|
Sina-1
''Sina-1'' ( fa, سینا ۱) is the first Iranian artificial satellite, launched at 6:52 UTC October 28, 2005 on board a Cosmos-3M Russian launch vehicle from the Plesetsk Cosmodrome. The rocket was also carrying a Russian military Mozhayets-5 satellite, a Chinese China-DMC, a British TopSat, a European Space Agency SSETI Express (Student Space Exploration and Technology Initiative-Express), a Norwegian nCube, a German UWE-1, and a Japanese XI-V. Sina-1 Satellite Catalog Number or USSPACECOM object number is 28893 . In 2003, then-Defense Minister Admiral Ali Shamkhani announced that Iran would launch its first satellite on a locally produced launch vehicle within eighteen months. The plan was to develop a booster based on the Shahab-3 medium-range ballistic missile. When difficulties arose with indigenous booster development, the Iranian Institute of Applied Research turned to the Omsk-based Russian company Polyot. Polyot provided the launch services aboard the Kosmos ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Iranian Space Agency
The Iranian Space Agency (ISA, Persian language, Persian: ''Sāzmān-e Fazāi-ye Irān'') is Iran's Government of Iran, governmental space agency. Iran became an Timeline of first orbital launches by country, orbital-launch-capable nation in 2009. Iran is one of the 24 founding members of the United Nations Committee on the Peaceful Uses of Outer Space (COPUOS), which was set up on 13 December 1958. History ISA was established on 28 February 2004, according to the Article 9 of the Law for Tasks and Authorizations of the Ministry of Information and Communications Technology of Iran, Ministry of Communications and Information Technology passed on 10 December 2003 by the Parliament of Iran. Based on the approved statute ISA mandated to cover and support all the activities in Iran concerning the peaceful applications of space science and technology under the leadership of a Supreme Council of Space chaired by the President of Iran. The council's main goals included policy makin ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
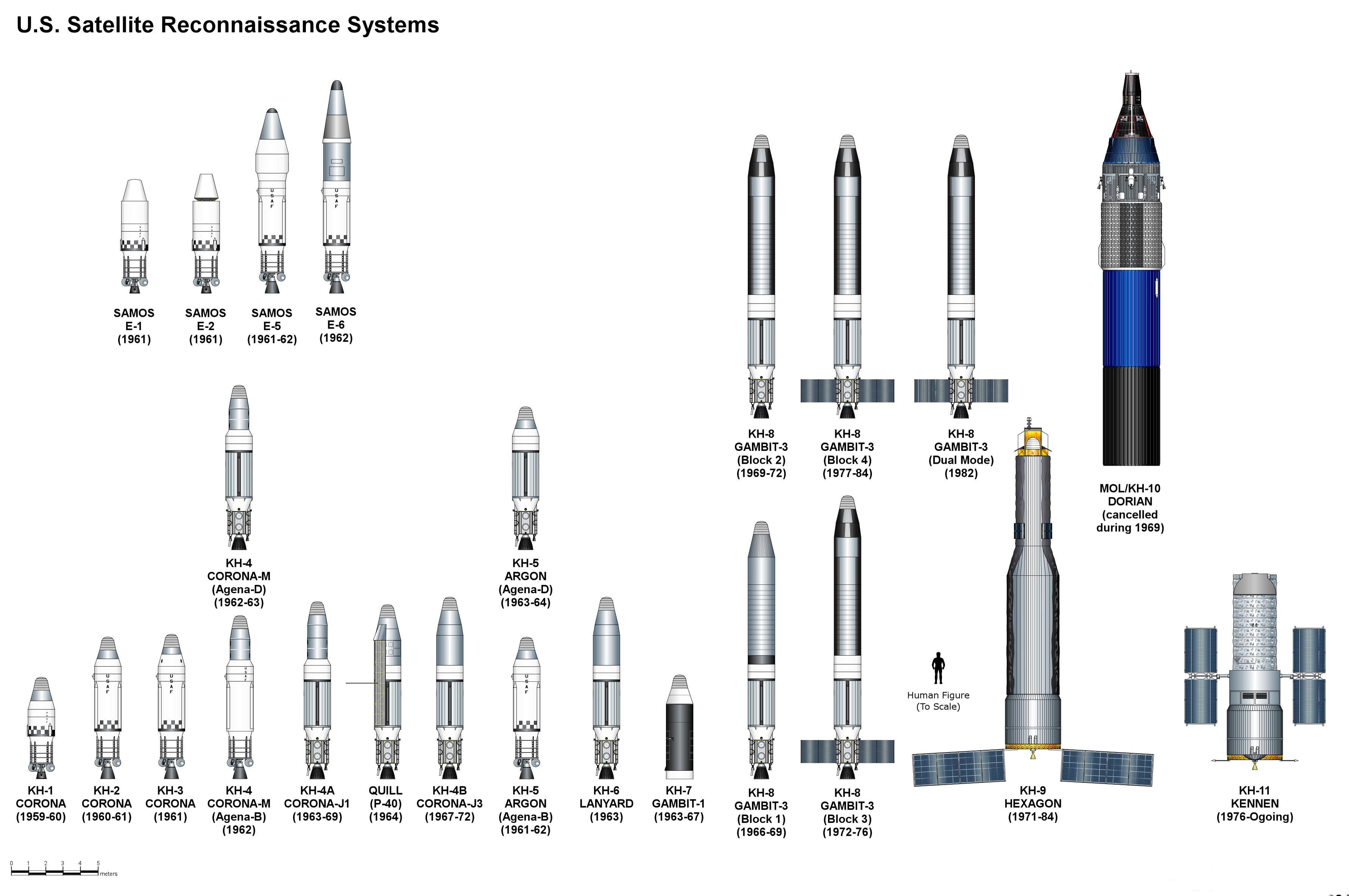
Reconnaissance Satellite
A reconnaissance satellite or intelligence satellite (commonly, although unofficially, referred to as a spy satellite) is an Earth observation satellite or communications satellite deployed for military or intelligence applications. The first generation type (i.e., Corona and Zenit) took photographs, then ejected canisters of photographic film which would descend back down into Earth's atmosphere. Corona capsules were retrieved in mid-air as they floated down on parachutes. Later, spacecraft had digital imaging systems and downloaded the images via encrypted radio links. In the United States, most information available about reconnaissance satellites is on programs that existed up to 1972, as this information has been declassified due to its age. Some information about programs before that time is still classified information, and a small amount of information is available on subsequent missions. A few up-to-date reconnaissance satellite images have been declassified o ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Miniaturized Satellite
A small satellite, miniaturized satellite, or smallsat is a satellite of low mass and size, usually under . While all such satellites can be referred to as "small", different classifications are used to categorize them based on mass. Satellites can be built small to reduce the large economic cost of launch vehicles and the costs associated with construction. Miniature satellites, especially in large numbers, may be more useful than fewer, larger ones for some purposes – for example, gathering of scientific data and radio relay. Technical challenges in the construction of small satellites may include the lack of sufficient power storage or of room for a propulsion system. Rationales One rationale for miniaturizing satellites is to reduce the cost; heavier satellites require larger rockets with greater thrust that also have greater cost to finance. In contrast, smaller and lighter satellites require smaller and cheaper launch vehicles and can sometimes be launched in multipl ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Omsk
Omsk (; rus, Омск, p=omsk) is the administrative center and largest city of Omsk Oblast, Russia. It is situated in southwestern Siberia, and has a population of over 1.1 million. Omsk is the third largest city in Siberia after Novosibirsk and Krasnoyarsk, and the twelfth-largest city in Russia. It is an essential transport node, serving as a train station for the Trans-Siberian Railway and as a staging post for the Irtysh River. During the Imperial era, Omsk was the seat of the Governor General of Western Siberia and, later, of the Governor General of the Steppes. For a brief period during the Russian Civil War in 1918–1920, it served as the capital of the anti-Bolshevik Russian State and held the imperial gold reserves. Omsk serves as the episcopal see of the bishop of Omsk and Tara, as well as the administrative seat of the Imam of Siberia. The mayor is Sergey Shelest. Etymology The city of Omsk is named after the Om river. This hydronym in the dialect of Bara ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Iranian Institute Of Applied Research
Iranian may refer to: * Iran, a sovereign state * Iranian peoples, the speakers of the Iranian languages. The term Iranic peoples is also used for this term to distinguish the pan ethnic term from Iranian, used for the people of Iran * Iranian languages, a branch of the Indo-Iranian languages * Iranian diaspora, Iranian people living outside Iran * Iranian architecture, architecture of Iran and parts of the rest of West Asia * Iranian foods, list of Iranian foods and dishes * Iranian.com, also known as ''The Iranian'' and ''The Iranian Times'' See also * Persian (other) * Iranians (other) * Languages of Iran * Ethnicities in Iran * Demographics of Iran * Indo-Iranian languages * Irani (other) * List of Iranians This is an alphabetic list of notable people from Iran or its historical predecessors. In the news * Ali Khamenei, supreme leader of Iran * Ebrahim Raisi, president of Iran, former Chief Justice of Iran. * Hassan Rouhani, former president of ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Shahab-3
The Shahab-3 ( fa, شهاب ۳, Šahâb 3; meaning "meteor-3") is a liquid-propelled medium-range ballistic missile (MRBM) developed by Iran and based on the North Korean Nodong-1. The Shahab-3 has a range of ; a MRBM variant can now reach (can hit targets as far as Israel, Egypt, Romania, Bulgaria and Greece). It was tested from 1998 to 2003 and added to the military arsenal on 7 July 2003, with an official unveiling by Ayatollah Khamenei on July 20. With an accuracy of 140 m CEP, the Shahab-3 missile is primarily effective against large, soft targets (like military airfields). Given the Shahab-3’s payload capacity, it would likely be capable of delivering nuclear warheads. According to the IAEA, Iran in the early 2000s may have explored various fuzing, arming and firing systems to make the Shahab-3 more capable of reliably delivering a nuclear warhead. The forerunners to this missile include the Shahab-1 and Shahab-2. In 2007, the then- Iranian Defence Minister Admiral Sham ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Ali Shamkhani
Ali Shamkhani (Persian: , born 29 September 1955) is an Iranian two-star general. He is the secretary of the Supreme National Security Council of Iran. Early life and education Shamkhani was born on 29 September 1955 in Ahvaz, Khuzestan. His family is of Iranian Arab origin. Before the Iranian Revolution, Shamkhani was member of a clandestine Islamist guerilla group named ''Mansouroun'' (), engaging in armed struggle against the Pahlavi dynasty. After the revolution, he joined the Mojahedin of the Islamic Revolution Organization. He studied engineering at Shahid Chamran University of Ahvaz. Career Shamkhani served as the commander of the IRGC navy with the rank of rear admiral. Later he also commanded the Artesh navy in addition to the IRGC navy. He was appointed the Minister of Revolutionary Guards in 1988. He held the post of the minister of defense from August 1997 until August 2005 in the government of Mohammad Khatami. Shamkani was replaced by Mostafa Mohammad-Najjar ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
USSPACECOM
United States Space Command (USSPACECOM or SPACECOM) is a unified combatant command of the United States Department of Defense, responsible for military operations in outer space, specifically all operations 100 kilometers (62 miles) and greater above mean sea level. U.S. Space Command is responsible for the operational employment of space forces that are provided by the uniformed services of the Department of Defense. Space Command was originally created in September 1985 to provide joint command and control for all military forces in outer space and coordinate with the other combatant commands. SPACECOM was disestablished in 2002, and its responsibilities and forces were merged into United States Strategic Command. A second incarnation of Space Command was established on 29 August 2019, with a reemphasized focus on space as a warfighting domain. Mission Space Command's mission is: ''"To conduct operations in, from, and through space to deter conflict, and if necessary, defe ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Satellite Catalog Number
The Satellite Catalog Number (SATCAT, also known as NORAD (North American Aerospace Defense) Catalog Number, NORAD ID, USSPACECOM object number or simply catalog number, among similar variants) is a sequential nine-digit number assigned by the United States Space Command (USSPACECOM) in the order of launch or discovery to all artificial objects in the orbits of Earth and those that left Earth's orbit. The first catalogued object, catalog number 1, is the Sputnik 1 launch vehicle, with the Sputnik 1 satellite having been assigned catalog number 2. __NOTOC__ Objects that fail to orbit or orbit for a short time are not catalogued. The minimum object size in the catalog is in diameter. , the catalog listed 54,200 objects, including 14,102 satellites that had been launched into orbit since 1957 of which 7,043 were still active. 24,146 of the objects were well tracked while 1,850 were lost. In addition USSPACECOM was also tracking 20,900 analyst objects. Analyst objects are variably tr ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Japan
Japan ( ja, 日本, or , and formally , ''Nihonkoku'') is an island country in East Asia. It is situated in the northwest Pacific Ocean, and is bordered on the west by the Sea of Japan, while extending from the Sea of Okhotsk in the north toward the East China Sea, Philippine Sea, and Taiwan in the south. Japan is a part of the Ring of Fire, and spans Japanese archipelago, an archipelago of List of islands of Japan, 6852 islands covering ; the five main islands are Hokkaido, Honshu (the "mainland"), Shikoku, Kyushu, and Okinawa Island, Okinawa. Tokyo is the Capital of Japan, nation's capital and largest city, followed by Yokohama, Osaka, Nagoya, Sapporo, Fukuoka, Kobe, and Kyoto. Japan is the List of countries and dependencies by population, eleventh most populous country in the world, as well as one of the List of countries and dependencies by population density, most densely populated and Urbanization by country, urbanized. About three-fourths of Geography of Japan, the c ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
UWE-1
UWE-1 (Universität Würzburg's Experimentalsatellit-1) was one of three CubeSats built by students of the University of Würzburg, launched on 27 October 2005 as part of the European Space Agency's SSETI Express mission from Plesetsk in Russia, orbiting Earth in a circular orbit. The cube-shaped satellite weighs about 1 kg and has an edge length of 10 cm, which corresponds to the CubeSat standard. Mission The primary mission of UWE-1 was to conduct telecommunication experiments. Among other things, it was about the data transmission on the Internet under space conditions: It was necessary to adapt the common Internet protocols to the difficult conditions in space environment on Earth, the transport of data on the Web works very reliable, but in space can increasingly delays and disruptions occur. Furthermore, UWE-1 also served as a test laboratory for highly efficient solar cells, whose performance and durability should be investigated. Downlink/uplink frequency wa ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |