|
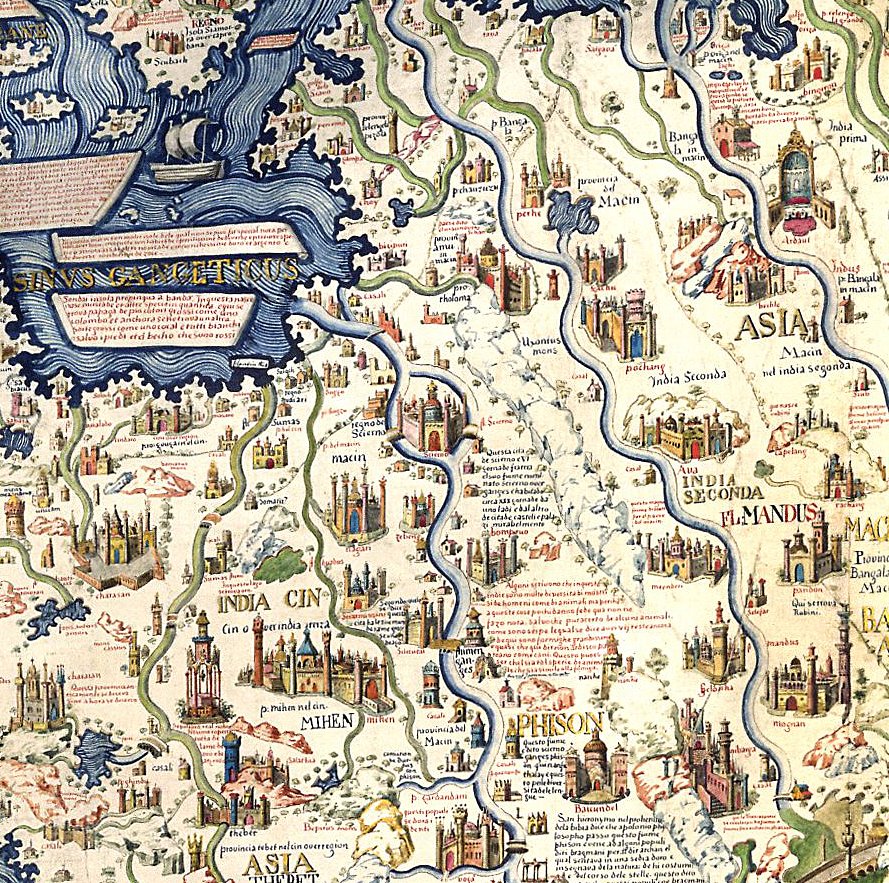
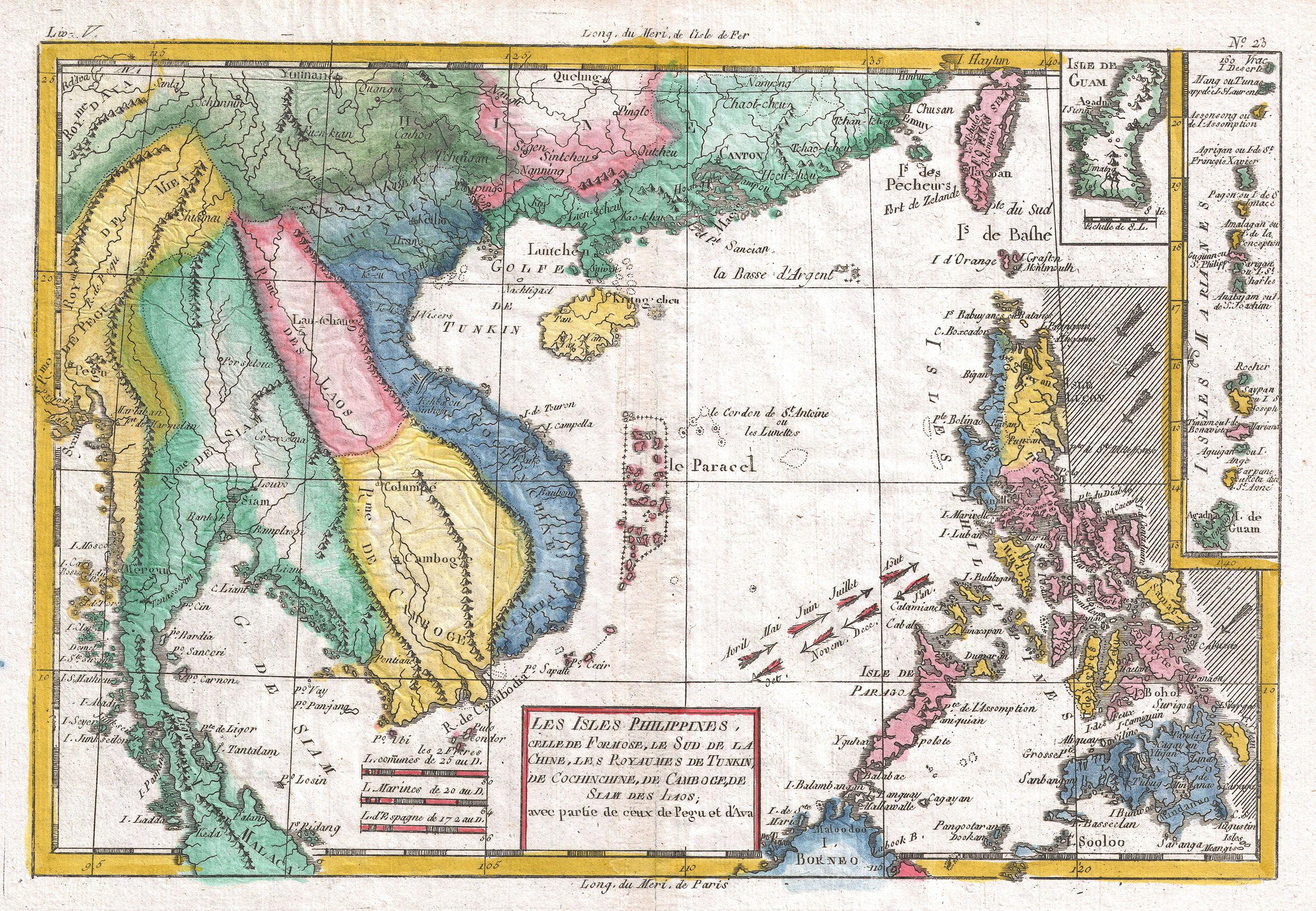
Siamese–Vietnamese War (1841–1845)
The Siamese–Vietnamese War of 1841–1845 ( th, อานามสยามยุทธ (พ.ศ. 2384 – พ.ศ. 2388), vi, Chiến tranh Việt–Xiêm (1841–1845)) was a military conflict between the Đại Nam, ruled by Emperor Thiệu Trị, and the Kingdom of Siam, under the rule of Chakkri King Nangklao. The rivalry between Vietnam and Siam over the control of the Cambodian heartlands in the Lower Mekong basin had intensified after Siam had attempted to conquer Cambodia during the previous Siamese–Vietnamese War (1831–1834). Vietnamese Emperor Minh Mạng installed Princess Ang Mey to rule Cambodia as a puppet queen regnant of his choice in 1834 and declared full suzerainty over Cambodia, which he demoted to Vietnam's 32nd province, the ''Western Commandery'' ( Tây Thành Province). In 1841, Siam seized the opportunity of discontent to aid the Khmer revolt against Vietnamese rule. King Rama III sent an army to enforce Prince Ang Duong's installation as Kin ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Siamese–Vietnamese Wars
The Siamese–Vietnamese wars were a series of armed conflicts between the Siamese Ayutthaya Kingdom and Rattanakosin Kingdom and the various dynasties of Vietnam mainly during the 18th and 19th centuries. Several of the wars took place in modern-day Cambodia. The political, dynastic, and military decline of the Khmer Empire after the 15th century, known as the Post-Angkor Period, left a power vacuum in the Mekong floodplains of central Indochina. United under strong dynastic rule, both Siam to the west and Vietnam to the east sought to achieve hegemony in the lowland region and the Lao mountains. The Siamese introduced - and Vietnam soon followed - the hostage system for Cambodian royals, who were relocated to their courts, actively undermining royal affairs and shaping future Cambodian policies. Eventually, territory was annexed by both powers, who conceived, maintained and supported their favorable Cambodian puppet kings. Actual combat mainly took place on Cambodian territory ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Chaophraya Yommarat (Kaew Singhaseni)
Yommarat ( th, ยมราช) is a Thai noble title historically given to the minister of the Krom Mueang or Nakhonban, one of the four ministries under the ''chatusadom'' system, charged with keeping the peace in the capital. Holders of the title were usually given the high rank of ''phraya'' or ''chaophraya''. List of titleholders Past holders of the title include: During the Thonburi period: *Phraya Yommarat (Baen) – Later became Chaophraya Aphaiphubet. During the Rattanakosin period #Phraya Yommarat (In) – Named by King Rama I when he assumed the throne and founded the Chakri Dynasty in 1782. Stripped of the title as punishment for mistakes made in the Burmese–Siamese War (1785–1786). #Chaophraya Yommarat (Bunnag) – Named following the war; later became Chaophraya Mahasena, the ''samuhakalahom''. #Chaophraya Yommarat (Bunma) – Later became Chaophraya Mahasena. #Chaophraya Yommarat (Noi Punyaratabandhu) – Served King Rama II; later became Chaophraya Aphaiphu ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Phra Nakhon Si Ayutthaya (city)
Phra Nakhon Si Ayutthaya ( th, พระนครศรีอยุธยา, ; also spelled "Ayudhya"), or locally and simply Ayutthaya, is the former capital of Phra Nakhon Si Ayutthaya province in Thailand. Located on an island at the confluence of the Chao Phraya and Pa Sak rivers, Ayutthaya is the birthplace of the founder of Bangkok, King Rama I. Etymology Ayutthaya is named after the city of Ayodhya in India, the birthplace of Rama in the ''Ramayana'' (Thai, ''Ramakien''); (from Khmer: ''preah'' ព្រះ ) is a prefix for a noun concerning a royal person; designates an important or capital city (from Sanskrit: ''nagara''); the Thai honorific ''sri'' or ''si'' is from the Indian term of veneration Shri. History Prior to Ayutthaya's traditional founding date, archaeological and written evidence has revealed that Ayutthaya may have existed as early as the late 13th century as a water-borne port town. Further evidence of this can be seen with Wat Phanan Choeng, w ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Ang Eng
Ang Eng ( km, អង្គអេង ; 1773 – 5 May 1796) was King of Cambodia from 1779 to his death in 1796. He reigned under the name of Neareay Reachea III ( km, នារាយណ៍រាជាទី៣, link=no). Ang Eng was a son of Outey II. He was installed the Cambodian king by Prince Talaha (Mu) ( km, ចៅហ្វ៊ាមូ, th, เจ้าฟ้าทะละหะ (มู)) in 1780. Prince Talaha (Mu) acted as regent, and was pro-Vietnamese. Talaha rebelled against Siam, Taksin decided on an invasion of Cambodia. A Siamese army under Somdej Chao Phraya Maha Kasatsuek was dispatched to Cambodia, to crown Inthraphithak as the new king of Cambodia. However, a coup occurred in the same year. Maha Kasatsuek and Maha Surasi marched back to Siam. Later, Maha Kasatsuek was crowned as the new Siamese king and became Rama I. In 1782, the Tây Sơn dynasty of Vietnam attacked Gia Định and defeated the Nguyễn lord. The Vietnamese lost their control of Cambodia ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Attrition Warfare
Attrition warfare is a military strategy consisting of belligerent attempts to win a war by wearing down the enemy to the point of collapse through continuous losses in personnel and materiel. The word ''attrition'' comes from the Latin root , meaning "to rub against", similar to the "grinding down" of the opponent's forces in attrition warfare. Strategic considerations Attrition warfare represents an attempt to grind down an opponent's ability to make war by destroying their military resources by any means including guerrilla warfare, people's war, scorched earth and all kind of battles apart from a decisive battle. Attrition warfare does not include all kinds of Blitzkrieg or using concentration of force and a decisive battle to win. The side that reinforces their army at a higher speed will normally win the war. Clausewitz called it the exhaustion of the adversary. A side that perceives itself to be at a marked disadvantage may deliberately seek out attrition warfare to neutr ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Rama III
Nangklao ( th, พระบาทสมเด็จพระนั่งเกล้าเจ้าอยู่หัว, ; 31 March 1788 – 2 April 1851), birth name Thap ( th, ทับ), also styled Rama III, was the third king of Siam under the House of Chakri, ruling from 21 July 1824 to 2 April 1851. Nangklao was the eldest surviving son of his predecessor, king Rama II. His mother Sri Sulalai was one of the king's secondary wives. Nangklao was likely designated as heir by his father, his accession was uncontested and smoothly confirmed by the grand council. Foreign observers, however, falsely perceived him as having usurped the prior claim of his half-brother Prince Mongkut, who was younger, but born to queen Sri Suriyendra and thus " legitimate" according to Western customs. Under the old concept of Thai monarchy, however, a proper king must emulate Maha Sammata in that he must be "elected by the people." Ironically, Prince Mongkut may have later contributed to thi ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Minh Mạng
Minh Mạng () or Minh Mệnh (, vi-hantu, 明 命, lit. "the bright favour of Heaven"; 25 May 1791 – 20 January 1841; born Nguyễn Phúc Đảm, also known as Nguyễn Phúc Kiểu) was the second emperor of the Nguyễn dynasty of Vietnam, reigning from 14 February 1820 until his death, on 20 January 1841. He was the fourth son of Emperor Gia Long, whose eldest son, Nguyễn Phúc Cảnh, had died in 1801. He was well known for his opposition to French involvement in Vietnam and his rigid Confucian orthodoxy. Early years Born Nguyễn Phúc Đảm at Gia Định in the middle of the Second Tây Sơn – Nguyễn War, Minh Mạng was the fourth son of lord Nguyễn Phúc Ánh – future Emperor Gia Long. His mother was Gia Long's second wife Trần Thị Đang (historically known as Empress Thuận Thiên). At the age of three, under the effect of a written agreement made by Gia Long with his first wife Tống Thị Lan (Empress Thừa Thiên), he was taken in an ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Siamese–Vietnamese War (1831–1834)
}, vi, Chiến tranh Việt–Xiêm (1831–1834)), also known as the Siamese-Cambodian War of 1831–1834, was sparked by a Siamese invasion force under General Bodindecha that was attempting to conquer Cambodia and southern Vietnam. After initial success and the defeat of the Khmer Army at the Battle of Kompong Cham in 1832, the Siamese advance was repelled in southern Vietnam in 1833 by the military forces of the Nguyễn dynasty. Upon the outbreak of a general uprising in Cambodia and Laos, the Siamese withdrew, and Vietnam was left in control of Cambodia. Background Both Siam and Vietnam emerged as the primary powers in Indochina by the early 19th century and increasingly sought to dominate Cambodia and Laos in their effort to gain hegemony over the Lower Mekong Basin. The internal struggles between factions of the Cambodian royal families during the Cambodian Dark Ages had Siam and Vietnam aggressively intervene on opposite sides to maximize their influences over Cambodia. ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Nangklao
Nangklao ( th, พระบาทสมเด็จพระนั่งเกล้าเจ้าอยู่หัว, ; 31 March 1788 – 2 April 1851), birth name Thap ( th, ทับ), also styled Rama III, was the third king of Siam under the House of Chakri, ruling from 21 July 1824 to 2 April 1851. Nangklao was the eldest surviving son of his predecessor, king Rama II. His mother Sri Sulalai was one of the king's secondary wives. Nangklao was likely designated as heir by his father, his accession was uncontested and smoothly confirmed by the grand council. Foreign observers, however, falsely perceived him as having usurped the prior claim of his half-brother Prince Mongkut, who was younger, but born to queen Sri Suriyendra and thus " legitimate" according to Western customs. Under the old concept of Thai monarchy, however, a proper king must emulate Maha Sammata in that he must be "elected by the people." Ironically, Prince Mongkut may have later contributed to this ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Chakkri Dynasty
Chakri may refer to: People * Chakri (composer) (1974–2014), Tollywood music director * Chakri Toleti, Indian American screenwriter, director, actor, and visual effects coordinator Other uses * Chakri (noble title), a historical Thai noble title for the king's chief minister * Chakri dynasty The Chakri dynasty ( th, ราชวงศ์ จักรี, , , ) is the current reigning dynasty of the Kingdom of Thailand, the head of the house is the king, who is head of state. The family has ruled Thailand since the founding of the ..., the royal house of Thailand * The Gujarati name for murukku, an Indian snack * Chakri or ''charkha'', Indian name for the spinning wheel used for making khadi cloth * A small chakram, a throwing weapon * Chakri or Chakri, a village in Jhelum, Pakistan * Chakri is an alternative name for the Indian snack Chakli {{disambiguation, geo ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Thiệu Trị
Thiệu Trị (, vi-hantu, 紹 治, lit. "inheritance of prosperity"; 6 June 1807 – 4 November 1847), personal name Nguyễn Phúc Miên Tông or Nguyễn Phúc Tuyền, was the third emperor of the Nguyễn dynasty. He was the eldest son of Emperor Minh Mạng, and reigned from 14 February 1841 until his death on 4 November 1847. Biography Emperor Thiệu Trị was much like his father, Minh Mạng, and carried on his conservative policies of isolationism and the entrenchment of Confucianism. Highly educated in the Confucian tradition, Thiệu Trị had some curiosity about the West, but like his father was very suspicious of all non-Vietnamese outsiders. At this same time, the French were in a colonial race with Great Britain and were pushing hard for stronger relations with Indochina. This, just as in the reign of Minh Mạng, also brought up Christian missionaries, mostly Spanish and French, who ignored the ban. When Trị began to imprison the missionaries, it prompted an ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |

.gif)



