|
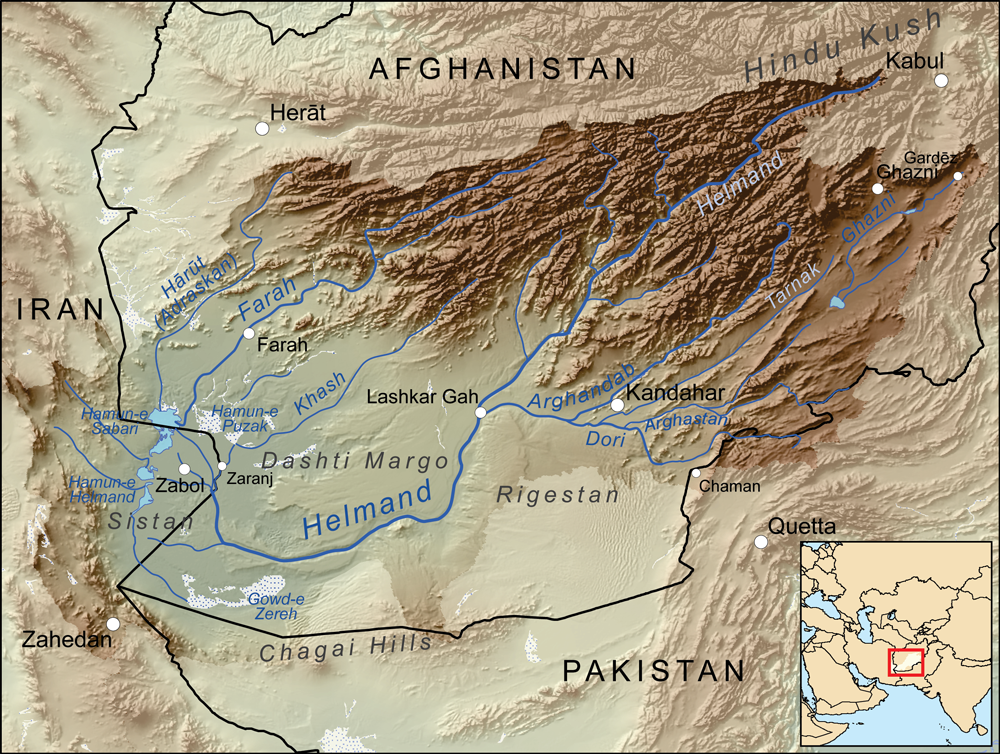
Sigal, Sakastan
Sigal was a city of the Helmund valley in south-west Afghanistan (ancient Sacastene). The presence of the Sakas in Sakastan in the 1st century BCE, with their capital at Sigal, is mentioned by Isidore of Charax in his "Parthian stations". He explained that they were bordered at that time by Greek cities to the east (Alexandria of the Caucasus and Alexandria of the Arachosians), and the Parthian-controlled territory of Arachosia to the south: :"Beyond is Sacastana of the Scythian Sacae, which is also Paraetacena, 63 schoeni. There are the city of Barda and the city of Min and the city of Palacenti and the city of Sigal; in that place is the royal residence of the Sacae; and nearby is the city of Alexandria (and nearby is the city of Alexandropolis), and six villages." Parthian stations, 18. Notes [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Helmund
The Helmand River (also spelled Helmend, or Helmund, Hirmand; Pashto/Persian: ; Greek: ' (''Etýmandros''); Latin: ') is the longest river in Afghanistan and the primary watershed for the endorheic Sistan Basin. It emerges in the Sanglakh Range of the Hindu Kush mountains in the northeastern part of Maidan Wardak Province, where it is separated from the watershed of the Kabul River by the Unai Pass. The Helmand feeds into the Hamun Lake on the border between Afghanistan and Iran. Etymology The name comes from the Avestan ''Haētumant'', literally "dammed, having a dam", which referred to the Helmand River and the irrigated areas around it. Geography The Helmand River stretches for . It rises in the northeastern part of Maidan Wardak Province in the Hindu Kush mountains, about 40 km west of Kabul (), flowing southwestward through Daykundi Province and Uruzgan Province. After passing through the city of Lashkargah in Helmand Province, it enters the desert of Dashti M ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Valley
A valley is an elongated low area often running between Hill, hills or Mountain, mountains, which will typically contain a river or stream running from one end to the other. Most valleys are formed by erosion of the land surface by rivers or streams over a very long period. Some valleys are formed through erosion by glacier, glacial ice. These glaciers may remain present in valleys in high mountains or polar areas. At lower latitudes and altitudes, these glaciation, glacially formed valleys may have been created or enlarged during ice ages but now are ice-free and occupied by streams or rivers. In desert areas, valleys may be entirely dry or carry a watercourse only rarely. In karst, areas of limestone bedrock, dry valleys may also result from drainage now taking place cave, underground rather than at the surface. Rift valleys arise principally from tectonics, earth movements, rather than erosion. Many different types of valleys are described by geographers, using terms th ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Afghanistan
Afghanistan, officially the Islamic Emirate of Afghanistan,; prs, امارت اسلامی افغانستان is a landlocked country located at the crossroads of Central Asia and South Asia. Referred to as the Heart of Asia, it is bordered by Pakistan to the Durand Line, east and south, Iran to the Afghanistan–Iran border, west, Turkmenistan to the Afghanistan–Turkmenistan border, northwest, Uzbekistan to the Afghanistan–Uzbekistan border, north, Tajikistan to the Afghanistan–Tajikistan border, northeast, and China to the Afghanistan–China border, northeast and east. Occupying of land, the country is predominantly mountainous with plains Afghan Turkestan, in the north and Sistan Basin, the southwest, which are separated by the Hindu Kush mountain range. , Demographics of Afghanistan, its population is 40.2 million (officially estimated to be 32.9 million), composed mostly of ethnic Pashtuns, Tajiks, Hazaras, and Uzbeks. Kabul is the country's largest city and ser ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Sakas
The Saka (Old Persian: ; Kharosthi, Kharoṣṭhī: ; Egyptian language, Ancient Egyptian: , ; , Old Chinese, old , Pinyin, mod. , ), Shaka (Sanskrit (Brahmi script, Brāhmī): , , ; Sanskrit (Devanagari, Devanāgarī): , ), or Sacae (Ancient Greek: ; Latin: ) were a group of nomadic Iranian peoples who historically inhabited the northern and eastern Eurasian Steppe and the Tarim Basin. "Modern scholars have mostly used the name Saka to refer specifically to Iranians of the Eastern Steppe and Tarim Basin" "In modern scholarship the name 'Sakas' is reserved for the ancient tribes of northern and eastern Central Asia and Eastern Turkestan to distinguish them from the related Massagetae of the Aral region and the Scythians of the Pontic steppes. These tribes spoke Iranian languages, and their chief occupation was nomadic pastoralism." The Sakas were closely related to the European Scythians, and both groups formed part of the wider Scythian cultures and ultimately derived f ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Sakastan
Sistān ( fa, سیستان), known in ancient times as Sakastān ( fa, سَكاستان, "the land of the Saka"), is a historical and Sistan Basin, geographical region in present-day Eastern Iran (Sistan and Baluchestan Province) and Southern Afghanistan (Nimruz Province, Nimruz, Helmand Province, Helmand, Kandahar Province, Kandahar). Largely desert, the region is bisected by the Helmand River, the largest river in Afghanistan, which empties into the Hamun Lake that forms part of the border between the two countries. Etymology Sistan derives its name from ''Sakastan'' ("the land of the Saka"). The Sakas were a Scythians, Scythian tribe which from the 2nd century BC to the 1st century migrated to the Iranian Plateau and Indus valley, where they carved a kingdom known as the Indo-Scythians, Indo-Scythian Kingdom. In the Bundahishn, a Zoroastrian scripture written in Middle Persian, Pahlavi, the province is called "Seyansih". After the Muslim conquest of Persia, Arab conquest of I ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Isidore Of Charax
Isidore of Charax (; grc, Ἰσίδωρος ὁ Χαρακηνός, ''Isídōros o Charakēnós''; la, Isidorus Characenus) was a Greco-Roman geographer of the 1st century BC and 1st century AD, a citizen of the Parthian Empire, about whom nothing is known but his name and that he wrote at least one work. Name Isidore's name has been interpreted by his editor and translator W.H. Schoff to indicate that he was from the city of Charax in Characene on the northern end of the present Persian Gulf. However, the Greek ''charax'' merely means "palisade" and there were several fortified towns that bore the name (''see Charax''). Parthian Stations Isidore's best known work is "The Parthian Stations" ( grc, Σταθμοί Παρθικοί, ''Stathmœ́ Parthicœ́''; la, Mansiones Parthicae), an itinerary of the overland trade route from Antioch to India along the caravan stations maintained by the Arsacid Empire. He seems to have given his distances in schoeni ("ropes") of debated ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Alexandria Of The Caucasus
Alexandria in the Caucasus ( grc, Ἀλεξάνδρεια) (medieval Kapisa, modern Bagram) was a colony of Alexander the Great (one of many colonies designated with the name ''Alexandria''). He founded the colony at an important junction of communications in the southern foothills of the Hindu Kush mountains, in the country of the Paropamisadae. In Classical times, the Hindu Kush were also designated as the "Caucasus" in parallel to their Western equivalent, the Caucasus Mountains between Europe and Asia. Alexander the Great Alexander populated the city with 7,000 Macedonians, 3,000 mercenaries and thousands of natives (according to Curtius VII.3.23), or some 7,000 natives and 3,000 non-military camp followers and a number of Greek mercenaries (Diodorus, XVII.83.2), in March 329 BC. He had also built forts in what is now Bagram, Afghanistan, at the foot of the Hindu Kush, replacing forts erected in much the same place by Persia's king Cyrus the Great c. 500 BC, Ale ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Alexandria Of The Arachosians
Alexandria in Arachosia ( el, Ἀλεξάνδρεια Ἀραχωσίας) also known as Alexandropolis (Ἀλεξανδρόπολις) was a city in ancient times that is now called Kandahar in Afghanistan. It was one of more than twenty cities founded or renamed by Alexander the Great. It was founded around 330 BCE, on the foundations of an earlier Achaemenid fortress. Arachosia is the Greek name of an ancient province of the Achaemenid, Seleucid and Parthian empires. The province of ''Arachosia'' was centered around the Argandab valley in Kandahar. It did not reach the Hindu Kush, but it apparently extended east as far as the Indus River, although its exact extents are not yet clear. History After the conquests of Alexander the Great, Arachosia was ruled by the Satrap Sybirtius. In the 3rd century BCE, it is thought that the ambassador to the Indian court Megasthenes departed from the city to visit India: Megasthenes lived with Sibyrtius, satrap of Arachosia, and oft ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Arachosia
Arachosia () is the Hellenized name of an ancient satrapy situated in the eastern parts of the Achaemenid empire. It was centred around the valley of the Arghandab River in modern-day southern Afghanistan, and extended as far east as the Indus River, in modern-day Pakistan. The Old Persian form of its name is ''Harauvatiš'', being the etymological equivalent of Vedic Sanskrit ''Sárasvatī''. The province name is derived after its main river, the modern Arghandab (in Greek called Arachōtós), a tributary of the Helmand river. The capital of Arachosia was Alexandria of Arachosia, an ancient Greek city that was situated over what is now known as Kandahar. Etymology "Arachosia" is the Latinized form of Greek (''Arachōsíā''). "The same region appears in the Avestan '' Vidēvdāt'' (1.12) under the indigenous dialect form 𐬵𐬀𐬭𐬀𐬓𐬀𐬌𐬙𐬍 - (whose ''-axva-'' is typical non-Avestan)." In Old Persian inscriptions, the region is referred to as 𐏃 ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Schoeni
Schoenus ( la, schœnus; grc-gre, σχοίνος, ''schoinos'', " rush rope"; egy, i͗trw, "river-measure") was an ancient Egyptian, Greek and Roman unit of length and area based on the knotted cords first used in Egyptian surveying. Length The Greeks, who adopted it from the Egyptians, generally considered the schoinos equal to 40 stades, but neither the schoinos nor the stadion had an absolute value, and there were several regional variants of each. Strabo noted that it also varied with terrain, and that when he "ascended the hills, the measures of these schoeni were not everywhere uniform, so that the same number sometimes designated a greater, sometimes a less actual extent of road, a variation which dates from the earliest time and exists in our days."Herodotus2.6an says, that schoenus is 60 stadia or about . This agrees with the distance implied by the Triacontaschoenus stretching south of the First Cataract in Roman-era Nubia. Pliny the Elderbr>5.11that is 30 ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |