiad and 1923 Women's World Games) in Monaco the interest for women's sports also grew internationally. In 1922 the "Women's Amateur Athletic Association" (WAAA) was founded in the UK, that year several ”national” women’s track meet were held. In 1923 the WAAA now organised the first official British women championships in track and field (WAAA Championships). In the US the "Amateur Athletic Union" (AAU) sponsored the first national championship for women in track and field on 29 September 1923. Events The meet was held on 18 August at the Oxo Sport Grounds in Downham, Bromley in South London. The athletes competed in 11 events: runn ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Women's Pentathlon
The pentathlon or women's pentathlon is a combined track and field event in which each woman competes in five separate events over one day (formerly two days). The distance or time for each event is converted to points via scoring tables, with the overall ranking determined by total points. Since 1949 the events have been sprint hurdling, high jump, shot put, long jump, and a flat race. The sprint hurdles distance was 80 m outdoors until 1969 and thereafter 100 m; in indoor pentathlon the distance is 60 m. The flat race was 200 m until 1976 and thereafter 800 m. In elite-level outdoor competition, the pentathlon was superseded in 1981 by the heptathlon, which has seven events, with both 200 m and 800 m, as well as the javelin throw. Pentathlon is still contested at school and masters level and indoors. History The word '' pentathlon'' is derived from the Greek ''pente'' (five) and ''athlon'' (contest). The ancient Olympic pentathlon ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Women's Olympiad
The Women's World Games were the first international women's sports events in track and field. The games were held four times between 1922 and 1934. They were established by Alice Milliat and the Fédération Sportive Féminine Internationale (FSFI) to compensate for the lack of women's sports at the Olympic Games. The games were an important step towards women's equality in sports. A forerunner tournament was held in Monte Carlo in March 1921. Background Women were allowed to take part in the Olympic games since 1900 ( II Olympiad in golf and tennis, III Olympiad in archery, IV Olympiad in archery, figure skating and tennis, at the V Olympiad swimming was added as well). In 1919 Milliat started discussions with the International Olympic Committee (IOC) and the IAAF to also include women's track and field athletics events in the 1924 Olympic Games. On refusal Milliat organised a first competition in 1921 called the Women's Olympiad in Monte Carlo; further editions were held ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
1923 Women's Olympiad
The 1923 Women's Olympiad (, and ) was the fourth international event in women's sports, the tournament was held 4 to 7 April 1923 in Monte Carlo, Monaco. The tournament was formally called "''Les Jeux Athlétiques Féminins à Monté Carlo''". The games were a runner-up to the 1921 Women's Olympiad and 1922 Women's Olympiad. Events The multi-sport event was as previous years organised by Fédération des Sociétés Féminines Sportives de France (FSFSF) under chairwoman Alice Milliat and Camille Blanc, director of the "International Sporting Club de Monaco" as a response to the International Olympic Committee (IOC) decision not to include women's events in the 1924 Olympic Games. The games were attended by participants from 8 nations: Belgium, Czechoslovakia, Denmark, France, Italy, Monaco, Switzerland and the United Kingdom. The tournament was a huge promotion for women's sports. The athletes competed in 11 events: running (60 metres, 250 metres, 8 ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
International Olympic Committee
The International Olympic Committee (IOC; french: link=no, Comité international olympique, ''CIO'') is a non-governmental sports organisation based in Lausanne, Switzerland. It is constituted in the form of an association under the Swiss Civil Code (articles 60–79). Founded by Pierre de Coubertin and Demetrios Vikelas in 1894, it is the authority responsible for organising the modern ( Summer, Winter, and Youth) Olympic Games. The IOC is the governing body of the National Olympic Committees (NOCs) and of the worldwide "Olympic Movement", the IOC's term for all entities and individuals involved in the Olympic Games. As of 2020, there are 206 NOCs officially recognised by the IOC. The current president of the IOC is Thomas Bach. The stated mission of the IOC is to promote the Olympics throughout the world and to lead the Olympic Movement: *To encourage and support the organization, development, and coordination of sport and sports competitions; *To ensure the regular c ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
High Jump
The high jump is a track and field event in which competitors must jump unaided over a horizontal bar placed at measured heights without dislodging it. In its modern, most-practiced format, a bar is placed between two standards with a crash mat for landing. Since ancient times, competitors have introduced increasingly effective techniques to arrive at the current form, and the current universally preferred method is the Fosbury Flop, in which athletes run towards the bar and leap head first with their back to the bar. The discipline is, alongside the pole vault, one of two vertical clearance events in the Olympic athletics program. It is contested at the World Championships in Athletics and the World Athletics Indoor Championships, and is a common occurrence at track and field meets. The high jump was among the first events deemed acceptable for women, having been held at the 1928 Olympic Games. Javier Sotomayor (Cuba) is the current men's record holder with a jump of set in 1 ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |





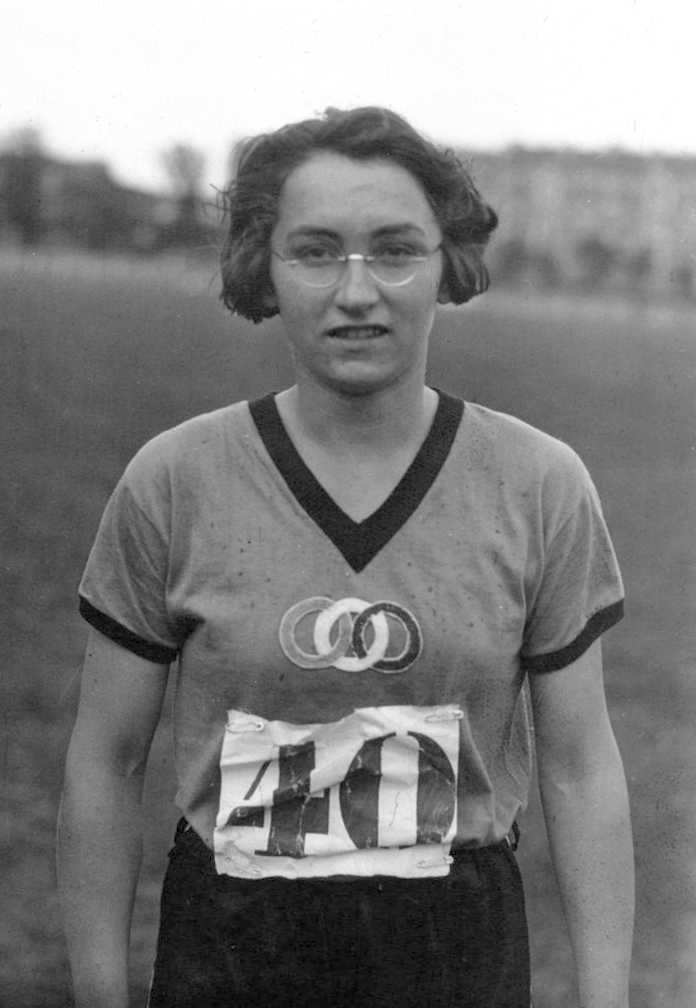


.jpg)