|
Sleeping Car
The sleeping car or sleeper (often ) is a railway passenger car (rail), passenger car that can accommodate all passengers in beds of one kind or another, for the purpose of sleeping. George Pullman was the American innovator of the sleeper car. The first such cars saw sporadic use on American and English railways in the 1830s; they could be configured for Coach (rail), coach seating during the day. History Possibly the earliest example of a sleeping car (or ''bed carriage'', as it was then called) was on the London & Birmingham and Grand Junction Railways between London and Lancashire, England. The bed carriage was first made available to first-class passengers in 1838. In the spring of 1839, the Cumberland Valley Railroad pioneered sleeping car service in America with a car named "Chambersburg", between Chambersburg, Pennsylvania, Chambersburg and Harrisburg, Pennsylvania. A couple of years later a second car, the "Carlisle", was introduced into service. [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Pullman Sleeping Car Circa 1860s
Pullman may refer to: Places in the United States *Pullman, Chicago, Illinois *Pullman, Michigan *Pullman, Texas *Pullman, Washington *Pullman, West Virginia *Pullman Lake, a lake in Minnesota *Pullman, Richmond, California, Pullman neighborhood, in the city of Richmond, California Surname * Alberte Pullman (1920–2011), theoretical and quantum chemist, wife of Bernard *Alfred Pullman (1916–1954), a British soldier and airman * Bernard Pullman (1919–1996), theoretical and quantum chemist, husband of Alberte * Bill Pullman (born 1953), American actor * George Pullman (1831–1897), founder of the Pullman Company * Joe Pullman (1876–1955), Wales international rugby union player * Lewis Pullman (born 1993), American actor * Philip Pullman (born 1946), English writer * Simon Pullman (1890–1942), violinist and founder of the Warsaw Ghetto Symphony Orchestra Transport Road * Humber Pullman, a large automobile manufactured in central England between 1930 and 1954 * Mercedes-May ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Pullman Company
The Pullman Company, founded by George Pullman, was a manufacturer of railroad cars in the mid-to-late 19th century through the first half of the 20th century, during the boom of railroads in the United States. Through rapid late-19th century development of mass production and takeover of rivals, the company developed a virtual monopoly on production and ownership of sleeper cars. During a severe economic downturn, the 1894 Pullman Strike by company workers proved a transforming moment in American labor history. At the company's peak in the early 20th century, its cars accommodated 26 million people a year, and it in effect operated "the largest hotel in the world". Its production workers initially lived in a planned worker community (or "company town") named Pullman, Chicago. Pullman developed the sleeping car, which carried his name into the 1980s. Pullman did not just manufacture the cars, it also operated them on most of the railroads in the United States, paying rail ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Jet Airliner
A jet airliner or jetliner is an airliner powered by jet engines (passenger jet aircraft). Airliners usually have two or four jet engines; three-engined designs were popular in the 1970s but are less common today. Airliners are commonly classified as either the large wide-body aircraft A wide-body aircraft, also known as a twin-aisle aircraft, is an airliner with a fuselage wide enough to accommodate two passenger aisles with seven or more seats abreast. The typical fuselage diameter is . In the typical wide-body economy cabi ..., medium narrow-body aircraft and smaller regional jet. Most airliners today are powered by jet engines, because they are capable of safely operating at high speeds and generate sufficient thrust to power large-capacity aircraft. The first jetliners, introduced in the 1950s, used the simpler turbojet engine; these were quickly supplanted by designs using turbofans, which are quieter and more fuel-efficient. History Early history The first air ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Interstate Highway System
The Dwight D. Eisenhower National System of Interstate and Defense Highways, commonly known as the Interstate Highway System, is a network of controlled-access highways that forms part of the National Highway System in the United States. The system extends throughout the contiguous United States and has routes in Hawaii, Alaska, and Puerto Rico. The U.S. federal government first funded roadways through the Federal Aid Road Act of 1916, and began an effort to construct a national road grid with the passage of the Federal Aid Highway Act of 1921. In 1926, the United States Numbered Highway System was established, creating the first national road numbering system for cross-country travel. The roads were still state-funded and maintained, however, and there was little in the way of national standards for road design. U.S. Highways could be anything from a two-lane country road to a major multi-lane freeway. After Dwight D. Eisenhower became president in 1953, his administration ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
World War II
World War II or the Second World War, often abbreviated as WWII or WW2, was a world war that lasted from 1939 to 1945. It involved the vast majority of the world's countries—including all of the great powers—forming two opposing military alliances: the Allies and the Axis powers. World War II was a total war that directly involved more than 100 million personnel from more than 30 countries. The major participants in the war threw their entire economic, industrial, and scientific capabilities behind the war effort, blurring the distinction between civilian and military resources. Aircraft played a major role in the conflict, enabling the strategic bombing of population centres and deploying the only two nuclear weapons ever used in war. World War II was by far the deadliest conflict in human history; it resulted in 70 to 85 million fatalities, mostly among civilians. Tens of millions died due to genocides (including the Holocaust), starvation, ma ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Chicago And Alton Railroad Pullman Car Interior C 1900
(''City in a Garden''); I Will , image_map = , map_caption = Interactive Map of Chicago , coordinates = , coordinates_footnotes = , subdivision_type = List of sovereign states, Country , subdivision_name = United States , subdivision_type1 = U.S. state, State , subdivision_type2 = List of counties in Illinois, Counties , subdivision_name1 = Illinois , subdivision_name2 = Cook County, Illinois, Cook and DuPage County, Illinois, DuPage , established_title = Settled , established_date = , established_title2 = Municipal corporation, Incorporated (city) , established_date2 = , founder = Jean Baptiste Point du Sable , government_type = Mayor–council government, Mayor–council , governing_body = Chicago City Council , leader_title = Mayor of Chicago, Mayor , leader_name = Lori Lightfo ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Atchison, Topeka And Santa Fe Railway
The Atchison, Topeka and Santa Fe Railway , often referred to as the Santa Fe or AT&SF, was one of the larger railroads in the United States. The railroad was chartered in February 1859 to serve the cities of Atchison, Kansas, Atchison and Topeka, Kansas, and Santa Fe, New Mexico. The railroad reached the Kansas–Colorado border in 1873 and Pueblo, Colorado, in 1876. To create a demand for its services, the railroad set up real estate offices and sold farmland from the land grants that it was awarded by United States Congress, Congress. Despite being chartered to serve the city, the railroad chose to bypass Santa Fe, due to the engineering challenges of the mountainous terrain. Eventually Santa Fe Southern Railway, a branch line from Lamy, New Mexico, brought the Santa Fe railroad to its namesake city. The Santa Fe was a pioneer in intermodal freight transport; at various times, it operated an airline, the short-lived Santa Fe Skyway, and the fleet of Santa Fe Railroad Tugboa ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Super Chief
The ''Super Chief'' was one of the named passenger trains and the flagship of the Atchison, Topeka and Santa Fe Railway. The streamliner claimed to be "The Train of the Stars" because of the various celebrities it carried between Chicago, Illinois, and Los Angeles, California. The ''Super Chief'' (Nos. 17 and 18) was the first diesel-electric powered cross-country passenger train in America. The train eclipsed the '' Chief'' as Santa Fe's standard bearer. The extra-fare ($10) ''Super Chief'' left Dearborn Station in Chicago for its first trip on May 12, 1936. Before starting scheduled service in May 1937, the lightweight version of the ''Super Chief'' ran from Los Angeles over recently upgraded tracks in 36 hours and 49 minutes, averaging overall and reaching . With one set of equipment, the train initially operated once a week from both Chicago and Los Angeles. After more cars had been delivered the ''Super Chief'' ran twice weekly beginning in 1938 and daily after 1948. ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Illinois Central Railroad
The Illinois Central Railroad , sometimes called the Main Line of Mid-America, was a railroad in the Central United States, with its primary routes connecting Chicago, Illinois, with New Orleans, Louisiana, and Mobile, Alabama. A line also connected Chicago with Sioux City, Iowa (1870). There was a significant branch to Omaha, Nebraska (1899), west of Fort Dodge, Iowa, and another branch reaching Sioux Falls, South Dakota (1877), starting from Cherokee, Iowa. The Sioux Falls branch has been abandoned in its entirety. The Canadian National Railway acquired control of the IC in 1998, and merged its operations in 1999. Illinois Central continues to exist as a paper railroad. History The IC was one of the oldest Class I railroads in the United States. The company was incorporated by the Illinois General Assembly on January 16, 1836. Within a few months Rep. Zadok Casey (D-Illinois) introduced a bill in the U.S. House of Representatives authorizing a land grant to the company to ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Panama Limited
The ''Panama Limited'' was a passenger train operated from 1911 to 1971 between Chicago, Illinois, and New Orleans, Louisiana. The flagship train of the Illinois Central Railroad, it took its name from the Panama Canal, which in 1911 was three years from completion. For most of its career, the train was "all- Pullman", carrying sleeping cars only. The ''Panama Limited'' was one of many trains discontinued when Amtrak began operations in 1971, though Amtrak revived the name later that year and continued it until 1981. Today, overnight service between Chicago and New Orleans is provided by Amtrak's ''City of New Orleans'', another former Illinois Central train that was originally the daytime counterpart of the ''Panama Limited.'' History In the early 1900s, the Illinois Central's premier train on the Chicago-New Orleans route was the ''Chicago and New Orleans Limited''. On February 4, 1911, the Illinois Central renamed this train the ''Panama Limited'', in honor of the anticipate ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
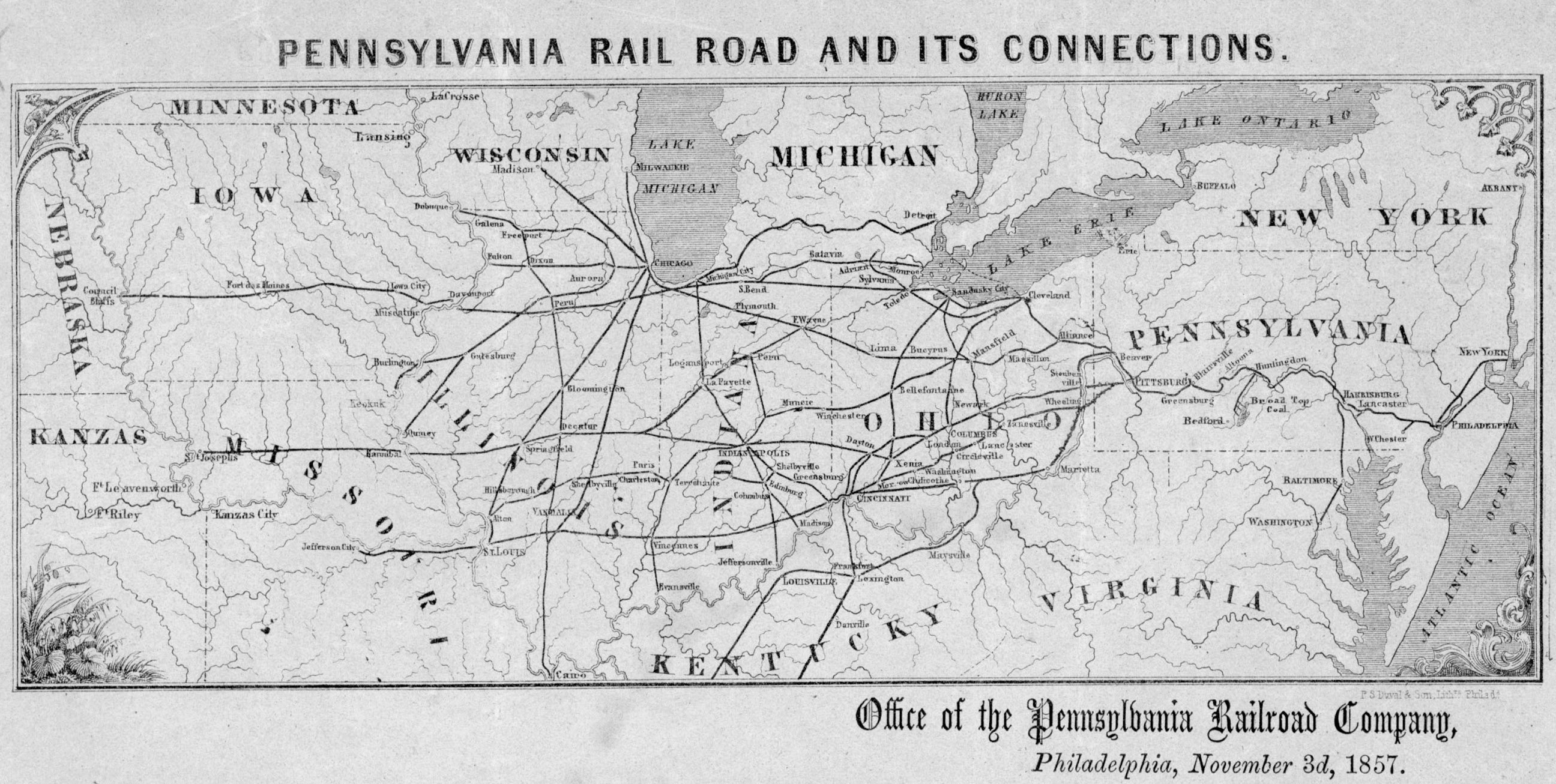
Pennsylvania Railroad
The Pennsylvania Railroad (reporting mark PRR), legal name The Pennsylvania Railroad Company also known as the "Pennsy", was an American Class I railroad that was established in 1846 and headquartered in Philadelphia, Pennsylvania. It was named for the commonwealth in which it was established. By 1882, Pennsylvania Railroad had become the largest railroad (by traffic and revenue), the largest transportation enterprise, and the largest corporation in the world. Its budget was second only to the U.S. government. Over the years, it acquired, merged with, or owned part of at least 800 other rail lines and companies. At the end of 1926, it operated of rail line;This mileage includes companies independently operated. PRR miles of all tracks, which includes first (or main), second, third, fourth, and sidings, totalled 28,040.49 at the end of 1926. in the 1920s, it carried nearly three times the traffic as other railroads of comparable length, such as the Union Pacific and Atchison, T ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Broadway Limited
The ''Broadway Limited'' was a passenger train operated by the Pennsylvania Railroad (PRR) between New York City and Chicago. It operated from 1912 to 1995. It was the Pennsylvania's premier train, competing directly with the New York Central Railroad's '' 20th Century Limited''. The ''Broadway Limited'' continued operating after the formation of Penn Central (PC) in February 1968, one of the few long-distance trains to do so. PC conveyed the train to Amtrak in 1971, who operated it until 1995. The train's name referred not to Broadway in Manhattan, but rather to the "broad way" of PRR's four-track right-of-way along the majority of its route. History Pennsylvania Railroad The ''Pennsylvania Special'' was one of nine express trains the Pennsylvania Railroad (PRR) operated between New York City and Chicago. On November 14, 1912, PRR renamed it the ''Broadway Limited'', to avoid confusion with the similarly-named ''Pennsylvania Limited''. The name, though spelled as "B ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |