|
Shoulder Examination
A shoulder examination (or shoulder exam) is a portion of a physical examination used to identify potential pathology involving the shoulder. It should be conducted with both shoulders exposed to assess for asymmetry and muscle wasting. Elements of the shoulder exam * Inspection * Palpation of sternoclavicular joint, clavicle, acromioclavicular joint, subacromial bursa, bicipital tendon. * Evaluation of passive and active range of motion: Neck range of motion should be assessed that may reveal a neck source of shoulder pain. The Apley scratch test specifically tests range of motion and in a normal exam, an individual should be able to reach C7 on external rotation, and T7 on internal rotation. * Evaluation of distal pulses * Strength testing: wrist extension tests the radial nerve, finger abduction tests the ulnar nerve, and thumb apposition tests the median nerve. * Sensation testing * Reflex testing: Triceps reflex tests C6-C8, biceps reflex tests C5 and C6, and brachioradialis ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Physical Examination
In a physical examination, medical examination, or clinical examination, a medical practitioner examines a patient for any possible medical signs or symptoms of a medical condition. It generally consists of a series of questions about the patient's medical history followed by an examination based on the reported symptoms. Together, the medical history and the physical examination help to determine a diagnosis and devise the treatment plan. These data then become part of the medical record. Types Routine The ''routine physical'', also known as ''general medical examination'', ''periodic health evaluation'', ''annual physical'', ''comprehensive medical exam'', ''general health check'', ''preventive health examination'', ''medical check-up'', or simply ''medical'', is a physical examination performed on an asymptomatic patient for medical screening purposes. These are normally performed by a pediatrician, family practice physician, physician assistant, a certified nurse pr ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Neer Impingement Test
The Neer Impingement Test is a test designed to reproduce symptoms of rotator cuff impingement through flexing the shoulder and pressure application. Symptoms should be reproduced if there is a problem with the supraspinatus or biceps brachii. This test is also associated with the Hawkins-Kennedy Test and Jobe's Test. Procedure The patient is asked to sit on the examination table or to stand next to it with arms in internal rotation. Examiner should stand on the side which is being tested. Examiner will place one hand on the patient's scapula The scapula (plural scapulae or scapulas), also known as the shoulder blade, is the bone that connects the humerus (upper arm bone) with the clavicle (collar bone). Like their connected bones, the scapulae are paired, with each scapula on eithe ..., and the other hand on the patient's arm below the elbow. The examiner will passively flex the shoulder forward. Mechanism When performing the Neer Impingement Test, the elbow should be exte ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Yergason's Test
Yergason's test is a special test used for orthopedic examination of the shoulder and upper arm region, specifically the biceps tendon.Thomas W. Woodward, Thomas M. Best. "The Painful Shoulder: Part 1. Clinical Evaluation." American Family Physicians. Ed. William E. Schekler. 1 May 2000. 9 March 2011. . Purpose It identifies the presence of a pathology involving the biceps tendon or glenoid labrum. The specific positive findings to the test include: pain in the bicipital groove indicating biceps tendinitis,Jeff G. Konin ''et al''. ''Special Tests for Orthopedic Examination: Third Edition.'' Thorofare, NJ. SLACK Incorporated, 2006.W. Ben Kibler, Aaron D. Sciascia, Peter Hester, David Dome, and Cale Jacobs. "Critical Utility of Traditional and New Tests in the Diagnosis of New Bicep Tendon Injuries in Superior Labrum Anterior and Posterior Lesions in the Shoulder." ''Am J Sports Med.'' 37 (2009): 1840-1847. subluxation of the long head of the biceps brachii muscle, and p ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Glenoid Labrum
The glenoid labrum (glenoid ligament) is a fibrocartilaginous structure (not a fibrocartilage as previously thought) rim attached around the margin of the glenoid cavity in the shoulder blade. The shoulder joint is considered a ball and socket joint. However, in bony terms the 'socket' (the glenoid fossa of the scapula) is quite shallow and small, covering at most only a third of the 'ball' (the head of the humerus). The socket is deepened by the glenoid labrum, stabilizing the shoulder joint. The labrum is triangular in section; the base is fixed to the circumference of the cavity, while the free edge is thin and sharp. It is continuous above with the tendon of the long head of the biceps brachii, which gives off two fascicles to blend with the fibrous tissue of the labrum. Structure Clinical significance Injury Tearing of the labrum can occur from either acute trauma or repetitive shoulder motion such as in the sports of swimming, baseball and football. Acute trauma m ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Bicipital Tenosynovitis
Bicipital tenosynovitis is tendinitis or inflammation of the tendon and sheath lining of the biceps muscle. It is often the result of many years of small tears or other degenerative changes in the tendon first manifesting in middle age, but can be due to a sudden injury. Calcification of the tendon, and osteophytes ("bone spurs") in the intertubercular groove can be apparent on x-rays. The condition (which can also occur in dogs) is commonly treated with physical therapy and cortisone Cortisone is a pregnene (21-carbon) steroid hormone. It is a naturally-occurring corticosteroid metabolite that is also used as a pharmaceutical prodrug; it is not synthesized in the adrenal glands. Cortisol is converted by the action of the enzy .... in Adult Orthopaedic Nursing, by Delores ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Subscapularis
The subscapularis is a large triangular muscle which fills the subscapular fossa and inserts into the lesser tubercle of the humerus and the front of the capsule of the shoulder-joint. Structure It arises from its medial two-thirds and Some fibers arise from tendinous laminae, which intersect the muscle and are attached to ridges on the bone; others from an aponeurosis, which separates the muscle from the teres major and the long head of the triceps brachii. The fibers pass laterally and coalesce into a tendon that is inserted into the lesser tubercle of the humerus and the anterior part of the shoulder-joint capsule. Tendinous fibers extend to the greater tubercle with insertions into the bicipital groove. Relations The tendon of the muscle is separated from the neck of the scapula by a large bursa, which communicates with the cavity of the shoulder-joint through an aperture in the capsule. The subscapularis is separated from the serratus anterior books.google.com/books? ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
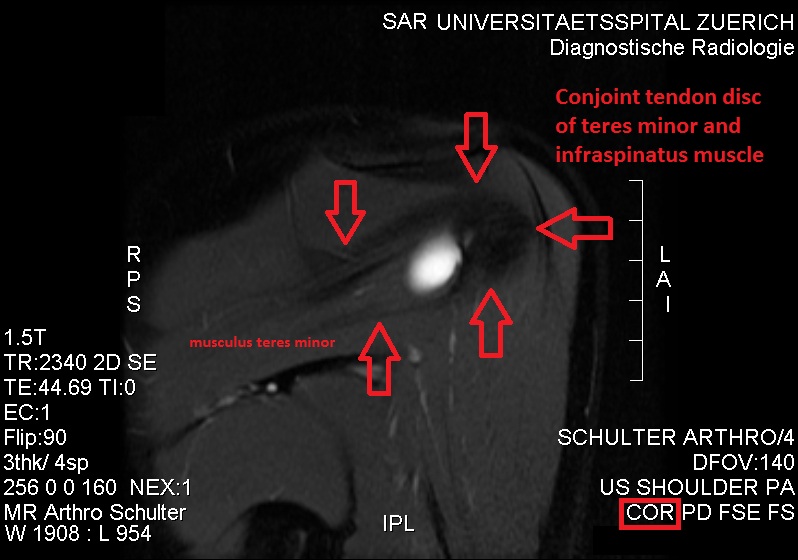
Teres Minor
The teres minor (Latin ''teres'' meaning 'rounded') is a narrow, elongated muscle of the rotator cuff. The muscle originates from the lateral border and adjacent posterior surface of the corresponding right or left scapula and inserts at both the greater tubercle of the humerus and the posterior surface of the joint capsule. The primary function of the teres minor is to modulate the action of the deltoid, preventing the humeral head from sliding upward as the arm is abducted. It also functions to rotate the humerus laterally. The teres minor is innervated by the axillary nerve. Structure It arises from the dorsal surface of the axillary border of the scapula for the upper two-thirds of its extent, and from two aponeurotic laminae, one of which separates it from the infraspinatus muscle, the other from the teres major muscle. Its fibers run obliquely upwards and laterally; the upper ones end in a tendon which is inserted into the lowest of the three impressions on the greater tub ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Infraspinatus
In human anatomy, the infraspinatus muscle is a thick triangular muscle, which occupies the chief part of the infraspinatous fossa.''Gray's Anatomy'', see infobox. As one of the four muscles of the rotator cuff, the main function of the infraspinatus is to externally rotate the humerus and stabilize the shoulder joint. Structure It attaches medially to the infraspinous fossa of the scapula and laterally to the middle facet of the greater tubercle of the humerus. The muscle arises by fleshy fibers from the medial two-thirds of the infraspinatous fossa, and by tendinous fibers from the ridges on its surface; it also arises from the infraspinatous fascia which covers it, and separates it from the teres major and teres minor. The fibers converge to a tendon, which glides over the lateral border of the spine of the scapula and passing across the posterior part of the capsule of the shoulder-joint, is inserted into the middle impression on the greater tubercle of the humerus. The trape ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Supraspinatus
The supraspinatus (plural ''supraspinati'') is a relatively small muscle of the upper back that runs from the supraspinous fossa superior portion of the scapula (shoulder blade) to the greater tubercle of the humerus. It is one of the four rotator cuff muscles and also abducts the arm at the shoulder. The spine of the scapula separates the supraspinatus muscle from the infraspinatus muscle, which originates below the spine. Structure The supraspinatus muscle arises from the supraspinous fossa, a shallow depression in the body of the scapula above its spine. The supraspinatus muscle tendon passes laterally beneath the cover of the acromion. Research in 1996 showed that the postero-lateral origin was more lateral than classically described. The supraspinatus tendon is inserted into the superior facet of the greater tubercle of the humerus. The distal attachments of the three rotator cuff muscles that insert into the greater tubercle of the humerus can be abbreviated as SIT when vie ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Drop Arm Test
The drop arm test is designed to determine a patient's ability to sustain humeral joint motion through eccentric contraction as the arm is taken through the full motion of abduction to adduction. It will determine if the patient has an underlying rotator cuff dysfunction. Procedure The patient is asked to either sit on an examination table or stand while performing this test. Examiner should be standing on the patient's lateral side or behind the arm being evaluated. Examiner will passively abduct the patient's shoulder (humerus) to 90 degrees. The patient is then asked to slowly lower or adduct the shoulder to their side. If the patient is unable to perform this motion, the examiner can hold the humerus at 90 degrees of abduction and apply slight pressure to the distal forearm. If the patient's arm falls to their side, this also indicates a rotator cuff dysfunction. Inability to controllably lower the arm can indicate a rotator cuff dysfunction, most commonly the supraspinatus. Me ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Supraspinatus Muscle
The supraspinatus (plural ''supraspinati'') is a relatively small muscle of the upper back that runs from the supraspinous fossa superior portion of the scapula (shoulder blade) to the greater tubercle of the humerus. It is one of the four rotator cuff muscles and also abducts the arm at the shoulder. The spine of the scapula separates the supraspinatus muscle from the infraspinatus muscle, which originates below the spine. Structure The supraspinatus muscle arises from the supraspinous fossa, a shallow depression in the body of the scapula above its spine. The supraspinatus muscle tendon passes laterally beneath the cover of the acromion. Research in 1996 showed that the postero-lateral origin was more lateral than classically described. The supraspinatus tendon is inserted into the superior facet of the greater tubercle of the humerus. The distal attachments of the three rotator cuff muscles that insert into the greater tubercle of the humerus can be abbreviated as SIT when vie ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
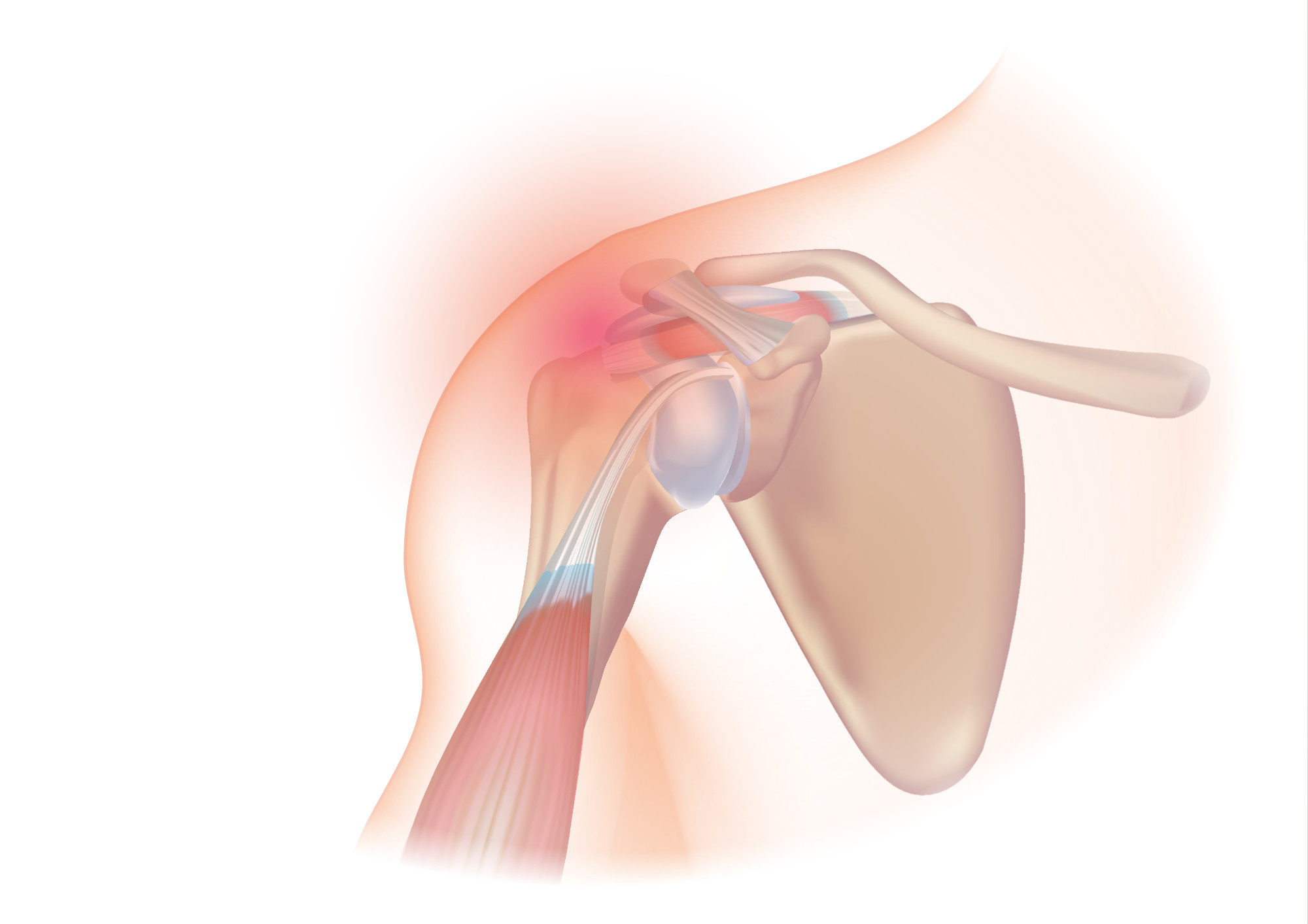
Rotator Cuff Tear
A rotator cuff tear is an injury where one or more of the tendons or muscles of the rotator cuff of the shoulder get torn. Symptoms may include shoulder pain, which is often worse with movement, limited range of motion, or weakness. This may limit people's ability to brush their hair or put on clothing. Clicking may also occur with movement of the arm. Tears may occur as the result of a sudden force or gradually over time. Risk factors include certain repetitive activities, smoking, and a family history of the condition. Diagnosis is based on symptoms, examination, and medical imaging. The rotator cuff is made up of the supraspinatus, infraspinatus, teres minor, and subscapularis. The supraspinatus is the most commonly affected. Treatment may include pain medication such as NSAIDs and specific exercises. It is recommended that people who are unable to raise their arm above 90 degrees after 2 weeks should be further assessed. In severe cases surgery may be tried, however ben ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |