|
Silyl Modified Polymers
Silyl-modified polymers (SMP; also ''silane-modified polymers'', ''modified-silane polymers'', ''MS polymers'', ''silane-terminated polymers'', etc.) are polymers terminating with a silane, silyl group. SMPs are the main components in solvent-free and isocyanate-free sealant and adhesive products.Jeffrey D. Umpleby "Polymer compositionU.S. patent 4574133 1986. Typically the sealant products manufactured with silyl-modified polymers have good adhesion on a wide range of substrate materials, and have good temperature and UV resistance. MS polymers consist of a polyether backbone with dimethoxy-silyl or trimethoxy-silyl ends, with trimethoxy-silyl groups being more reactive. Backbones can be linear with single or double ends, or branched for an increased amount of cross linking. Precursors can also be varied in the molecular weight and reactive silyl group concentration, resulting in variable cure times, strength, density, and hardness. Curing process The products cure from a liquid o ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Polymer
A polymer (; Greek '' poly-'', "many" + ''-mer'', "part") is a substance or material consisting of very large molecules called macromolecules, composed of many repeating subunits. Due to their broad spectrum of properties, both synthetic and natural polymers play essential and ubiquitous roles in everyday life. Polymers range from familiar synthetic plastics such as polystyrene to natural biopolymers such as DNA and proteins that are fundamental to biological structure and function. Polymers, both natural and synthetic, are created via polymerization of many small molecules, known as monomers. Their consequently large molecular mass, relative to small molecule compounds, produces unique physical properties including toughness, high elasticity, viscoelasticity, and a tendency to form amorphous and semicrystalline structures rather than crystals. The term "polymer" derives from the Greek word πολύς (''polus'', meaning "many, much") and μέρος (''meros'' ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Silane
Silane is an inorganic compound with chemical formula, . It is a colourless, pyrophoric, toxic gas with a sharp, repulsive smell, somewhat similar to that of acetic acid. Silane is of practical interest as a precursor to elemental silicon. Silane with alkyl groups are effective water repellents for mineral surfaces such as concrete and masonry. Silanes with both organic and inorganic attachments are used as coupling agents. Production Commercial-scale routes Silane can be produced by several routes. Typically, it arises from the reaction of hydrogen chloride with magnesium silicide: : Mg2Si + 4 HCl -> 2 MgCl2 + SiH4 It is also prepared from metallurgical-grade silicon in a two-step process. First, silicon is treated with hydrogen chloride at about 300 °C to produce trichlorosilane, HSiCl3, along with hydrogen gas, according to the chemical equation : Si + 3 HCl -> HSiCl3 + H2 The trichlorosilane is then converted to a mixture of silane and silicon tetrachloride: : 4 HS ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Solvent
A solvent (s) (from the Latin '' solvō'', "loosen, untie, solve") is a substance that dissolves a solute, resulting in a solution. A solvent is usually a liquid but can also be a solid, a gas, or a supercritical fluid. Water is a solvent for polar molecules and the most common solvent used by living things; all the ions and proteins in a cell are dissolved in water within the cell. The quantity of solute that can dissolve in a specific volume of solvent varies with temperature. Major uses of solvents are in paints, paint removers, inks, and dry cleaning. Specific uses for organic solvents are in dry cleaning (e.g. tetrachloroethylene); as paint thinners (toluene, turpentine); as nail polish removers and solvents of glue (acetone, methyl acetate, ethyl acetate); in spot removers (hexane, petrol ether); in detergents ( citrus terpenes); and in perfumes (ethanol). Solvents find various applications in chemical, pharmaceutical, oil, and gas industries, including in chemical syn ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Isocyanate
In organic chemistry, isocyanate is the functional group with the formula . Organic compounds that contain an isocyanate group are referred to as isocyanates. An organic compound with two isocyanate groups is known as a diisocyanate. Diisocyanates are manufactured for the production of polyurethanes, a class of polymers. Isocyanates should not be confused with cyanate esters and isocyanides, very different families of compounds. The cyanate (cyanate ester) functional group () is arranged differently from the isocyanate group (). Isocyanides have the connectivity , lacking the oxygen of the cyanate groups. Structure and bonding In terms of bonding, isocyanates are closely related to carbon dioxide (CO2) and carbodiimides (C(NR)2). The C−N=C=O unit that defines isocyanates is planar, and the N=C=O linkage is nearly linear. In phenyl isocyanate, the C=N and C=O distances are respectively 1.195 and 1.173 Å. The C-N=C angle is 134.9° and the N=C=O angle is 173.1°. ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Adhesive
Adhesive, also known as glue, cement, mucilage, or paste, is any non-metallic substance applied to one or both surfaces of two separate items that binds them together and resists their separation. The use of adhesives offers certain advantages over other binding techniques such as sewing, mechanical fastenings, or welding. These include the ability to bind different materials together, the more efficient distribution of stress across a joint, the cost-effectiveness of an easily mechanized process, and greater flexibility in design. Disadvantages of adhesive use include decreased stability at high temperatures, relative weakness in bonding large objects with a small bonding surface area, and greater difficulty in separating objects during testing. Adhesives are typically organized by the method of adhesion followed by ''reactive'' or ''non-reactive'', a term which refers to whether the adhesive chemically reacts in order to harden. Alternatively, they can be organized eithe ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Silyl Ether
Silyl ethers are a group of chemical compounds which contain a silicon atom covalently bonded to an alkoxy group. The general structure is R1R2R3Si−O−R4 where R4 is an alkyl group or an aryl group. Silyl ethers are usually used as protecting groups for alcohols in organic synthesis. Since R1R2R3 can be combinations of differing groups which can be varied in order to provide a number of silyl ethers, this group of chemical compounds provides a wide spectrum of selectivity for protecting group chemistry. Common silyl ethers are: trimethylsilyl (TMS), ''tert''-butyldiphenylsilyl (TBDPS), ''tert''-butyldimethylsilyl (TBS/TBDMS) and triisopropylsilyl (TIPS). They are particularly useful because they can be installed and removed very selectively under mild conditions. Common silyl ethers Formation Commonly silylation of alcohols requires a silyl chloride and an amine base. One reliable and rapid procedure is the Corey protocol in which the alcohol is reacted with a silyl chlori ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Catalyst
Catalysis () is the process of increasing the rate of a chemical reaction by adding a substance known as a catalyst (). Catalysts are not consumed in the reaction and remain unchanged after it. If the reaction is rapid and the catalyst recycles quickly, very small amounts of catalyst often suffice; mixing, surface area, and temperature are important factors in reaction rate. Catalysts generally react with one or more reactants to form intermediates that subsequently give the final reaction product, in the process of regenerating the catalyst. Catalysis may be classified as either homogeneous, whose components are dispersed in the same phase (usually gaseous or liquid) as the reactant, or heterogeneous, whose components are not in the same phase. Enzymes and other biocatalysts are often considered as a third category. Catalysis is ubiquitous in chemical industry of all kinds. Estimates are that 90% of all commercially produced chemical products involve catalysts at some s ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Moisture
Moisture is the presence of a liquid, especially water, often in trace amounts. Small amounts of water may be found, for example, in the air (humidity), in foods, and in some commercial products. Moisture also refers to the amount of water vapor present in the air. Moisture control in products Control of moisture in products can be a vital part of the process of the product. There is a substantial amount of moisture in what seems to be dry matter. Ranging in products from cornflake cereals to washing powders, moisture can play an important role in the final quality of the product. There are two main aspects of concern in moisture control in products: allowing too much moisture or too little of it. For example, adding some water to cornflake cereal, which is sold by weight, reduces costs and prevents it from tasting too dry, but adding too much water can affect the crunchiness of the cereal and the freshness because water content contributes to bacteria growth. Water content o ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
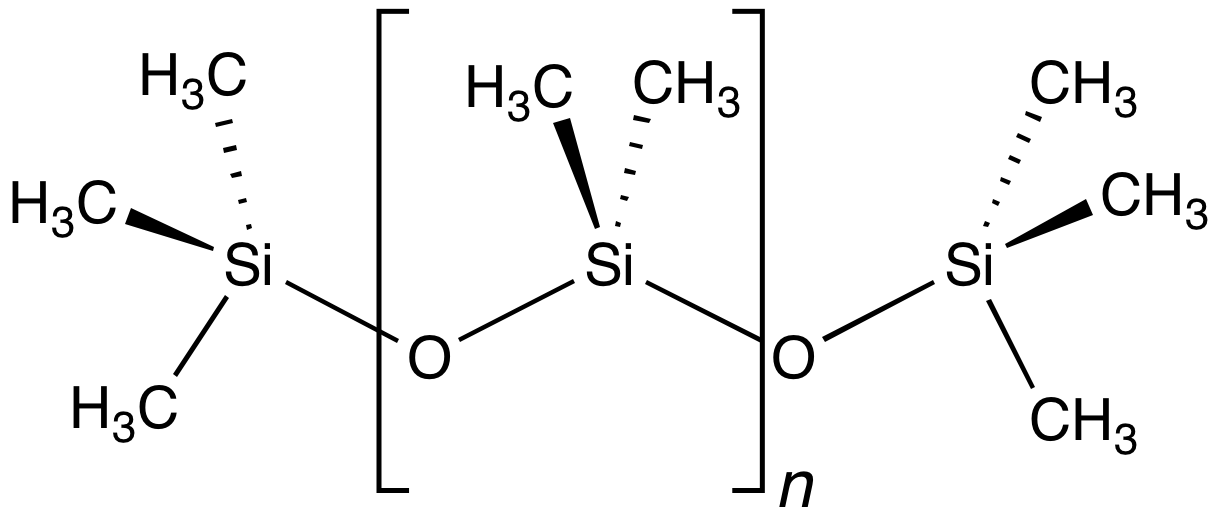
Siloxane
A siloxane is a functional group in organosilicon chemistry with the Si−O−Si linkage. The parent siloxanes include the oligomeric and polymeric hydrides with the formulae H(OSiH2)''n''OH and (OSiH2)n. Siloxanes also include branched compounds, the defining feature of which is that each pair of silicon centres is separated by one oxygen (O2-) atom. The siloxane functional group forms the backbone of silicones, the premier example of which is polydimethylsiloxane (PDMS). The functional group R3SiO− (where the three Rs may be different) is called siloxy. Siloxanes are manmade and have many commercial and industrial applications because of the compounds’ hydrophobicity, low thermal conductivity, and high flexibility. Structure Siloxanes generally adopt structures expected for linked tetrahedral ("''sp''3-like") centers. The Si−O bond length is 1.64 Å (vs Si–C distance of 1.92 Å) and the Si-O-Si angle is rather open at 142.5°. By contrast, the C−O ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |