|
Sir Hugh Willoughby
Sir Hugh Willoughby (fl. 1544; died 1554) was an English soldier and an early Arctic voyager. He served in the court of and fought in the Scottish campaign where he was knighted for his valour. In 1553, he was selected by a company of London merchants to lead a fleet of three vessels in search of a Northeast Passage. Willoughby and the crews of two ships died on the voyage while the third vessel , under the command of Richard Chancellor, went on to open a successful, long-lasting trading arrangement with Russia. Biography Willoughby was the third and youngest son of Sir Henry Willoughby of Middleton, Derbyshire, a wealthy and influential gentleman who served in the courts of Richard III and Henry VII and was knighted by Henry VII following the Battle of Stoke Field in 1487. Hugh Willoughby served various roles in the court of Henry VIIIEvans 2014 and then joined the military to serve as a captain in the Scottish campaign of 1544. He was knighted at Leith by Edward Seymour, ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Sir Hugh Willoughby
Sir Hugh Willoughby (fl. 1544; died 1554) was an English soldier and an early Arctic voyager. He served in the court of and fought in the Scottish campaign where he was knighted for his valour. In 1553, he was selected by a company of London merchants to lead a fleet of three vessels in search of a Northeast Passage. Willoughby and the crews of two ships died on the voyage while the third vessel , under the command of Richard Chancellor, went on to open a successful, long-lasting trading arrangement with Russia. Biography Willoughby was the third and youngest son of Sir Henry Willoughby of Middleton, Derbyshire, a wealthy and influential gentleman who served in the courts of Richard III and Henry VII and was knighted by Henry VII following the Battle of Stoke Field in 1487. Hugh Willoughby served various roles in the court of Henry VIIIEvans 2014 and then joined the military to serve as a captain in the Scottish campaign of 1544. He was knighted at Leith by Edward Seymour, ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
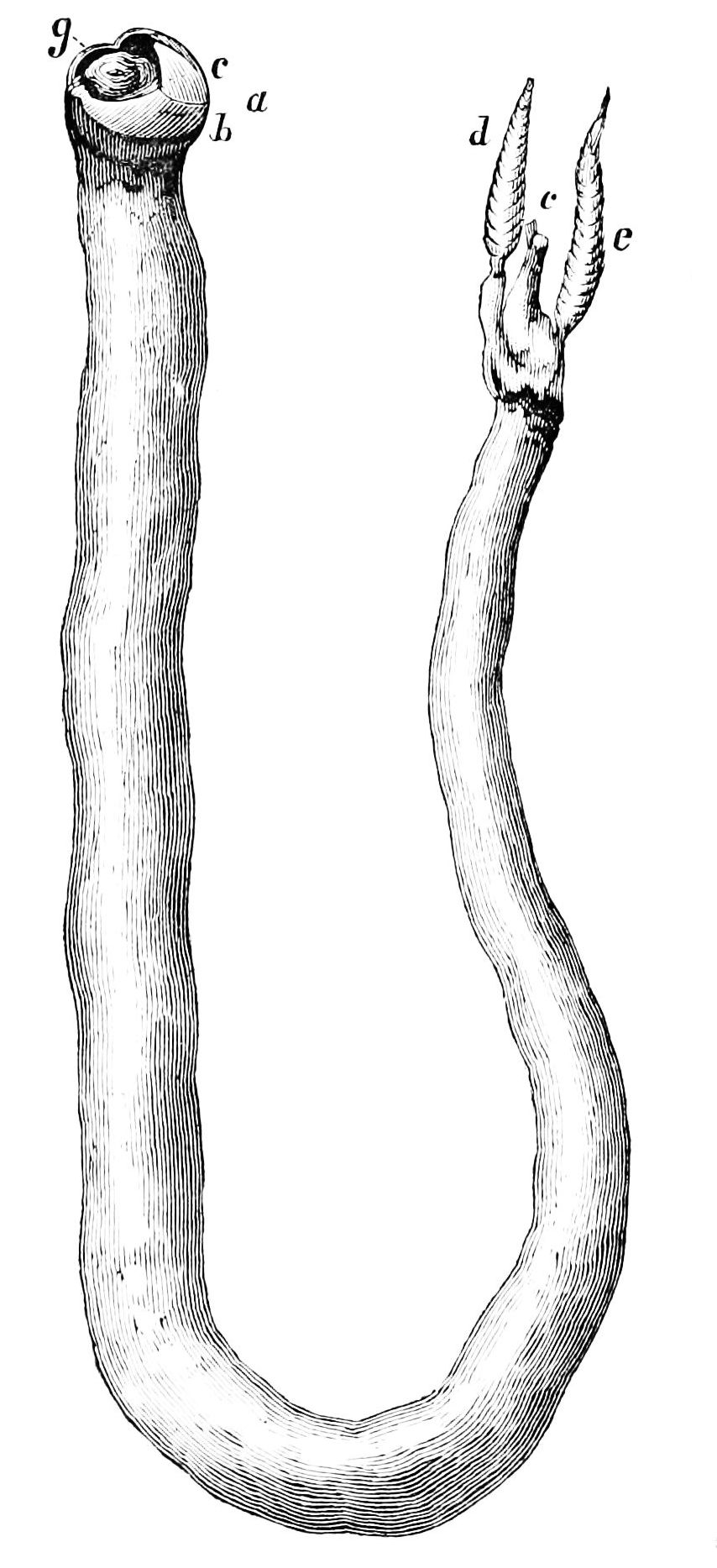
Shipworms
The shipworms are marine bivalve molluscs in the family Teredinidae: a group of saltwater clams with long, soft, naked bodies. They are notorious for boring into (and commonly eventually destroying) wood that is immersed in sea water, including such structures as wooden piers, docks and ships; they drill passages by means of a pair of very small shells (“valves”) borne at one end, with which they rasp their way through. Sometimes called "termites of the sea", they also are known as " Teredo worms" or simply Teredo (from grc, τερηδών, , translit=terēdṓn, lit=wood-worm via ). Carl Linnaeus assigned the common name '' Teredo'' to the best-known genus of shipworms in the 10th edition of his taxonomic ''magnum opus'', '' Systema Naturæ'' (1758). Description Removed from its burrow, the fully grown teredo ranges from several centimetres to about a metre in length, depending on the species. The body is cylindrical, slender, naked and superficially vermiform, meaning "w ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Russian Tsardom
The Tsardom of Russia or Tsardom of Rus' also externally referenced as the Tsardom of Muscovy, was the centralized Russian state from the assumption of the title of Tsar by Ivan IV in 1547 until the foundation of the Russian Empire by Peter I in 1721. From 1551 to 1700, Russia grew by 35,000 km2 per year. The period includes the upheavals of the transition from the Rurik to the Romanov dynasties, wars with the Polish–Lithuanian Commonwealth, Sweden and the Ottoman Empire, and the Russian conquest of Siberia, to the reign of Peter the Great, who took power in 1689 and transformed the Tsardom into the Russian Empire. During the Great Northern War, he implemented substantial reforms and proclaimed the Russian Empire after victory over Sweden in 1721. Name While the oldest endonyms of the Grand Duchy of Moscow used in its documents were "Rus'" () and the "Russian land" (), a new form of its name, ''Rusia'' or ''Russia'', appeared and became common in the 15th century. In ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Ivan The Terrible
Ivan IV Vasilyevich (russian: Ива́н Васи́льевич; 25 August 1530 – ), commonly known in English as Ivan the Terrible, was the grand prince of Moscow from 1533 to 1547 and the first Tsar of all Russia from 1547 to 1584. Ivan was the son of Vasili III, the Rurikid ruler of the Grand Duchy of Moscow. He was appointed grand prince after his father's death, when he was three years old. A group of reformers known as the "Chosen Council" united around the young Ivan, declaring him tsar (emperor) of all Rus' in 1547 at the age of 16 and establishing the Tsardom of Russia with Moscow as the predominant state. Ivan's reign was characterised by Russia's transformation from a medieval state to an empire under the tsar but at an immense cost to its people and its broader, long-term economy. During his youth, he conquered the khanates of Kazan and Astrakhan. After he had consolidated his power, Ivan rid himself of the advisers from the "Chosen Council" and triggered the ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Moscow
Moscow ( , US chiefly ; rus, links=no, Москва, r=Moskva, p=mɐskˈva, a=Москва.ogg) is the capital and largest city of Russia. The city stands on the Moskva River in Central Russia, with a population estimated at 13.0 million residents within the city limits, over 17 million residents in the urban area, and over 21.5 million residents in the metropolitan area. The city covers an area of , while the urban area covers , and the metropolitan area covers over . Moscow is among the world's largest cities; being the most populous city entirely in Europe, the largest urban and metropolitan area in Europe, and the largest city by land area on the European continent. First documented in 1147, Moscow grew to become a prosperous and powerful city that served as the capital of the Grand Duchy that bears its name. When the Grand Duchy of Moscow evolved into the Tsardom of Russia, Moscow remained the political and economic center for most of the Tsardom's history. When th ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Salt Production
Salt is a mineral composed primarily of sodium chloride (NaCl), a chemical compound belonging to the larger class of salts; salt in the form of a natural crystalline mineral is known as rock salt or halite. Salt is present in vast quantities in seawater. The open ocean has about of solids per liter of sea water, a salinity of 3.5%. Salt is essential for life in general, and saltiness is one of the basic human tastes. Salt is one of the oldest and most ubiquitous food seasonings, and is known to uniformly improve the taste perception of food, including otherwise unpalatable food. Salting, brining, and pickling are also ancient and important methods of food preservation. Some of the earliest evidence of salt processing dates to around 6,000 BC, when people living in the area of present-day Romania boiled spring water to extract salts; a salt-works in China dates to approximately the same period. Salt was also prized by the ancient Hebrews, Greeks, Romans, Byzantines, Hi ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Nyonoksa
Nyonoksa, also Nenoksa, (russian: Нёнокса ) is a rural locality (a '' selo'') under the administrative jurisdiction of Severodvinsk Town of Oblast Significance, Arkhangelsk Oblast, Russia. It is located at the coast of the Dvina Bay of the White Sea (the Summer Coast) northwest of the city of Severodvinsk. The Nyonoksa railway station is from Nyonoksa at the mostly military village of Sopka along the Northern Railway line from Severodvinsk. Nyonoksa is accessible by land vehicles only during the winter months when the nearby swampland freezes. Missile testing site Established in 1954 near Nyonoksa is “The State Central Navy Testing Range” (russian: «Государственный центральный морской полигон») which is the main rocket launching site of the Soviet Navy and later the Russian Navy and is also called Nyonoksa. Since 1965 numerous rockets of the types R-27, R-29, R-39 Rif and R-39M were launched from Nyonoksa. These rock ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
White Sea
The White Sea (russian: Белое море, ''Béloye móre''; Karelian and fi, Vienanmeri, lit. Dvina Sea; yrk, Сэрако ямʼ, ''Serako yam'') is a southern inlet of the Barents Sea located on the northwest coast of Russia. It is surrounded by Karelia to the west, the Kola Peninsula to the north, and the Kanin Peninsula to the northeast. The whole of the White Sea is under Russian sovereignty and considered to be part of the internal waters of Russia.A. D. Dobrovolskyi and B. S. Zalogi"Seas of USSR. White Sea" Moscow University (1982) (in Russian) Administratively, it is divided between Arkhangelsk and Murmansk oblasts and the Republic of Karelia. The major port of Arkhangelsk is located on the White Sea. For much of Russia's history this was Russia's main centre of international maritime trade, conducted by the Pomors ("seaside settlers") from Kholmogory. In the modern era it became an important Soviet naval and submarine base. The White Sea–Baltic Canal connec ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
North Cape, Norway
North Cape ( no, Nordkapp; sme, Davvenjárga) is a cape on the northern coast of the island of Magerøya in Northern Norway. The cape is in Nordkapp Municipality in Troms og Finnmark county, Norway. The European route E69 highway has its northern terminus at North Cape, which makes it the northernmost point in Europe that can be accessed by car and makes the E69 the northernmost public road in Europe. The plateau is a popular tourist attraction. The cape includes a with a large flat plateau on top, where visitors, weather permitting, can watch the midnight sun and views of the Barents Sea to the north. North Cape Hall, a visitor centre, was built in 1988 on the plateau. It includes a café, restaurant, post office, souvenir shop, a small museum, and video cinema. Geography The steep cliff of the North Cape is located at , about from the North Pole. Nordkapp is often inaccurately referred to as the northernmost point of Europe. However, the neighbouring Knivskjellodden Cape a ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Vardø
( fi, Vuoreija, fkv, Vuorea, se, Várggát) is a municipality in Troms og Finnmark county in the extreme northeastern part of Norway. Vardø is the easternmost town in Norway, more to the east than Saint Petersburg or Istanbul. The administrative centre of the municipality is the town of Vardø. Two of the larger villages in the municipality are Kiberg and Svartnes. The municipality is the 189th largest by area out of the 356 municipalities in Norway. Vardø is the 284th most populous municipality in Norway with a population of 1,897. The municipality's population density is and its population has decreased by 10.6% over the previous 10-year period. General information The town of Vardø and the rural district around it was established as a municipality on 1 January 1838 (see formannskapsdistrikt law). The law required that all towns be separated from their rural districts, but because of a low population and very few voters, this was impossible to carry out for Vardø in ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Vardøhus Fortress
Vardøhus Fortress ( no, Vardøhus festning) is located in Vardø Municipality in Troms og Finnmark county, Norway. It is located in the town of Vardø on the island of Vardøya on the Barents Sea near the mouth of the Varangerfjord in northeastern Norway near the Russian border. History In 1251, an embassy from the Republic of Novgorod to King Haakon IV Haakonson of Norway complained of clashes between the Norwegians and the Karelians in northern Finnmark. A Norwegian embassy was dispatched to Novgorod where a treaty (the original of which is now lost) was signed to conclude a peace between the two countries, including the Novgorod tributary land of Karelia.Stagg 1952: p. 61-63 The Finnmark coast was originally important as a source of furs from the trade with the Karelians, but this trade dropped off as the Hanseatic League increased the fur trade through their Novgorod centre. Finnmark remained important as a fishery; the fish was shipped as stockfish to Bergen and traded the ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Edward VI
Edward VI (12 October 1537 – 6 July 1553) was King of England and Ireland from 28 January 1547 until his death in 1553. He was crowned on 20 February 1547 at the age of nine. Edward was the son of Henry VIII and Jane Seymour and the first English monarch to be raised as a Protestant. During his reign, the realm was governed by a regency council because he never reached maturity. The council was first led by his uncle Edward Seymour, 1st Duke of Somerset (1547–1549), and then by John Dudley, 1st Earl of Warwick (1550–1553), who from 1551 was Duke of Northumberland. Edward's reign was marked by economic problems and social unrest that in 1549 erupted into riot and rebellion. An expensive war with Scotland, at first successful, ended with military withdrawal from Scotland and Boulogne-sur-Mer in exchange for peace. The transformation of the Church of England into a recognisably Protestant body also occurred under Edward, who took great interest in religious matters. His fat ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |