|
Smeaton's Tower
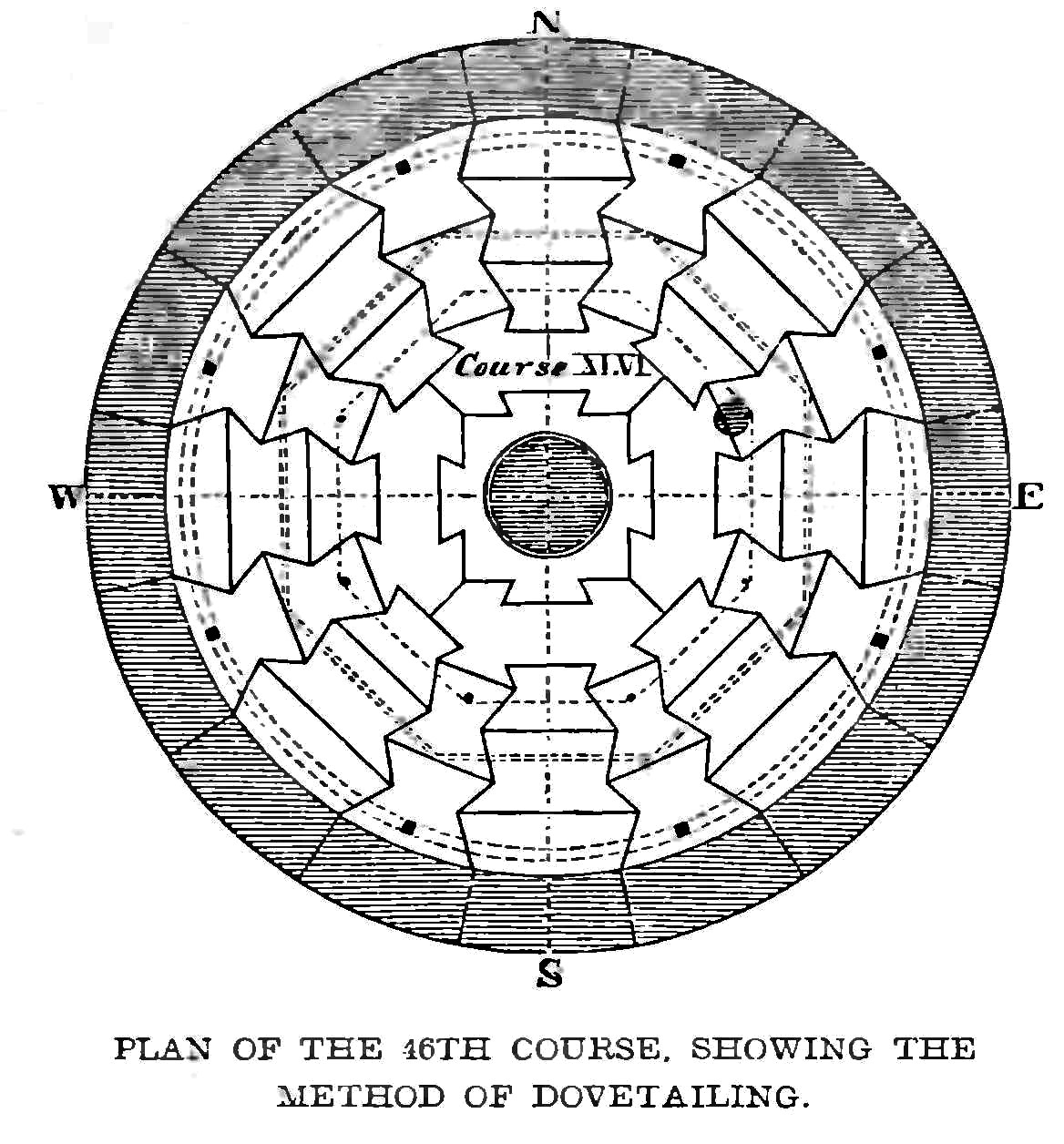
Smeaton's Tower is a memorial to civil engineer John Smeaton, designer of the third and most notable Eddystone Lighthouse. A major step forward in lighthouse design, Smeaton's structure was in use from 1759 to 1877, until erosion of the ledge it was built upon forced new construction. The tower was largely dismantled and rebuilt on Plymouth Hoe in Plymouth, Devon, where it stands today. History Background England’s coasts are notorious for rough weather, dangerous seas and deathly obstacles. The Eddystone rocks are among them. There were several attempts were made to place a marker on these reefs. The first attempt was called the Winstanley Lighthouse. After it was destroyed in the 1703 storm, a second one called the Rudyard lighthouse was built. This one was also destroyed, this time by a fire in 1755. Born in Austhorpe, Yorkshire, England in 1724, John Smeaton is considered the father of civil engineering. Recognized for his scientific achievements, including the increa ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Plymouth
Plymouth () is a port city and unitary authority in South West England. It is located on the south coast of Devon, approximately south-west of Exeter and south-west of London. It is bordered by Cornwall to the west and south-west. Plymouth's early history extends to the Bronze Age when a first settlement emerged at Mount Batten. This settlement continued as a trading post for the Roman Empire, until it was surpassed by the more prosperous village of Sutton founded in the ninth century, now called Plymouth. In 1588, an English fleet based in Plymouth intercepted and defeated the Spanish Armada. In 1620, the Pilgrim Fathers departed Plymouth for the New World and established Plymouth Colony, the second English settlement in what is now the United States of America. During the English Civil War, the town was held by the Roundhead, Parliamentarians and was besieged between 1642 and 1646. Throughout the Industrial Revolution, Plymouth grew as a commercial shipping port, handling ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Trinity House
"Three In One" , formation = , founding_location = Deptford, London, England , status = Royal Charter corporation and registered charity , purpose = Maintenance of lighthouses, buoys and beacons , headquarters = Trinity House, Tower Hill, London, England , region = , membership = , leader_title = Master , leader_name = Anne, Princess Royal , leader_title2 = Deputy Master , leader_name2 = Captain Ian McNaught , revenue = £38,405,000 (2020) , expenses = £46,801,000 (2020) , staff = 312 (2020) , website trinityhouse.co.uk The Corporation of Trinity House of Deptford Strond, also known as Trinity House (and formally as The Master, Wardens and Assistants of the Guild Fraternity or Brotherhood of the most glorious and undivided Trinity and of St Clement in the Parish of Deptford Strond in the County of Kent), is the offi ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Sir John Barrow
Sir John Barrow, 1st Baronet, (19 June 1764 – 23 November 1848) was an English geographer, linguist, writer and civil servant best known for term as the Second Secretary to the Admiralty from 1804 until 1845. Early life Barrow was born the only child of Roger Barrow, a tanner in the village of Dragley Beck, in the parish of Ulverston, Lancashire.Prior to 1 April 1974 Ulverston was in Lancashire He was a pupil at Town Bank Grammar School, Ulverston, but left at age 13 to found a Sunday school for the poor. Barrow was employed as superintending clerk of an iron foundry at Liverpool. At only 16, he went on a whaling expedition to Greenland. By his twenties, he was teaching mathematics, in which he had always excelled, at a private school in Greenwich. China Barrow taught mathematics to the son of Sir George Leonard Staunton; through Staunton's interest, he was attached on the first British embassy to China from 1792 to 1794 as comptroller of the household to Lord Macar ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Cumbria
Cumbria ( ) is a ceremonial and non-metropolitan county in North West England, bordering Scotland. The county and Cumbria County Council, its local government, came into existence in 1974 after the passage of the Local Government Act 1972. Cumbria's county town is Carlisle, in the north of the county. Other major settlements include Barrow-in-Furness, Kendal, Whitehaven and Workington. The administrative county of Cumbria consists of six districts ( Allerdale, Barrow-in-Furness, Carlisle, Copeland, Eden and South Lakeland) and, in 2019, had a population of 500,012. Cumbria is one of the most sparsely populated counties in England, with 73.4 people per km2 (190/sq mi). On 1 April 2023, the administrative county of Cumbria will be abolished and replaced with two new unitary authorities: Westmorland and Furness (Barrow-in-Furness, Eden, South Lakeland) and Cumberland ( Allerdale, Carlisle, Copeland). Cumbria is the third largest ceremonial county in England by area. It i ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Ulverston
Ulverston is a market town and a civil parish in the South Lakeland district of Cumbria, England. In the 2001 census the parish had a population of 11,524, increasing at the 2011 census to 11,678. Historically in Lancashire, it lies a few miles south of the Lake District National Park and just north-west of Morecambe Bay, within the Furness Peninsula. Lancaster is to the east, Barrow-in-Furness to the south-west and Kendal to the north-east. History The name ''Ulverston'', first noted as ''Ulurestun'' in the Domesday Book of 1086, consists of an Old Norse personal name, ''Úlfarr'', or the Old English ''Wulfhere'', with the Old English ''tūn'', meaning farmstead or village. The personal names ''Úlfarr'' and ''Wulfhere'' both imply "wolf warrior" or "wolf army", which explains the presence of a wolf on the town's coat of arms. The loss of the initial W in ''Wulfhere'' can be linked to Scandinavian influence in the region. Locally, the town has traditionally been kn ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Hoad Monument
Hoad Monument (proper name: the '' Sir John Barrow Monument'') is a tower at the top of the Hoad Hill, near Ulverston in the Cumbria. England. It commemorates Sir John Barrow (1764-1848), who was born in Ulverston, and was built in 1850 at a cost of £1250. The cost being met mainly by public subscription Sir John Barrow was a founding member of the Royal Geographical Society. He travelled to China and South Africa as a diplomat and held the post of Second Secretary to the Admiralty from 1804 until 1845. Description left, upThe view from the top of the monument, 2010 The monument is not a lighthouse: it has never had a functional light. However, it was designed to resemble one, and is similar to the Third Eddystone Lighthouse (Smeaton's Tower). It is a Grade II* listed building, meaning that it is of more than local interest, and the monument stands as one of the symbols of the Northwest of England. It is built of limestone quarried locally at Birkrigg Common. Due to its el ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Token Coin
In numismatics, token coins or trade tokens are coin-like objects used instead of coins. The field of token coins is part of exonumia and token coins are token money. Their denomination is shown or implied by size, color or shape. They are often made of cheaper metals like copper, pewter, aluminium, brass and tin, or non-metals like bakelite, leather and porcelain. A legal tender coin is issued by a governmental authority and is freely exchangeable for goods. A token coin is less useful and issued by a private entity. Trade or barter Coin-like objects from the Roman Empire called have been interpreted as an early form of token. Their functions are not documented, but they appear to have been brothel tokens or possibly gaming tokens. Medieval English monasteries issued tokens to pay for services from outsiders. These tokens circulated in nearby villages, where they were called "Abbot's money". Also, counters called jetons were used as small change without official blessing. ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Britannia
Britannia () is the national personification of Britain as a helmeted female warrior holding a trident and shield. An image first used in classical antiquity, the Latin ''Britannia'' was the name variously applied to the British Isles, Great Britain, and the Roman province of Britain during the Roman Empire. Typically depicted reclining or seated with spear and shield since appearing thus on Roman coins of the 2nd century AD, the classical national allegory was revived in the early modern period. On coins of the pound sterling issued by Charles II of England, Scotland, and Ireland, Britannia appears with her shield bearing the Union Flag. To symbolise the Royal Navy's victories, Britannia's spear became the characteristic trident in 1797, and a helmet was added to the coinage in 1825. By the 1st century BC, Britannia replaced Albion as the prevalent Latin name for the island of Great Britain. After the Roman conquest in 43 AD, ''Britannia'' also came to refer to the Roman ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
History Of The British Penny (1714–1901)
The penny of Great Britain and the United Kingdom from 1714 to 1901, the period in which the House of Hanover reigned, saw the transformation of the penny from a little-used small silver coin to the bronze piece recognisable to modern-day Britons. All bear the portrait of the monarch on the obverse Obverse and its opposite, reverse, refer to the two flat faces of coins and some other two-sided objects, including paper money, flags, seals, medals, drawings, old master prints and other works of art, and printed fabrics. In this usage, ''o ...; copper and bronze pennies have a depiction of Britannia, the female personification of Britain, on the reverse. During most of the 18th century, the penny was a small silver coin rarely seen in circulation, and that was principally struck to be used for Maundy money or other royal charity. Beginning in 1787, the chronic shortage of good money resulted in the wide circulation of conder token, private tokens, including large coppers valu ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Eddystone Rocks
The Eddystone or Eddystone Rocks are a seaswept and eroded group of rocks ranging southwest of Rame Head in Cornwall, England, United Kingdom. Although the nearest point on the mainland to the Eddystone is in Cornwall, the rocks fall within the city limits of Plymouth, and hence within the county of Devon. For centuries the rocks have been a hazard for the ships in the approaches to the English Channel and the port city of Plymouth. There have been four lighthouses on the Eddystone Rocks. Winstanley (two versions; the second replaced the top of the structure), Rudyard, Smeaton and finally the Douglass Lighthouse, which is the present one. When the Douglass Lighthouse was completed, the people of Plymouth paid for the dismantling of the Smeaton Lighthouse from the red rocks of Eddystone and its reassembly at Plymouth Hoe, where it is a popular tourist attraction today. View at 1:50000 scale. The stub of the Smeaton lighthouse still remains on the rocks. In the 1970s, the question ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
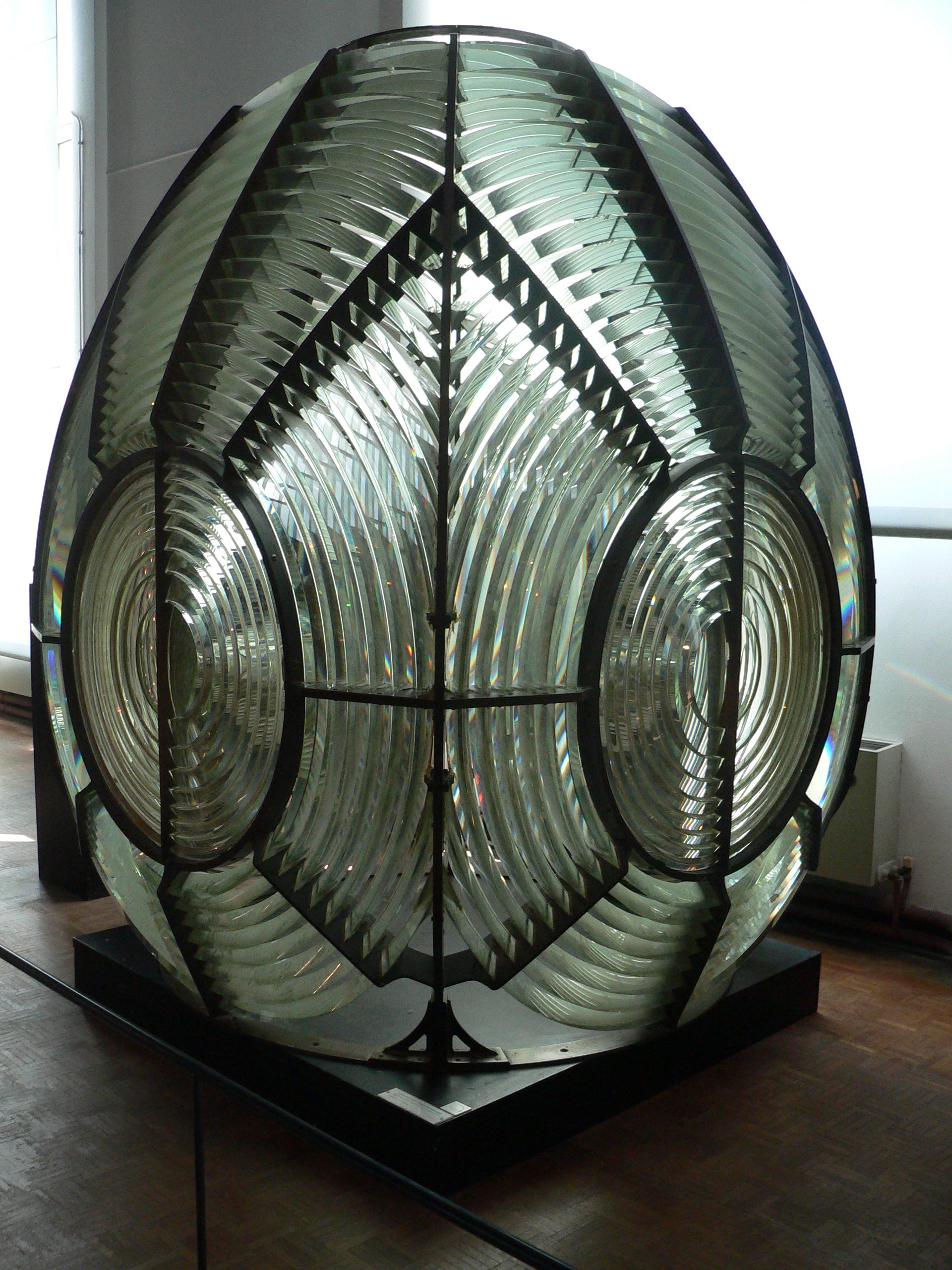
Fresnel Lens
A Fresnel lens ( ; ; or ) is a type of composite compact lens developed by the French physicist Augustin-Jean Fresnel (1788–1827) for use in lighthouses. It has been called "the invention that saved a million ships." The design allows the construction of lenses of large aperture and short focal length without the mass and volume of material that would be required by a lens of conventional design. A Fresnel lens can be made much thinner than a comparable conventional lens, in some cases taking the form of a flat sheet. The simpler dioptric (purely refractive) form of the lens was first proposed by Count Buffon and independently reinvented by Fresnel. The ''catadioptric'' form of the lens, entirely invented by Fresnel, has outer elements that use total internal reflection as well as refraction; it can capture more oblique light from a light source and add it to the beam of a lighthouse, making the light visible from greater distances. Description The Fresnel lens redu ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |





_-_HMS_'Forte'_Passing_the_Eddystone_Lighthouse_-_BHC3737_-_Royal_Museums_Greenwich.jpg)
