|
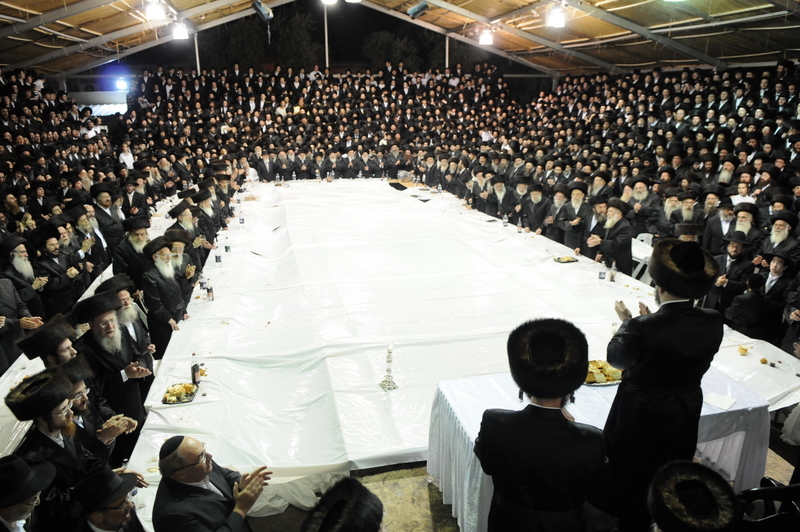
Simchat Torah
Simchat Torah or Simhat Torah (, lit., "Rejoicing with/of the Torah", Ashkenazi: ''Simchas Torah'') is a Jewish holiday that celebrates and marks the conclusion of the annual cycle of public Torah readings, and the beginning of a new cycle. Simchat Torah is a component of the Biblical Jewish holiday of ''Shemini Atzeret'' ("Eighth Day of Assembly"), which follows immediately after the festival of Sukkot in the month of Tishrei (occurring in mid-September to early October on the Gregorian calendar). The main celebrations of Simchat Torah take place in the synagogue during evening and morning services. In many Orthodox as well as many Conservative congregations, this is the only time of year on which the Torah scrolls are taken out of the ark and read at ''night''. In the morning, the last ''parashah'' of Deuteronomy and the first ''parashah'' of Genesis are read in the synagogue. On each occasion, when the ark is opened, the worshippers leave their seats to dance and sing with the ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Leghorn, Italy
Livorno () is a port city on the Ligurian Sea on the western coast of Tuscany, Italy. It is the capital of the Province of Livorno, having a population of 158,493 residents in December 2017. It is traditionally known in English as Leghorn (pronounced , "Leghorn" in the . or ). During the , Livorno was designed as an "". Developing c ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Conservative Judaism
Conservative Judaism, known as Masorti Judaism outside North America, is a Jewish religious movement which regards the authority of ''halakha'' (Jewish law) and traditions as coming primarily from its people and community through the generations moreso than from any divine revelation. It therefore views ''halakha'' as both binding and subject to historical development. The Conservative rabbinate employs modern historical-critical research, rather than only traditional methods and sources, and lends great weight to its constituency when determining its stance on matters of practice. The movement considers its approach as the authentic and most appropriate continuation of ''halakhic'' discourse, maintaining both fealty to received forms and flexibility in their interpretation. It also eschews strict theological definitions, lacking a consensus in matters of faith and allowing great pluralism. While regarding itself as the heir of Rabbi Zecharias Frankel's 19th-century Positive-H ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Ark (synagogue)
A Torah ark (also known as the ''Heikhal'', or the ''Aron Kodesh'') refers to an ornamental chamber in the synagogue that houses the Torah scrolls. History The ark, also known as the ''ark of law'', or in Hebrew the ''Aron Kodesh'' or ''aron ha-Kodesh'' ("holy ark") by Ashkenazi communities and as the ''Heikhal'' ("sanctuary") among Sefardi communities. ''Aron Kodesh'' comes from Hebrew אָרוֹן קׄדֶש ''ʼārōn qōdeš'' (i.e. A''ron Kodesh''), ''Holy Ark''. This name is a reference to the ''’ārōn haqqōdeš'', the Hebrew name for the Ark of the Covenant which was stored in the Holy of Holies in the inner sanctuary of both the ancient Tabernacle and the Temple in Jerusalem. Similarly, ''Hekhál'', also written ''hechal'', ''echal'' or ''heichal'' — and sometimes also ''Echal Kodesh'' (mainly among Balkan Sephardim) comes from Hebrew הֵיכָל ''hēkhāl'' (palace), was used in the same time period to refer to the inner sanctuary. The ''hekhal'' contained the M ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Arutz Sheva
''Arutz Sheva'' ( he, ערוץ 7, lit=''Channel 7''), also known in English as ''Israel National News'', is an Israeli media network identifying with religious Zionism. It offers online news articles in Hebrew, English, and Russian as well as live streaming radio, video and free podcasts. It also publishes a weekly newspaper, ''B'Sheva'', with the third-largest weekend circulation in the country. History In the 1970s an offshore radio station Voice of Peace was launched, broadcasting pacifistic messages. In response, Rabbi Zalman Baruch Melamed launched radio station ''Arutz Sheva'' in 1988, aimed at Israelis opposed to negotiations with the Palestine Liberation Organization. Based in Beit El, the station generated its broadcast on the Israeli airwaves from the ship MV ''Eretz HaTzvi'' in the Mediterranean Sea. It was one of the first Internet radio stations and was used as a beta tester for RealPlayer. From 1996 to 2002, ''Arutz Sheva'' broadcast in Russian. In 2003, ''Arutz S ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Yedidya Frankel
Yedidia, Yedidya, Yedidiah, etc. ( he, יְדִידְיָה) is both a given name and a surname, a variant of Jedediah. *The Hebrew name of the Hellenistic Jewish philosopher Philo of Alexandria * Yedidia Be'eri (1931–2004), Israeli politician *Yedidia Shofet (1908–2005), Iranian rabbi * Yedidya Ya'ari (born 1947) Former commander of the Israeli Navy *Yedidya Eisenshtat, Israeli architect, author of the Anzac Memorial (Israel) See also * * *Kfar Yedidia Kfar Yedidia ( he, כְּפַר יְדִידְיָה, ''lit.'' Yedidia Village) is a moshav in central Israel on the coastal plain. With an area of 3,000 dunams, it falls under the jurisdiction of Hefer Valley Regional Council. In it had a popu ..., a ''moshav'' named after Philo of Alexandria {{given name, type=both Hebrew-language names ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Hakafot
Hakafot (הקפות plural); Hakafah (הקפה singular)—meaning " ocircle" or "going around" in Hebrew—are a Jewish '' minhag'' (tradition) in which people walk or dance around a specific object, generally in a religious setting. In Judaism, there is a custom on Sukkot to encircle the reader's platform ( bimah) with the Four species on each of the seven days of the holiday. On Simchat Torah, the custom is to take the Torah scrolls out of the Ark and to encircle the reader’s platform and throughout the synagogue with great joy, singing, and dancing. Circular Hakafot are a symbol of perfection and unity, or sometimes a symbol of communal cooperation. According to the story told in the Book of Joshua, the People of Israel (Israelites) walked around the city of Jericho once a day for a week and seven times on the seventh day, with the priests leading the way, carrying the Ark of the Covenant each time. On the seventh day, the people blew shofar (ram's horns) and shouted, ca ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Reform Judaism
Reform Judaism, also known as Liberal Judaism or Progressive Judaism, is a major Jewish denomination that emphasizes the evolving nature of Judaism, the superiority of its ethical aspects to its ceremonial ones, and belief in a continuous search for truth and knowledge, which is closely intertwined with human reason and not limited to the theophany at Mount Sinai. A highly liberal strand of Judaism, it is characterized by lessened stress on ritual and personal observance, regarding ''halakha ''Halakha'' (; he, הֲלָכָה, ), also transliterated as ''halacha'', ''halakhah'', and ''halocho'' ( ), is the collective body of Jewish religious laws which is derived from the written and Oral Torah. Halakha is based on biblical commandm ...'' (Jewish law) as non-binding and the individual Jew as autonomous, and great openness to external influences and progressive values. The origins of Reform Judaism lie in German Confederation, 19th-century Germany, where Rabbi Abraham Geige ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Israel
Israel (; he, יִשְׂרָאֵל, ; ar, إِسْرَائِيل, ), officially the State of Israel ( he, מְדִינַת יִשְׂרָאֵל, label=none, translit=Medīnat Yīsrāʾēl; ), is a country in Western Asia. It is situated on the southeastern shore of the Mediterranean Sea and the northern shore of the Red Sea, and shares borders with Lebanon to the north, Syria to the northeast, Jordan to the east, and Egypt to the southwest. Israel also is bordered by the Palestinian territories of the West Bank and the Gaza Strip to the east and west, respectively. Tel Aviv is the economic and technological center of the country, while its seat of government is in its proclaimed capital of Jerusalem, although Israeli sovereignty over East Jerusalem is unrecognized internationally. The land held by present-day Israel witnessed some of the earliest human occupations outside Africa and was among the earliest known sites of agriculture. It was inhabited by the Canaanites ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Hasidic Judaism
Hasidism, sometimes spelled Chassidism, and also known as Hasidic Judaism (Ashkenazi Hebrew: חסידות ''Ḥăsīdus'', ; originally, "piety"), is a Judaism, Jewish religious group that arose as a spiritual revival movement in the territory of contemporary Western Ukraine during the 18th century, and spread rapidly throughout Eastern Europe. Today, most affiliates reside in Israel and the United States. Israel Ben Eliezer, the "Baal Shem Tov", is regarded as its founding father, and his disciples developed and disseminated it. Present-day Hasidism is a sub-group within Haredi Judaism and is noted for its religious conservatism and social seclusion. Its members adhere closely both to Orthodox Judaism, Orthodox Jewish practice – with the movement's own unique emphases – and the traditions of Eastern European Jews. Many of the latter, including various special styles of dress and the use of the Yiddish language, are nowadays associated almost exclusively with Hasidism. Hasi ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Halakha
''Halakha'' (; he, הֲלָכָה, ), also transliterated as ''halacha'', ''halakhah'', and ''halocho'' ( ), is the collective body of Jewish religious laws which is derived from the written and Oral Torah. Halakha is based on biblical commandments ('' mitzvot''), subsequent Talmudic and rabbinic laws, and the customs and traditions which were compiled in the many books such as the ''Shulchan Aruch''. ''Halakha'' is often translated as "Jewish law", although a more literal translation of it might be "the way to behave" or "the way of walking". The word is derived from the root which means "to behave" (also "to go" or "to walk"). ''Halakha'' not only guides religious practices and beliefs, it also guides numerous aspects of day-to-day life. Historically, in the Jewish diaspora, ''halakha'' served many Jewish communities as an enforceable avenue of law – both civil and religious, since no differentiation of them exists in classical Judaism. Since the Jewish Enlightenment (''Hask ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
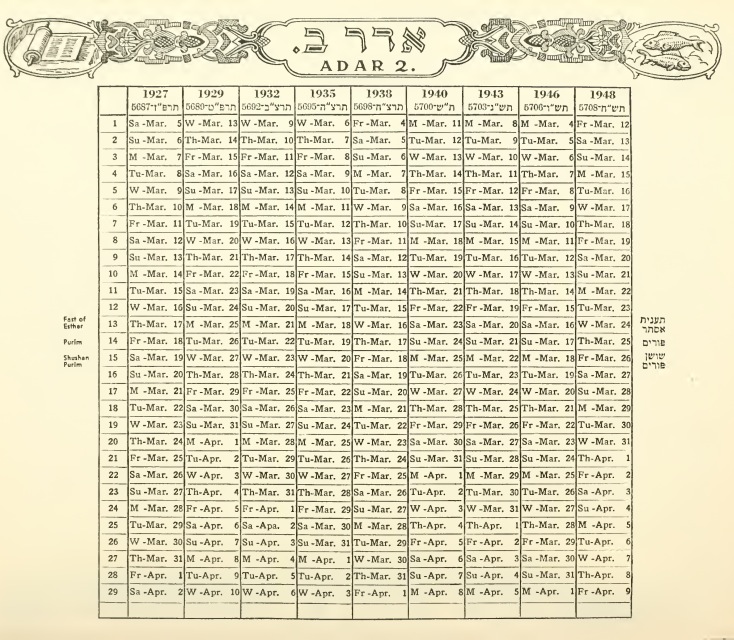
Hebrew Calendar
The Hebrew calendar ( he, הַלּוּחַ הָעִבְרִי, translit=HaLuah HaIvri), also called the Jewish calendar, is a lunisolar calendar used today for Jewish religious observance, and as an official calendar of the state of Israel. It determines the dates for Jewish holidays and the appropriate Torah reading, public reading of Weekly Torah portion, Torah portions, ''yahrzeits'' (dates to commemorate the death of a relative), and daily Psalm readings, among many ceremonial uses. In Israel, it is used for religious purposes, provides a time frame for agriculture, and is an official calendar for civil holidays, alongside the Gregorian calendar. The present Hebrew calendar is the result of a process of development, including a Babylonian calendar, Babylonian influence. Until the Tannaitic period (approximately 10–220 Common Era, CE), the calendar employed a new lunar phase, crescent moon, with an Intercalation (timekeeping), additional month normally added every two or ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Aliyah (Torah)
An aliyah (Hebrew עליה, or aliya and other variant English spellings) is the calling of a member of a Jewish congregation up to the '' bimah'' for a segment of the formal Torah reading. The person who receives the aliyah goes up to the ''bimah'' before the reading and recites a blessing for reading of the Torah. After the portion of the Torah is read, the recipient recites another blessing. In many congregations, the recipient will stand to the side of the ''bimah'' during the next person's reading. Process A synagogue official, called a '' gabbai'', calls up several people (men in Orthodox and some Conservative congregations, or both men and women in others), in turn, to be honored with an ''aliyah'' ( he, עליה; pl. עליות, ''aliyot''; "ascent" or "going up"). The honoree (or, more usually, a designated reader) recites a blessing over the Torah, between each verse. Each reads a section of the day's Torah portion. There are always at least three ''olim'' (people called ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |



.jpg)