|
Sinomacrops
''Sinomacrops'' is a genus of extinct anurognathid pterosaur from the Middle to Late Jurassic periods of what is now the Daohugou Beds of the Tiaojishan Formation in Mutoudeng, Qinglong County of the Hebei province. The remains of ''Sinomacrops'' date back to around 164 to 158 million years ago. The type and only known species is ''Sinomacrops bondei''. Etymology ''Sinomacrops'' derives from the Ancient Greek word roots ''Sino~'', referring to China, ''macro~'' (''makros''), meaning large, and ''ops'', meaning eyes/face. The name ''Sinomacrops'' is in reference to both the large eyes of and the broad faces that are typical of the family Anurognathidae, as well as to the Chinese origin of the animal. The specific name, ''bondei'', honors paleontologist Niels Bonde. Description ''Sinomacrops'' exhibits two autapomorphies (distinguishing traits) that distinguish it from other pterosaurs: one of them is having the first three maxillary alveoli (tooth sockets) closely spaced, and ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Sinomacrops Foot
''Sinomacrops'' is a genus of extinct anurognathid pterosaur from the Middle to Late Jurassic periods of what is now the Daohugou Beds of the Tiaojishan Formation in Mutoudeng, Qinglong County of the Hebei province. The remains of ''Sinomacrops'' date back to around 164 to 158 million years ago. The type and only known species is ''Sinomacrops bondei''. Etymology ''Sinomacrops'' derives from the Ancient Greek word roots ''Sino~'', referring to China, ''macro~'' (''makros''), meaning large, and ''ops'', meaning eyes/face. The name ''Sinomacrops'' is in reference to both the large eyes of and the broad faces that are typical of the family Anurognathidae, as well as to the Chinese origin of the animal. The specific name, ''bondei'', honors paleontologist Niels Bonde. Description ''Sinomacrops'' exhibits two autapomorphies (distinguishing traits) that distinguish it from other pterosaurs: one of them is having the first three maxillary alveoli (tooth sockets) closely spaced, and ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Tiaojishan Formation
The Tiaojishan Formation is a geological formation in Hebei and Liaoning, People's Republic of China, dating to the middle-late Jurassic period (Bathonian- Oxfordian stages). It is known for its exceptionally preserved fossils, including those of plants, insects and vertebrates. It is made up mainly of pyroclastic rock interspersed with basic volcanic and sedimentary rocks. Previously, the Tiaojishan Formation was grouped together with the underlying Haifanggou Formation (also known as the Jiulongshan Formation) as a single "Lanqi Formation." The Tiaojishan Formation forms a key part of the Yanliao Biota assemblage, alongside the Haifanggou Formation. Age Using Argon–argon dating, Wang and colleagues in 2005 dated part of the Tiaojishan Formation to about 160 million years ago, the beginning of the Oxfordian stage, the first stage of the Upper Jurassic epoch. In 2006, a study by Liu and colleagues used U-Pb zircon dating to conclude that the Tiaojishan Formation correlates wi ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Anurognathidae
Anurognathidae is a family (biology), family of small, short-tailed pterosaurs that lived in Europe, Asia, and possibly North America during the Jurassic and Cretaceous periods. Five genera are known: ''Anurognathus'', from the Late Jurassic of Germany; ''Jeholopterus'', from the Middle Jurassic, Middle to Late Jurassic of China; ''Dendrorhynchoides'', from the Middle Jurassic of China; ''Batrachognathus'', from the Late Jurassic of Kazakhstan; and ''Vesperopterylus'', from the Early Cretaceous of China. Bennett (2007) suggested that the holotype of ''Mesadactylus'', Brigham Young University Museum of Paleontology, BYU 2024, a synsacrum, belonged to an anurognathid, though this affinity has been questioned by other authors. ''Mesadactylus'' is from the Late Jurassic Morrison Formation of the United States. Indeterminate anurognathid remains have also been reported from the Middle Jurassic Bakhar Svita of Mongolia and the Early Cretaceous of North Korea. Classification A family A ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
2021 In Archosaur Paleontology
This article records new taxa of fossil archosaurs of every kind that are scheduled binomial nomenclature, described during the year 2021, as well as other significant discoveries and events related to paleontology of archosaurs that are scheduled to occur in the year 2021. General research * A study on the relationship between full potential joint mobility and the poses used during locomotion in extant American alligator and helmeted guineafowl, evaluating its implications for reconstructions of locomotion of extinct archosaurs, is published by Manafzadeh, Kambic & Gatesy (2021). * A study on the Femur, femoral shape variation and on the relationship between femoral morphology and locomotor habits in early archosaurs and non-archosaur Archosauriformes, archosauriforms is published by Pintore ''et al.'' (2021). * A study estimating moment arms for major Pelvis, pelvic limb muscles in extant and fossil archosaurs, aiming to investigate the idea that bird-line archosaurs switched fr ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Anurognathid
Anurognathidae is a family of small, short-tailed pterosaurs that lived in Europe, Asia, and possibly North America during the Jurassic and Cretaceous periods. Five genera are known: ''Anurognathus'', from the Late Jurassic of Germany; ''Jeholopterus'', from the Middle to Late Jurassic of China; ''Dendrorhynchoides'', from the Middle Jurassic of China; ''Batrachognathus'', from the Late Jurassic of Kazakhstan; and ''Vesperopterylus'', from the Early Cretaceous of China. Bennett (2007) suggested that the holotype of ''Mesadactylus'', BYU 2024, a synsacrum, belonged to an anurognathid, though this affinity has been questioned by other authors. ''Mesadactylus'' is from the Late Jurassic Morrison Formation of the United States. Indeterminate anurognathid remains have also been reported from the Middle Jurassic Bakhar Svita of Mongolia and the Early Cretaceous of North Korea. Classification A family Anurognathidae was named in 1928 by Franz Nopcsa von Felső-Szilvás (as the subfa ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Autapomorphies
In phylogenetics, an autapomorphy is a distinctive feature, known as a derived trait, that is unique to a given taxon. That is, it is found only in one taxon, but not found in any others or outgroup taxa, not even those most closely related to the focal taxon (which may be a species, family or in general any clade). It can therefore be considered an apomorphy in relation to a single taxon. The word ''autapomorphy'', first introduced in 1950 by German entomologist Willi Hennig, is derived from the Greek words αὐτός, ''autos'' "self"; ἀπό, ''apo'' "away from"; and μορφή, ''morphḗ'' = "shape". Discussion Because autapomorphies are only present in a single taxon, they do not convey information about relationship. Therefore, autapomorphies are not useful to infer phylogenetic relationships. However, autapomorphy, like synapomorphy and plesiomorphy is a relative concept depending on the taxon in question. An autapomorphy at a given level may well be a synapomorphy at ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
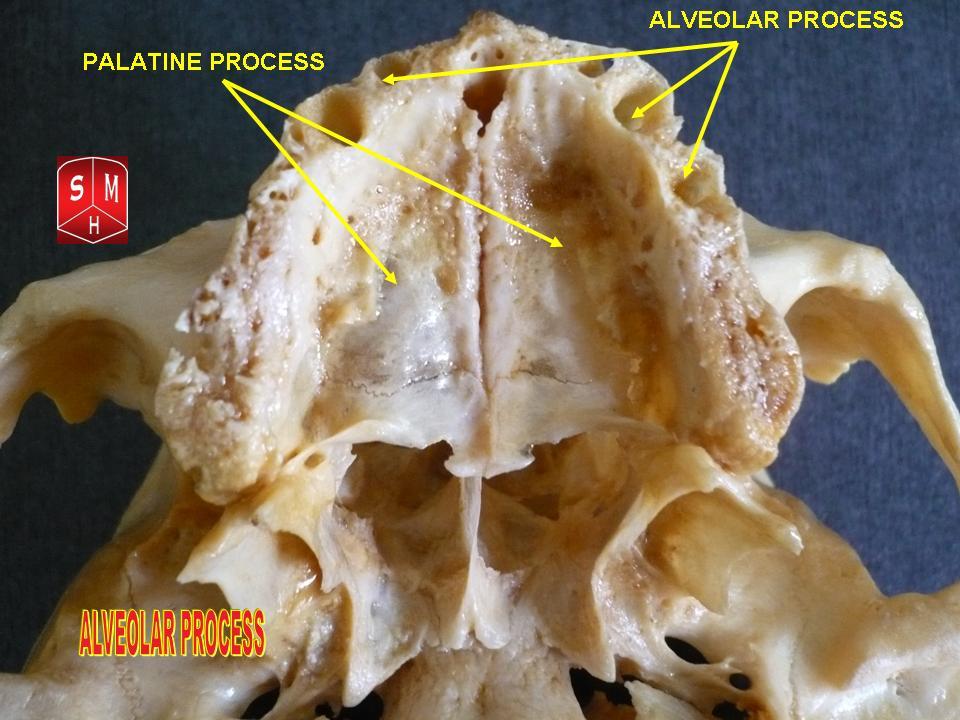
Maxilla
The maxilla (plural: ''maxillae'' ) in vertebrates is the upper fixed (not fixed in Neopterygii) bone of the jaw formed from the fusion of two maxillary bones. In humans, the upper jaw includes the hard palate in the front of the mouth. The two maxillary bones are fused at the intermaxillary suture, forming the anterior nasal spine. This is similar to the mandible (lower jaw), which is also a fusion of two mandibular bones at the mandibular symphysis. The mandible is the movable part of the jaw. Structure In humans, the maxilla consists of: * The body of the maxilla * Four processes ** the zygomatic process ** the frontal process of maxilla ** the alveolar process ** the palatine process * three surfaces – anterior, posterior, medial * the Infraorbital foramen * the maxillary sinus * the incisive foramen Articulations Each maxilla articulates with nine bones: * two of the cranium: the frontal and ethmoid * seven of the face: the nasal, zygomatic, lacrimal, inferior n ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Dental Alveolus
Dental alveoli (singular ''alveolus'') are sockets in the jaws in which the roots of teeth are held in the alveolar process with the periodontal ligament. The lay term for dental alveoli is tooth sockets. A joint that connects the roots of the teeth and the alveolus is called ''gomphosis'' (plural ''gomphoses''). Alveolar bone is the bone that surrounds the roots of the teeth forming bone sockets. In mammals, tooth sockets are found in the maxilla, the premaxilla, and the mandible. Etymology 1706, "a hollow," especially "the socket of a tooth," from Latin alveolus "a tray, trough, basin; bed of a small river; small hollow or cavity," diminutive of alvus "belly, stomach, paunch, bowels; hold of a ship," from PIE root *aulo- "hole, cavity" (source also of Greek aulos "flute, tube, pipe;" Serbo-Croatian, Polish, Russian ulica "street," originally "narrow opening;" Old Church Slavonic uliji, Lithuanian aulys "beehive" (hollow trunk), Armenian yli "pregnant"). The word was extended in ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Tibiotarsus
The tibiotarsus is the large bone between the femur and the tarsometatarsus in the leg of a bird. It is the fusion of the proximal part of the tarsus with the tibia. A similar structure also occurred in the Mesozoic Heterodontosauridae. These small ornithischian dinosaurs were unrelated to birds and the similarity of their foot bones is best explained by convergent evolution. See also *Bird anatomy References * Proctor, Nobel S. ''Manual of Ornithology: Avian Structure and Function''. Yale University Press Yale University Press is the university press of Yale University. It was founded in 1908 by George Parmly Day, and became an official department of Yale University in 1961, but it remains financially and operationally autonomous. , Yale Universi .... (1993) Bird anatomy {{ornithology-stub ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Holotype
A holotype is a single physical example (or illustration) of an organism, known to have been used when the species (or lower-ranked taxon) was formally described. It is either the single such physical example (or illustration) or one of several examples, but explicitly designated as the holotype. Under the International Code of Zoological Nomenclature (ICZN), a holotype is one of several kinds of name-bearing types. In the International Code of Nomenclature for algae, fungi, and plants (ICN) and ICZN, the definitions of types are similar in intent but not identical in terminology or underlying concept. For example, the holotype for the butterfly '' Plebejus idas longinus'' is a preserved specimen of that subspecies, held by the Museum of Comparative Zoology at Harvard University. In botany, an isotype is a duplicate of the holotype, where holotype and isotypes are often pieces from the same individual plant or samples from the same gathering. A holotype is not necessarily "typ ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Femur
The femur (; ), or thigh bone, is the proximal bone of the hindlimb in tetrapod vertebrates. The head of the femur articulates with the acetabulum in the pelvic bone forming the hip joint, while the distal part of the femur articulates with the tibia (shinbone) and patella (kneecap), forming the knee joint. By most measures the two (left and right) femurs are the strongest bones of the body, and in humans, the largest and thickest. Structure The femur is the only bone in the upper leg. The two femurs converge medially toward the knees, where they articulate with the proximal ends of the tibiae. The angle of convergence of the femora is a major factor in determining the femoral-tibial angle. Human females have thicker pelvic bones, causing their femora to converge more than in males. In the condition ''genu valgum'' (knock knee) the femurs converge so much that the knees touch one another. The opposite extreme is ''genu varum'' (bow-leggedness). In the general populatio ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Specific Name (zoology)
In zoological nomenclature, the specific name (also specific epithet or species epithet) is the second part (the second name) within the scientific name of a species (a binomen). The first part of the name of a species is the name of the genus or the generic name. The rules and regulations governing the giving of a new species name are explained in the article species description. For example, the scientific name for humans is ''Homo sapiens'', which is the species name, consisting of two names: ''Homo'' is the " generic name" (the name of the genus) and ''sapiens'' is the "specific name". Historically, ''specific name'' referred to the combination of what are now called the generic and specific names. Carl Linnaeus, who formalized binomial nomenclature, made explicit distinctions between specific, generic, and trivial names. The generic name was that of the genus, the first in the binomial, the trivial name was the second name in the binomial, and the specific the proper term for ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |