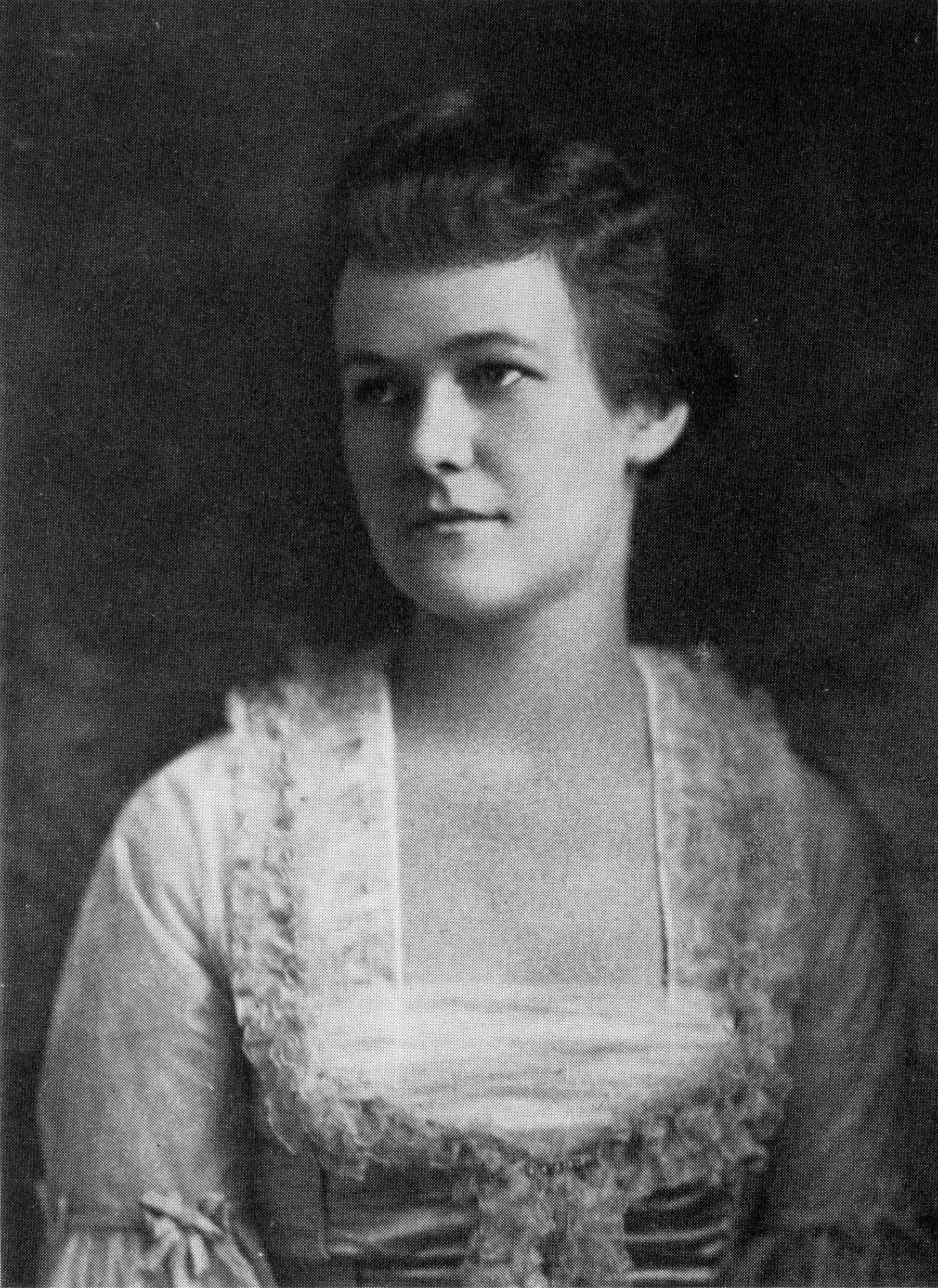|
Skunk Hour
'Skunk Hour' is one of Robert Lowell's most frequently anthologized poems. It was published in his groundbreaking book of poems, ''Life Studies,'' and is regarded as a key early example of Confessional poetry. Composition 'Skunk Hour' was the final poem in ''Life Studies'', but it was the first to be completed. Lowell began work on the poem in August 1957, and the poem was first published, alongside the poems "Man and Wife" and "Memories of West Street and Lepke" in the January 1958 issue of the ''Partisan Review''. He describes the writing of it thus: "I began writing lines in a new style. No poem, however, got finished and soon I left off and tried to forget the whole headache. ... When I began writing 'Skunk Hour', I felt that most of what I knew about writing was a hindrance. The dedication is to Elizabeth Bishop, because re-reading her suggested a way of breaking through the shell of my old manner." The poem was in part based on Bishop's poem "Armadillo" and Lowell wrot ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Robert Lowell
Robert Traill Spence Lowell IV (; March 1, 1917 – September 12, 1977) was an American poet. He was born into a Boston Brahmin family that could trace its origins back to the ''Mayflower''. His family, past and present, were important subjects in his poetry. Growing up in Boston also informed his poems, which were frequently set in Boston and the New England region. The literary scholar Paula Hayes believes that Lowell mythologized New England, particularly in his early work. Lowell stated, "The poets who most directly influenced me ... were Allen Tate, Elizabeth Bishop, and William Carlos Williams. An unlikely combination! ... but you can see that Bishop is a sort of bridge between Tate's formalism and Williams's informal art." Lowell wrote in both formal, metered verse as well as free verse; his verse in some poems from ''Life Studies'' and ''Notebook'' fell somewhere in between metered and free verse. After the publication of his 1959 book ''Life Studies'', which won the 1960 ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Life Studies
''Life Studies'' is the fourth book of poems by Robert Lowell. Most critics (including Helen Vendler, Steven Gould Axelrod, Adam Kirsch, and others) consider it one of Lowell's most important books, and the Academy of American Poets named it one of their ''Groundbreaking Books.'' Helen Vendler called ''Life Studies'' Lowell's "most original book." It won the National Book Award for Poetry in 1960."National Book Awards – 1960" . Retrieved 2012-02-25. (With acceptance speech by Lowell and essay by Dilruba Ahmed from the Awards 60-year anniversary blog.) Publication ''Life Studies'' was first published i ...[...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Confessional Poetry
Confessional poetry or "Confessionalism" is a style of poetry that emerged in the United States during the late 1950s and early 1960s. It is sometimes classified as a form of Postmodernism. It has been described as poetry of the personal or "I", focusing on extreme moments of individual experience, the psyche, and personal trauma, including previously and occasionally still taboo matters such as mental illness, sexuality, and suicide, often set in relation to broader social themes.Ousby 1998, pp 89 The confessional poet's engagement with personal experience has been explained by literary critics as an effort to distance oneself from the horrifying social realities of the twentieth century. Events like the Holocaust, the Cold War, and existential threat brought by the proliferation of nuclear weapons had made public matters daunting for both confessional poets and their readers. The confessional poets also worked in opposition to the idealization of domesticity in the 1950s, by rev ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Al Alvarez
Alfred Alvarez (5 August 1929 – 23 September 2019) was an English poet, novelist, essayist and critic who published under the name A. Alvarez and Al Alvarez. Background Alfred Alvarez was born in London, to an Ashkenazic Jewish mother and a father from a Sephardic Jewish family. He was educated at The Hall School in Hampstead, London, and then Oundle School and Corpus Christi College, Oxford, where he took a First in English. He was subsequently elected as a Jane Eliza Procter Visiting Fellow at Princeton University. After teaching briefly in Oxford and the United States, he became a full-time writer in his late twenties. From 1956 to 1966, he was the poetry editor and critic for ''The Observer'', where he introduced British readers to John Berryman, Robert Lowell, Sylvia Plath, Zbigniew Herbert, and Miroslav Holub. Alvarez was the author of many non-fiction books. His renowned study of suicide, '' The Savage God'', gained added resonance from his friendship with Plath. He ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Ian Hamilton (critic)
Robert Ian Hamilton (24 March 1938 – 27 December 2001) was a British literary critic, reviewer, biographer, poet, magazine editor and publisher. Early life and education He was born in King's Lynn, Norfolk. His parents were Scottish and had moved to Norfolk in 1936. The family moved to Darlington in 1951. Hamilton's civil engineer father died a few months later. A keen soccer player, at the age of 15 Hamilton was diagnosed with a heart complaint. Unable to play games, he developed his interest in poetry. At the age of 17, in sixth form at Darlington Grammar School, Hamilton produced two issues of his own magazine, which was called ''The Scorpion''. For the second issue he sent a questionnaire to various literary figures in London asking if there was any advice they could give young authors. Around 50 or so replies were received from figures such as Louis Golding. After leaving school, Hamilton did his National Service in Mönchengladbach, Germany. He then attended Keble Coll ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Partisan Review
''Partisan Review'' (''PR'') was a small-circulation quarterly "little magazine" dealing with literature, politics, and cultural commentary published in New York City. The magazine was launched in 1934 by the Communist Party USA–affiliated John Reed Club of New York and was initially part of the Communist political orbit. Growing disaffection on the part of ''PR''s primary editors began to make itself felt, and the magazine abruptly suspended publication in the fall of 1936. When the magazine reemerged late in 1937, it came with additional editors and new writers who advanced a political line deeply critical of Joseph Stalin's Soviet Union. By the 1950s, the magazine had evolved towards a moderate social democratic and staunchly anti-Stalinist perspective and was generally supportive of American foreign policy. ''Partisan Review'' received covert funding from the Central Intelligence Agency (CIA) during the 1950s and 1960s as part of the agency's efforts to shape intellectual op ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Elizabeth Bishop
Elizabeth Bishop (February 8, 1911 – October 6, 1979) was an American people, American poet and short-story writer. She was Consultant in Poetry to the Library of Congress from 1949 to 1950, the Pulitzer Prize winner for Poetry in 1956, the National Book Award winner in 1970, and the recipient of the Neustadt International Prize for Literature in 1976. Dwight Garner argued that she was perhaps "the most purely gifted poet of the 20th century". Early life Bishop, an only child, was born in Worcester, Massachusetts, to William Thomas and Gertrude May (Bulmer) Bishop. After her father, a successful builder, died when she was eight months old, Bishop's mother became mentally ill and was institutionalized in 1916. (Bishop would later write about the time of her mother's struggles in her short story "In the Village".) [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Stanza
In poetry, a stanza (; from Italian language, Italian ''stanza'' , "room") is a group of lines within a poem, usually set off from others by a blank line or Indentation (typesetting), indentation. Stanzas can have regular rhyme scheme, rhyme and Metre (poetry), metrical schemes, but they are not required to have either. There are many different : Stanzaic form, forms of stanzas. Some stanzaic forms are simple, such as four-line quatrains. Other forms are more complex, such as the Spenserian stanza. Fixed verse, Fixed verse poems, such as sestinas, can be defined by the number and form of their stanzas. The stanza has also been known by terms such as ''batch'', ''fit'', and ''stave''. The term ''stanza'' has a similar meaning to ''strophe'', though ''strophe'' sometimes refers to an irregular set of lines, as opposed to regular, rhymed stanzas. Even though the term "stanza" is taken from Italian, in the Italian language the word "strofa" is more commonly used. In music, groups of ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
The New Testament
The New Testament grc, Ἡ Καινὴ Διαθήκη, transl. ; la, Novum Testamentum. (NT) is the second division of the Christian biblical canon. It discusses the teachings and person of Jesus, as well as events in first-century Christianity. The New Testament's background, the first division of the Christian Bible, is called the Old Testament, which is based primarily upon the Hebrew Bible; together they are regarded as sacred scripture by Christians. The New Testament is a collection of Christian texts originally written in the Koine Greek language, at different times by various authors. While the Old Testament canon varies somewhat between different Christian denominations, the 27-book canon of the New Testament has been almost universally recognized within Christianity since at least Late Antiquity. Thus, in almost all Christian traditions today, the New Testament consists of 27 books: * 4 canonical gospels (Matthew, Mark, Luke, and John) * The Acts of the Apostles ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
John Milton
John Milton (9 December 1608 – 8 November 1674) was an English poet and intellectual. His 1667 epic poem '' Paradise Lost'', written in blank verse and including over ten chapters, was written in a time of immense religious flux and political upheaval. It addressed the fall of man, including the temptation of Adam and Eve by the fallen angel Satan and God's expulsion of them from the Garden of Eden. ''Paradise Lost'' is widely considered one of the greatest works of literature ever written, and it elevated Milton's widely-held reputation as one of history's greatest poets. He also served as a civil servant for the Commonwealth of England under its Council of State and later under Oliver Cromwell. Writing in English, Latin, and Italian, Milton achieved global fame and recognition during his lifetime; his celebrated ''Areopagitica'' (1644), written in condemnation of pre-publication censorship, is among history's most influential and impassioned defences of freedom of spe ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Paradise Lost
''Paradise Lost'' is an epic poem in blank verse by the 17th-century English poet John Milton (1608–1674). The first version, published in 1667, consists of ten books with over ten thousand lines of verse (poetry), verse. A second edition followed in 1674, arranged into twelve books (in the manner of Virgil's ''Aeneid'') with minor revisions throughout. It is considered to be Milton's masterpiece, and it helped solidify his reputation as one of the greatest English poets of all time. The poem concerns the The Bible, biblical story of the Fall of Man: the temptation of Adam and Eve by the fallen angel Satan and their expulsion from the Garden of Eden. Composition In his introduction to the Penguin Books, Penguin edition of ''Paradise Lost'', the Milton scholar John Leonard notes, "John Milton was nearly sixty when he published ''Paradise Lost'' in 1667. The biographer John Aubrey (1626–1697) tells us that the poem was begun in about 1658 and finished in about 1663. However, ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Careless Love
"Careless Love" is a traditional song, with several popular blues versions. It has been called a "nineteenth-century ballad and Dixieland standard". The death referenced in an old version was the son of a Kentucky governor. Although published accounts have cited 1926 as the copyright date, W. C. Handy copyrighted "Loveless Love" in 1921 under Pace & Handy Music Co. A recording by Bessie Smith titled "Careless Love Blues" was very popular in 1925. The same year it was recorded by Papa Celestin and his Tuxedo Dixieland Jazz Band and released as a single by OKeh. New Orleans cornetist Chris Kelly was famous for his emotional rendition of the piece. Many other artists have recorded "Careless Love" including Lonnie Johnson (musician), Dr. John, Brook Benton, Connie Francis, Dinah Washington, Snooks Eaglin, Fats Domino, Frankie Laine, Madeleine Peyroux, Nat King Cole, Ray Charles, Rosemary Clooney, Shirley Bassey and Ronnie Lane. Noh Sa-yeon released a Korean version of this song, "Nim ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |