|
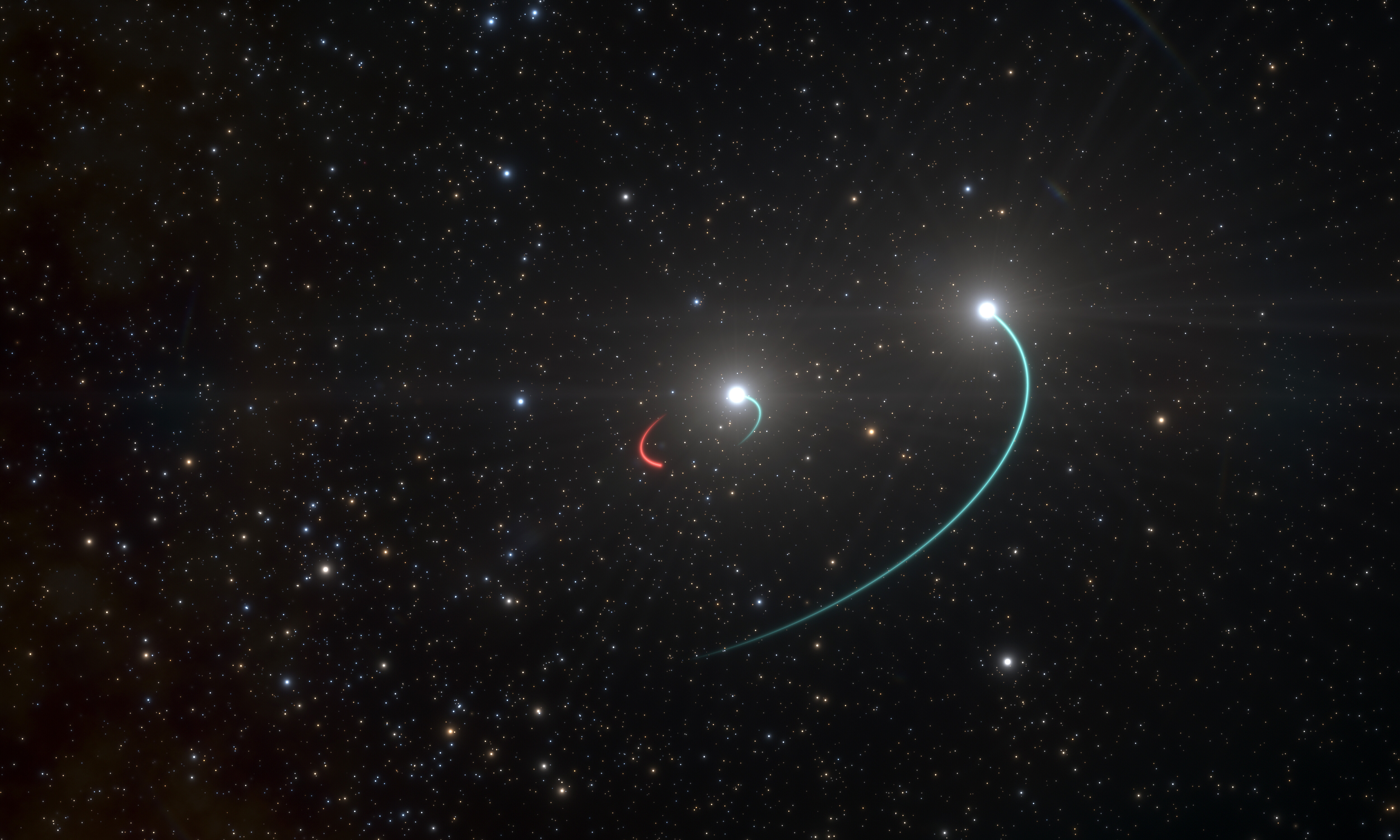
Sigma Scorpii
Sigma Scorpii (or σ Scorpii, abbreviated Sigma Sco or σ Sco), is a multiple star system in the constellation of Scorpius, located near the red supergiant Antares, which outshines it. This system has a combined apparent visual magnitude of +2.88, making it one of the brighter members of the constellation. Based upon parallax measurements made during the Hipparcos mission, the distance to Sigma Scorpii is roughly 696 light-years (214 parsecs). North ''et al.'' (2007) computed a more accurate estimate of light years ( parsecs). The system consists of a spectroscopic binary with components designated Sigma Scorpii Aa1 (officially named Alniyat , the traditional name for the entire star system) and a Beta Cephei variable) and Aa2; a third component (designated Sigma Scorpii Ab) at 0.4 arcseconds from the spectroscopic pair, and a fourth component (Sigma Scorpii B) at about 20 arcseconds. Nomenclature ''σ Scorpii'' ( Latinised to ''Sigma Scorp ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
J2000
In astronomy, an epoch or reference epoch is a instant, moment in time used as a reference point for some time-varying astronomical quantity. It is useful for the celestial coordinates or orbital elements of a Astronomical object, celestial body, as they are subject to Perturbation (astronomy), perturbations and vary with time. These time-varying astronomical quantities might include, for example, the mean longitude or mean anomaly of a body, the node of its orbit relative to a reference plane, the direction of the apogee or Perihelion and aphelion, aphelion of its orbit, or the size of the major axis of its orbit. The main use of astronomical quantities specified in this way is to calculate other relevant parameters of motion, in order to predict future positions and velocities. The applied tools of the disciplines of celestial mechanics or its subfield orbital mechanics (for predicting orbital paths and positions for bodies in motion under the gravitational effects of other bodi ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Parsec
The parsec (symbol: pc) is a unit of length used to measure the large distances to astronomical objects outside the Solar System, approximately equal to or (au), i.e. . The parsec unit is obtained by the use of parallax and trigonometry, and is defined as the distance at which 1 au subtends an angle of one arcsecond ( of a degree). This corresponds to astronomical units, i.e. 1\, \mathrm = 1/\tan \left( \ \mathrm \right)\, \mathrm. The nearest star, Proxima Centauri, is about from the Sun. Most stars visible to the naked eye are within a few hundred parsecs of the Sun, with the most distant at a few thousand. The word ''parsec'' is a portmanteau of "parallax of one second" and was coined by the British astronomer Herbert Hall Turner in 1913 to make calculations of astronomical distances from only raw observational data easy for astronomers. Partly for this reason, it is the unit preferred in astronomy and astrophysics, though the light-year remains prominent in popular s ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Chinese Astronomy
Astronomy in China has a long history stretching from the Shang dynasty, being refined over a period of more than 3,000 years. The ancient Chinese people have identified stars from 1300 BCE, as Chinese star names later categorized in the twenty-eight mansions have been found on oracle bones unearthed at Anyang, dating back to the mid-Shang dynasty. The core of the "mansion" (宿 ''xiù'') system also took shape around this period, by the time of King Wu Ding (1250–1192 BCE). Detailed records of astronomical observations began during the Warring States period (fourth century BCE) and flourished from the Han period onward. Chinese astronomy was equatorial, centered on close observation of circumpolar stars, and was based on different principles from those in traditional Western astronomy, where heliacal risings and settings of zodiac constellations formed the basic ecliptic framework. Joseph Needham has described the ancient Chinese as the most persistent and accurate obser ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Multiple Star
A star system or stellar system is a small number of stars that orbit each other, bound by gravitational attraction. A large group of stars bound by gravitation is generally called a ''star cluster'' or ''galaxy'', although, broadly speaking, they are also star systems. Star systems are not to be confused with planetary systems, which include planets and similar bodies (such as comets). A star system of two stars is known as a ''binary star'', ''binary star system'' or ''physical double star''. If there are no tidal effects, no perturbation from other forces, and no transfer of mass from one star to the other, such a system is stable, and both stars will trace out an elliptical orbit around the barycenter of the system indefinitely. ''(See Two-body problem)''. Examples of binary systems are Sirius, Procyon and Cygnus X-1, the last of which probably consists of a star and a black hole. Multiple star systems A multiple star system consists of three or more stars that appear f ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
IAU Working Group On Star Names
The International Astronomical Union (IAU) established a Working Group on Star Names (WGSN) in May 2016 to catalog and standardize proper names for stars for the international astronomical community. It operates under Division C – Education, Outreach and Heritage. The IAU states that it is keen to make a distinction between the terms ''name'' and ''designation''. To the IAU, ''name'' refers to the (usually colloquial) term used for a star in everyday conversation, while ''designation'' is solely alphanumerical, and used almost exclusively in official catalogues and for professional astronomy. (The WGSN notes that transliterated Bayer designations (e.g., Tau Ceti) are considered a special historical case and are treated as designations.) Terms of reference The terms of reference for the WGSN for the period 2016–2018 were approved by the IAU Executive Committee at its meeting on 6 May 2016. In summary, these are to: * establish IAU guidelines for the proposal and a ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Arabic
Arabic (, ' ; , ' or ) is a Semitic languages, Semitic language spoken primarily across the Arab world.Semitic languages: an international handbook / edited by Stefan Weninger; in collaboration with Geoffrey Khan, Michael P. Streck, Janet C. E.Watson; Walter de Gruyter GmbH & Co. KG, Berlin/Boston, 2011. Having emerged in the 1st century, it is named after the Arabs, Arab people; the term "Arab" was initially used to describe those living in the Arabian Peninsula, as perceived by geographers from ancient Greece. Since the 7th century, Arabic has been characterized by diglossia, with an opposition between a standard Prestige (sociolinguistics), prestige language—i.e., Literary Arabic: Modern Standard Arabic (MSA) or Classical Arabic—and diverse vernacular varieties, which serve as First language, mother tongues. Colloquial dialects vary significantly from MSA, impeding mutual intelligibility. MSA is only acquired through formal education and is not spoken natively. It is ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Tau Scorpii
Tau Scorpii, Latinized from τ Scorpii, formally known as Paikauhale , is a star in the southern zodiac constellation of Scorpius. The apparent visual magnitude of Tau Scorpii is +2.8, while parallax measurements yield a distance estimate of roughly 470 light-years (150 parsecs) from Earth. Description Compared to the Sun, Tau Scorpii is a massive OB star with 15 times the Sun's mass and more than six times the radius of the Sun. It is radiating about 20,400 times the Sun's luminosity from its outer envelope at an effective temperature of 31,440 K. This gives it the blue-white hue characteristic of B-type stars. As yet there is no evidence of a companion in orbit around τ Sco. It is a magnetic star whose surface magnetic field was mapped by means of Zeeman–Doppler imaging. Tau Scorpii is rotating relatively slowly with a period of 41 days. The spectrum of this star shows triply ionized oxygen (O IV) that is being generated by X-rays and ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
International Astronomical Union
The International Astronomical Union (IAU; french: link=yes, Union astronomique internationale, UAI) is a nongovernmental organisation with the objective of advancing astronomy in all aspects, including promoting astronomical research, outreach, education, and development through global cooperation. It was founded in 1919 and is based in Paris, France. The IAU is composed of individual members, who include both professional astronomers and junior scientists, and national members, such as professional associations, national societies, or academic institutions. Individual members are organised into divisions, committees, and working groups centered on particular subdisciplines, subjects, or initiatives. As of 2018, the Union had over 13,700 individual members, spanning 90 countries, and 82 national members. Among the key activities of the IAU is serving as a forum for scientific conferences. It sponsors nine annual symposia and holds a triannual General Assembly that sets policy ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Star System
A star system or stellar system is a small number of stars that orbit each other, bound by gravitational attraction. A large group of stars bound by gravitation is generally called a '' star cluster'' or '' galaxy'', although, broadly speaking, they are also star systems. Star systems are not to be confused with planetary systems, which include planets and similar bodies (such as comets). A star system of two stars is known as a '' binary star'', ''binary star system'' or ''physical double star''. If there are no tidal effects, no perturbation from other forces, and no transfer of mass from one star to the other, such a system is stable, and both stars will trace out an elliptical orbit around the barycenter of the system indefinitely. ''(See Two-body problem)''. Examples of binary systems are Sirius, Procyon and Cygnus X-1, the last of which probably consists of a star and a black hole. Multiple star systems A multiple star system consists of three or more stars that ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Bayer Designation
A Bayer designation is a stellar designation in which a specific star is identified by a Greek or Latin letter followed by the genitive form of its parent constellation's Latin name. The original list of Bayer designations contained 1,564 stars. The brighter stars were assigned their first systematic names by the German astronomer Johann Bayer in 1603, in his star atlas ''Uranometria''. Bayer catalogued only a few stars too far south to be seen from Germany, but later astronomers (including Nicolas-Louis de Lacaille and Benjamin Apthorp Gould) supplemented Bayer's catalog with entries for southern constellations. Scheme Bayer assigned a lowercase Greek letter (alpha (α), beta (β), gamma (γ), etc.) or a Latin letter (A, b, c, etc.) to each star he catalogued, combined with the Latin name of the star's parent constellation in genitive (possessive) form. The constellation name is frequently abbreviated to a standard three-letter form. For example, Aldebaran in the constellation ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Latinisation Of Names
Latinisation (or Latinization) of names, also known as onomastic Latinisation, is the practice of rendering a ''non''-Latin name in a Latin style. It is commonly found with historical proper names, including personal names and toponyms, and in the standard binomial nomenclature of the life sciences. It goes further than romanisation, which is the transliteration of a word to the Latin alphabet from another script (e.g. Cyrillic). For authors writing in Latin, this change allows the name to function grammatically in a sentence through declension. In a scientific context, the main purpose of Latinisation may be to produce a name which is internationally consistent. Latinisation may be carried out by: * transforming the name into Latin sounds (e.g. for ), or * adding Latinate suffixes to the end of a name (e.g. for '' Meibom),'' or * translating a name with a specific meaning into Latin (e.g. for Italian ; both mean 'hunter'), or * choosing a new name based on some attribut ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Rho Ophiuchi
Rho Ophiuchi (ρ Ophiuchi) is a multiple star system in the constellation Ophiuchus. The central system has an apparent magnitude of 4.63. Based on the central system's parallax of 9.03 mas, it is located about 360 light-years (110 parsecs) away. The other stars in the system are slightly farther away. System The central pair is known as Rho Ophiuchi AB. It consists of at least two blue-colored subgiants or main-sequence stars, designated Rho Ophiuchi A and B, respectively. Rho Ophiuchi AB is a visual binary, and the sky-projected distance between the two stars appears to be 3.1″, corresponding to a separation of at least 344 astronomical units (au). However, the actual separation is larger, and the two take about 2,400 years to complete an orbit. The two stars dominate the radiation field around the Rho Ophiuchi cloud complex. Rho Ophiuchi A emits X-rays, and exhibits strong variability in emission over periods of about 1.2 days, corresponding to its rotation per ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |