|
Sierra (supercomputer)
Sierra or ATS-2 is a supercomputer built for the Lawrence Livermore National Laboratory for use by the National Nuclear Security Administration as the second Advanced Technology System. It is primarily used for predictive applications in stockpile stewardship, helping to assure the safety, reliability and effectiveness of the United States' nuclear weapons. Sierra is very similar in architecture to the Summit supercomputer built for the Oak Ridge National Laboratory. The Sierra system uses IBM POWER9 CPUs in conjunction with Nvidia Tesla V100 GPUs. The nodes in Sierra are Witherspoon IBM S922LC OpenPOWER servers with two GPUs per CPU and four GPUs per node. These nodes are connected with EDR InfiniBand. In 2019 Sierra was upgraded with IBM Power System AC922 nodes.Sierrahas consistently appeared on the Top500 list, peaking a#2 in November 2018 See also * Trinity (supercomputer) – ATS-1, the first Advanced Technology System * OpenBMC The OpenBMC project is a Linux ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
ATS-2
ATS-2 (Applications Technology Satellite) was a communications satellite launched by NASA on April 6, 1967, on an Atlas-Agena D rocket from Cape Canaveral. Objectives The ATS-2 had the following objectives: test new concepts in spacecraft design, propulsion and stabilization; capture high quality images of cloud cover; collect data measurements in an aerospace environment; and test improved communication systems. Features The satellite had a cylindrical shape with a diameter and a height of . After including the motor cover, the satellite was about tall. The surface of the satellite was covered by solar panels, and it utilized gravity-gradient stabilization for control. Experiments The following 12 experiments were conducted: * Radio astronomy * Magnetospheric electric fields * Electron magnetic spectrometer deflection * Particle telescope * Omnidirectional proton and electron detectors * Very low frequency (VLF) receiver * Earth's albedo ( DoD) * Microwave comm ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Summit (supercomputer)
Summit or OLCF-4 is a supercomputer developed by IBM for use at Oak Ridge Leadership Computing Facility (OLCF), a facility at the Oak Ridge National Laboratory, capable of 200 petaFLOPS thus making it the 4th fastest supercomputer in the world after Frontier (OLCF-5), Fugaku, and LUMI. It held the number 1 position from November 2018 to June 2020. Its current LINPACK benchmark is clocked at 148.6 petaFLOPS. As of November 2019, the supercomputer had ranked as the 5th most energy efficient in the world with a measured power efficiency of 14.668 gigaFLOPS/watt. Summit was the first supercomputer to reach exaflop (a quintillion operations per second) speed, achieving 1.88 exaflops during a genomic analysis and is expected to reach 3.3 exaflops using mixed-precision calculations. History The United States Department of Energy awarded a $325 million contract in November 2014 to IBM, NVIDIA and Mellanox. The effort resulted in construction of Summit and Sierra. Summit is ta ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
GPGPU Supercomputers
General-purpose computing on graphics processing units (GPGPU, or less often GPGP) is the use of a graphics processing unit (GPU), which typically handles computation only for computer graphics, to perform computation in applications traditionally handled by the central processing unit (CPU). The use of multiple video cards in one computer, or large numbers of graphics chips, further parallelizes the already parallel nature of graphics processing. Essentially, a GPGPU pipeline is a kind of parallel processing between one or more GPUs and CPUs that analyzes data as if it were in image or other graphic form. While GPUs operate at lower frequencies, they typically have many times the number of cores. Thus, GPUs can process far more pictures and graphical data per second than a traditional CPU. Migrating data into graphical form and then using the GPU to scan and analyze it can create a large speedup. GPGPU pipelines were developed at the beginning of the 21st century for graphic ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
The Verge
''The Verge'' is an American technology news website operated by Vox Media, publishing news, feature stories, guidebooks, product reviews, consumer electronics news, and podcasts. The website launched on November 1, 2011, and uses Vox Media's proprietary multimedia publishing platform Chorus. In 2014, Nilay Patel was named editor-in-chief and Dieter Bohn executive editor; Helen Havlak was named editorial director in 2017. ''The Verge'' won five Webby Awards for the year 2012 including awards for Best Writing (Editorial), Best Podcast for ''The Vergecast'', Best Visual Design, Best Consumer Electronics Site, and Best Mobile News App. History Origins Between March and April 2011, up to nine of ''Engadget''s writers, editors, and product developers, including editor-in-chief Joshua Topolsky, left AOL, the company behind that website, to start a new gadget site. The other departing editors included managing editor Nilay Patel and staffers Paul Miller, Ross Miller, Joann ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
OpenBMC
The OpenBMC project is a Linux Foundation collaborative open-source project whose goal is to produce an open source implementation of the Baseboard Management Controllers (BMC) Firmware Stack. OpenBMC is a Linux distribution for BMCs meant to work across heterogeneous systems that include enterprise, high-performance computing (HPC), telecommunications, and cloud-scale data centers. History In 2014, four Facebook programmers at a Facebook hackathon event created a prototype open-source BMC firmware stack named OpenBMC. In 2015, IBM collaborated with Rackspace on an open-source BMC firmware stack also named OpenBMC. These projects were similar in name and concept only. In March 2018, OpenBMC became a Linux Foundation project and converged on the IBM stack. Founding organizations of the OpenBMC project are Microsoft, Intel, IBM, Google, and Facebook. A technical steering committee was formed to guide the project with representation from the five founding companies. Brad Bishop from ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Trinity (supercomputer)
Trinity (or ATS-1) is a United States supercomputer built by the National Nuclear Security Administration (NNSA) for the Advanced Simulation and Computing Program (ASC). The aim of the ASC program is to simulate, test, and maintain the United States nuclear stockpile. History * December 2013, The National Energy Research Scientific Computing Center (NERSC) and The Alliance for Computing at Extreme Scale (ACES) releases a joint RFP with technical requirements for Trinity. * July 2014, Cray announces that they were awarded the $174 Million contract by the National Nuclear Security Administration to provide a next generation supercomputer to Los Alamos National Laboratory. * June 2015, Haswell Partition installation begins. * November 2015, Trinity appears on the Supercomputing Top500 list at #6. * June 2016, Knights Landing Partition installation begins. * November 2016, Trinity falls to #10 on the Top500 list. * July 2017, The Haswell and KNL partitions are merged. * November 20 ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
IBM Power System
Power Systems is a family of server computers from IBM that are based on its Power processors. It was created in 2008 as a merger of the System p and System i product lines. History IBM had two distinct POWER- and PowerPC-based hardware lines since the early 1990s: * Servers running processors based on the IBM PowerPC-AS architecture in the AS/400 family (later known as iSeries, then System i) running OS/400 (later known as i5/OS, and now IBM i) * Servers and workstations using POWER and PowerPC processors in the RS/6000 family (later known as pSeries, then System p), running IBM AIX and Linux on Power. After the introduction of the POWER4 processor in 2001, there was little difference between both the "p" and the "i" hardware; the only differences were in the software and services offerings. With the introduction of the POWER5 processor in 2004, even the product numbering was synchronized. The ''System i5 570'' was virtually identical to the ''System p5 570''. In April ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Nvidia
Nvidia CorporationOfficially written as NVIDIA and stylized in its logo as VIDIA with the lowercase "n" the same height as the uppercase "VIDIA"; formerly stylized as VIDIA with a large italicized lowercase "n" on products from the mid 1990s to early-mid 2000s. Though unofficial, second letter capitalization of NVIDIA, i.e. nVidia, may be found within enthusiast communities and publications. ( ) is an American multinational technology company incorporated in Delaware and based in Santa Clara, California. It is a software and fabless company which designs graphics processing units (GPUs), application programming interface (APIs) for data science and high-performance computing as well as system on a chip units (SoCs) for the mobile computing and automotive market. Nvidia is a global leader in artificial intelligence hardware and software. Its professional line of GPUs are used in workstations for applications in such fields as architecture, engineering and construction, media ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Oak Ridge National Laboratory
Oak Ridge National Laboratory (ORNL) is a U.S. multiprogram science and technology national laboratory sponsored by the U.S. Department of Energy (DOE) and administered, managed, and operated by UT–Battelle as a federally funded research and development center (FFRDC) under a contract with the DOE, located in Oak Ridge, Tennessee. Established in 1943, ORNL is the largest science and energy national laboratory in the Department of Energy system (by size) and third largest by annual budget. It is located in the Roane County section of Oak Ridge, Tennessee. Its scientific programs focus on materials, nuclear science, neutron science, energy, high-performance computing, systems biology and national security, sometimes in partnership with the state of Tennessee, universities and other industries. ORNL has several of the world's top supercomputers, including Frontier, ranked by the TOP500 as the world's most powerful. The lab is a leading neutron and nuclear power research f ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
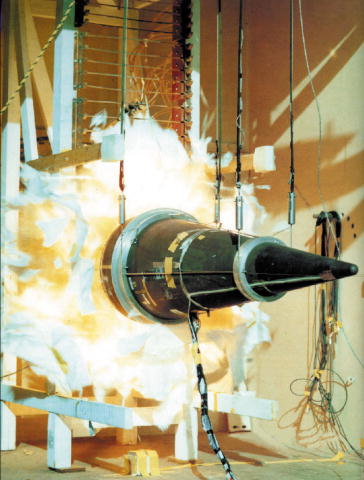
Stockpile Stewardship
Stockpile stewardship refers to the United States program of reliability testing and maintenance of its nuclear weapons without the use of nuclear testing. Because no new nuclear weapons have been developed by the United States since 1992, even its youngest weapons are at least years old (as of ). Aging weapons can fail or act unpredictably in a number of ways: the high explosives that compress their fissile material can chemically degrade, their electronic components can suffer from decay, their radioactive plutonium/uranium cores are potentially unreliable, and the isotopes used by thermonuclear weapons may be chemically unstable as well. Since the United States has also not tested nuclear weapons since 1992, this leaves the task of its stockpile maintenance resting on the use of simulations (using non-nuclear explosives tests and supercomputers, among other methods) and applications of scientific knowledge about physics and chemistry to the specific problems of weapons aging ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
National Nuclear Security Administration
The National Nuclear Security Administration (NNSA) is a United States federal agency responsible for safeguarding national security through the military application of nuclear science. NNSA maintains and enhances the safety, security, and effectiveness of the U.S. nuclear weapons stockpile; works to reduce the global danger from weapons of mass destruction; provides the United States Navy with safe and effective nuclear propulsion; and responds to nuclear and radiological emergencies in the United States and abroad. Established by the United States Congress in 2000, NNSA is a semiautonomous agency within the United States Department of Energy. The current Administrator is Jill Hruby. History The National Nuclear Security Administration was created by Congressional action in 1999, in the wake of the Wen Ho Lee spy scandal (for which Dr. Lee was exonerated) and other allegations that lax administration by the Department of Energy had resulted in the loss of U.S. nuclear s ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
.jpg)

.jpg)