|
Solar Prominence
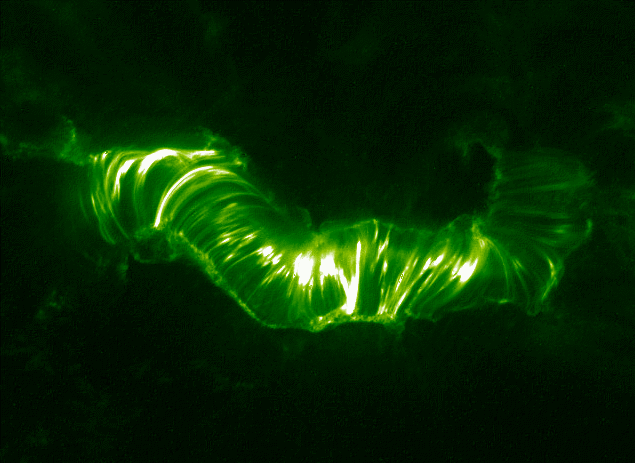
A prominence, sometimes referred to as a filament, is a large plasma and magnetic field structure extending outward from the Sun's surface, often in a loop shape. Prominences are anchored to the Sun's surface in the photosphere, and extend outwards into the solar corona. While the corona consists of extremely hot plasma, prominences contain much cooler plasma, similar in composition to that of the chromosphere. Prominences form over timescales of about a day and may persist in the corona for several weeks or months, looping hundreds of thousands of kilometers into space. Some prominences may give rise to coronal mass ejections. Scientists are currently researching how and why prominences are formed. A typical prominence extends over many thousands of kilometers; the largest on record was estimated at over long, roughly a solar radius. History The first detailed description of a solar prominence was in 14th-century Laurentian Codex, describing the Solar eclipse of 1 M ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Solar Prominence 2011-04-14T202956
Solar may refer to: Astronomy * Of or relating to the Sun ** Solar telescope, a special purpose telescope used to observe the Sun ** A device that utilizes solar energy (e.g. "solar panels") ** Solar calendar, a calendar whose dates indicate the position of the Earth on its revolution around the Sun * Solar Maximum Mission, a satellite * SOLAR (ISS), an observatory on International Space Station Music * "Solar" (composition), attributed to Miles Davis * ''Solar'' (Red Garland album), 1962 * ''Solar'' (Taeyang album), 2010 * ''Solar'', a 2011 album by Rubik * "Solar", a song by Northlane from ''Mesmer'', 2017 * SOLAR Records, a record label Geography * Solar (Spanish term), a type of urban site * Solar, County Antrim, Northern Ireland, United Kingdom * Solar, Erode, India * Solar, Iran, Iran Companies * Solar Entertainment Corporation, a Philippines television and radio media company * Solar TV, a former TV channel * Solar Television Network, Inc., a former name o ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Helium
Helium (from el, ἥλιος, helios, lit=sun) is a chemical element with the symbol He and atomic number 2. It is a colorless, odorless, tasteless, non-toxic, inert, monatomic gas and the first in the noble gas group in the periodic table. Its boiling and melting point are the lowest among all the elements. It is the second lightest and second most abundant element in the observable universe (hydrogen is the lightest and most abundant). It is present at about 24% of the total elemental mass, which is more than 12 times the mass of all the heavier elements combined. Its abundance is similar to this in both the Sun and in Jupiter, due to the very high nuclear binding energy (per nucleon) of helium-4, with respect to the next three elements after helium. This helium-4 binding energy also accounts for why it is a product of both nuclear fusion and radioactive decay. The most common isotope of helium in the universe is helium-4, the vast majority of which was formed during t ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Solar Flare
A solar flare is an intense localized eruption of electromagnetic radiation in the Sun's atmosphere. Flares occur in active regions and are often, but not always, accompanied by coronal mass ejections, solar particle events, and other solar phenomena. The occurrence of solar flares varies with the 11-year solar cycle. Solar flares are thought to occur when stored magnetic energy in the Sun's atmosphere accelerates charged particles in the surrounding plasma. This results in the emission of electromagnetic radiation across the electromagnetic spectrum. High-energy electromagnetic radiation from solar flares is absorbed by the daylight side of Earth's upper atmosphere, in particular the ionosphere, and does not reach the surface. This absorption can temporarily increase the ionization of the ionosphere which may interfere with short-wave radio communication. The prediction of solar flares is an active area of research. Flares also occur on other stars, where the term ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Hyder Flare
A Hyder flare is slow, large-scale brightening that occurs in the solar chromosphere.Space Weather Services: Hyder Flares at the Australian Government Bureau of Meteorology; retrieved February 6, 2016 It resembles a large but feeble and is identifiable as the signature of the sudden disappearance of a (a "disparition brusque"). These events occur in the quiet Sun, away from s or |
Active Region
An active region is a temporary region in the Sun's atmosphere characterized by a strong and complex magnetic field. They are often associated with sunspots and are commonly the source of violent eruptions such as coronal mass ejections and solar flares. The number and location of active regions on the solar disk at any given time is dependent on the solar cycle. Region numbers Newly observed active regions on the solar disk are assigned 4-digit region numbers by the Space Weather Prediction Center (SWPC) on the day following the initial observation. The region number assigned to a particular active region is one added to the previously assigned number. For example, the first observation of active region 8090, or AR8090, was followed by AR8091. According to the SWPC, a number is assigned to a region if it meets at least one of the following criteria: # It contains a sunspot group of class C or larger based on the Modified Zurich Class sunspot classification system. # It contains ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
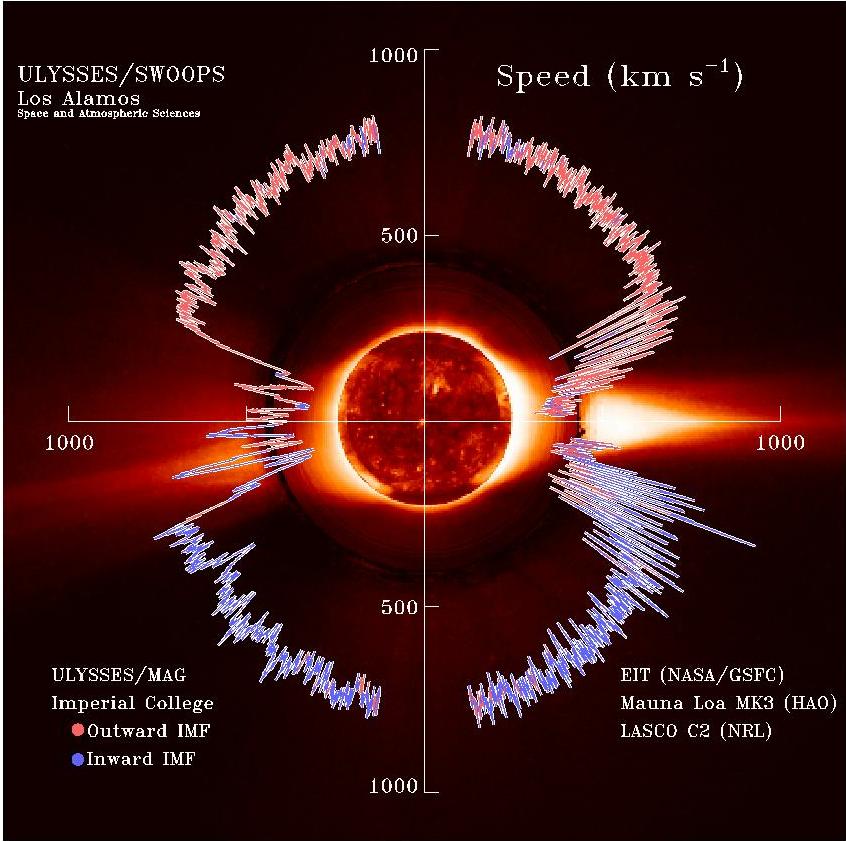
Solar Wind
The solar wind is a stream of charged particles released from the upper atmosphere of the Sun, called the corona. This plasma mostly consists of electrons, protons and alpha particles with kinetic energy between . The composition of the solar wind plasma also includes a mixture of materials found in the solar plasma: trace amounts of heavy ions and atomic nuclei such as C, N, O, Ne, Mg, Si, S, and Fe. There are also rarer traces of some other nuclei and isotopes such as P, Ti, Cr, 54Fe and 56Fe, and 58Ni, 60Ni, and 62Ni. Superposed with the solar-wind plasma is the interplanetary magnetic field. The solar wind varies in density, temperature and speed over time and over solar latitude and longitude. Its particles can escape the Sun's gravity because of their high energy resulting from the high temperature of the corona, which in turn is a result of the coronal magnetic field. The boundary separating the corona from the solar wind is called the Alfvén surface. At a dist ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Solar Prominence
A prominence, sometimes referred to as a filament, is a large plasma and magnetic field structure extending outward from the Sun's surface, often in a loop shape. Prominences are anchored to the Sun's surface in the photosphere, and extend outwards into the solar corona. While the corona consists of extremely hot plasma, prominences contain much cooler plasma, similar in composition to that of the chromosphere. Prominences form over timescales of about a day and may persist in the corona for several weeks or months, looping hundreds of thousands of kilometers into space. Some prominences may give rise to coronal mass ejections. Scientists are currently researching how and why prominences are formed. A typical prominence extends over many thousands of kilometers; the largest on record was estimated at over long, roughly a solar radius. History The first detailed description of a solar prominence was in 14th-century Laurentian Codex, describing the Solar eclipse of 1 M ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Chirality
Chirality is a property of asymmetry important in several branches of science. The word ''chirality'' is derived from the Greek (''kheir''), "hand", a familiar chiral object. An object or a system is ''chiral'' if it is distinguishable from its mirror image; that is, it cannot be superimposed onto it. Conversely, a mirror image of an ''achiral'' object, such as a sphere, cannot be distinguished from the object. A chiral object and its mirror image are called ''enantiomorphs'' (Greek, "opposite forms") or, when referring to molecules, '' enantiomers''. A non-chiral object is called ''achiral'' (sometimes also ''amphichiral'') and can be superposed on its mirror image. The term was first used by Lord Kelvin in 1893 in the second Robert Boyle Lecture at the Oxford University Junior Scientific Club which was published in 1894: Human hands are perhaps the most recognized example of chirality. The left hand is a non-superimposable mirror image of the right hand; no matter how t ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Helmet Streamer
Helmet streamers, also known as coronal streamers, are elongated cusp-like structures in the Sun's corona which are often visible in white-light coronagraphs and during solar eclipses. They are closed magnetic loops which lie above divisions between regions of opposite magnetic polarity on the Sun's surface. The solar wind elongates these loops to pointed tips which can extend a solar radius or more into the corona. During solar minimum, helmet streamers are found closer to the heliographic equator, whereas during solar maximum they are found more symmetrically distributed around the Sun. Structure Helmet streamers have cusp-like bases that taper radially outward away from the Sun forming long stalks. The base typically extends up to 1.5 solar radii above the surface, whereas the stalk—stretched outward by the solar wind—can extend over many solar radii. Helmet streamers are structured by closed magnetic fields and lie above boundaries separating opposite magnetic pola ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Chromospheric Fibril
In solar physics, a spicule, also known as a fibril or mottle, is a dynamic jet of plasma in the Sun's chromosphere about 300 km in diameter.Quantifying Spicules, Tiago M. D. Pereira, Bart De Pontieu, and Mats Carlsson, ''The Astrophysical Journal'' 759, #1 (October 2012), pp. 18-34, , . They move upwards with speeds between 15 and 110 km/s from the photosphere and last a few minutes each. They were discovered in 1877 by Angelo Secchi, but the physical mechanism that generates them is still hotly debated. Description Spicules last for about 15 minutes; at the solar limb they appear elongated (if seen on the disk, they are known as "mottles" or "fibrils"). They are usually associated with regions of high magnetic flux; their mass flux is about 100 times that of the solar wind. They rise at a rate of 20 km/s (or 72,000 km/h) and can reach several thousand kilometers in height before collapsing and fading away. Prevalence There are about 3,000,000 active spicu ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Electromagnetic Spectrum
The electromagnetic spectrum is the range of frequencies (the spectrum) of electromagnetic radiation and their respective wavelengths and photon energies. The electromagnetic spectrum covers electromagnetic waves with frequencies ranging from below one hertz to above 1025 hertz, corresponding to wavelengths from thousands of kilometers down to a fraction of the size of an atomic nucleus. This frequency range is divided into separate bands, and the electromagnetic waves within each frequency band are called by different names; beginning at the low frequency (long wavelength) end of the spectrum these are: radio waves, microwaves, infrared, visible light, ultraviolet, X-rays, and gamma rays at the high-frequency (short wavelength) end. The electromagnetic waves in each of these bands have different characteristics, such as how they are produced, how they interact with matter, and their practical applications. There is no known limit for long and short wavelengths. Extreme ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Solar Plage
A plage is a bright region in the Sun's chromosphere, typically found in and around active regions. Historically, they have been referred to as ''bright flocculi'', in contrast to dark flocculi, and as ''chromospheric faculae'', in contrast to photospheric faculae. Etymology The term is often believed to be poetically taken from the French word for "beach"; however, this is likely a misunderstanding of an 1893 article by Henri-Alexandre Deslandres where the name ''facular flames'' was suggested. In the article, Deslandres also refers to them as ''plages brillantes'', meaning ''bright regions'', which became the more commonly used term. Description Classically plage have been defined as regions that are bright in Hα and other chromospheric emission lines. but nowadays most researchers identify plage based on the photospheric magnetic field concentration of the faculae below. The magnetic field of plage is confined to the intergranular lanes in the photosphere with a streng ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |






.jpg)