|
Shibaniba
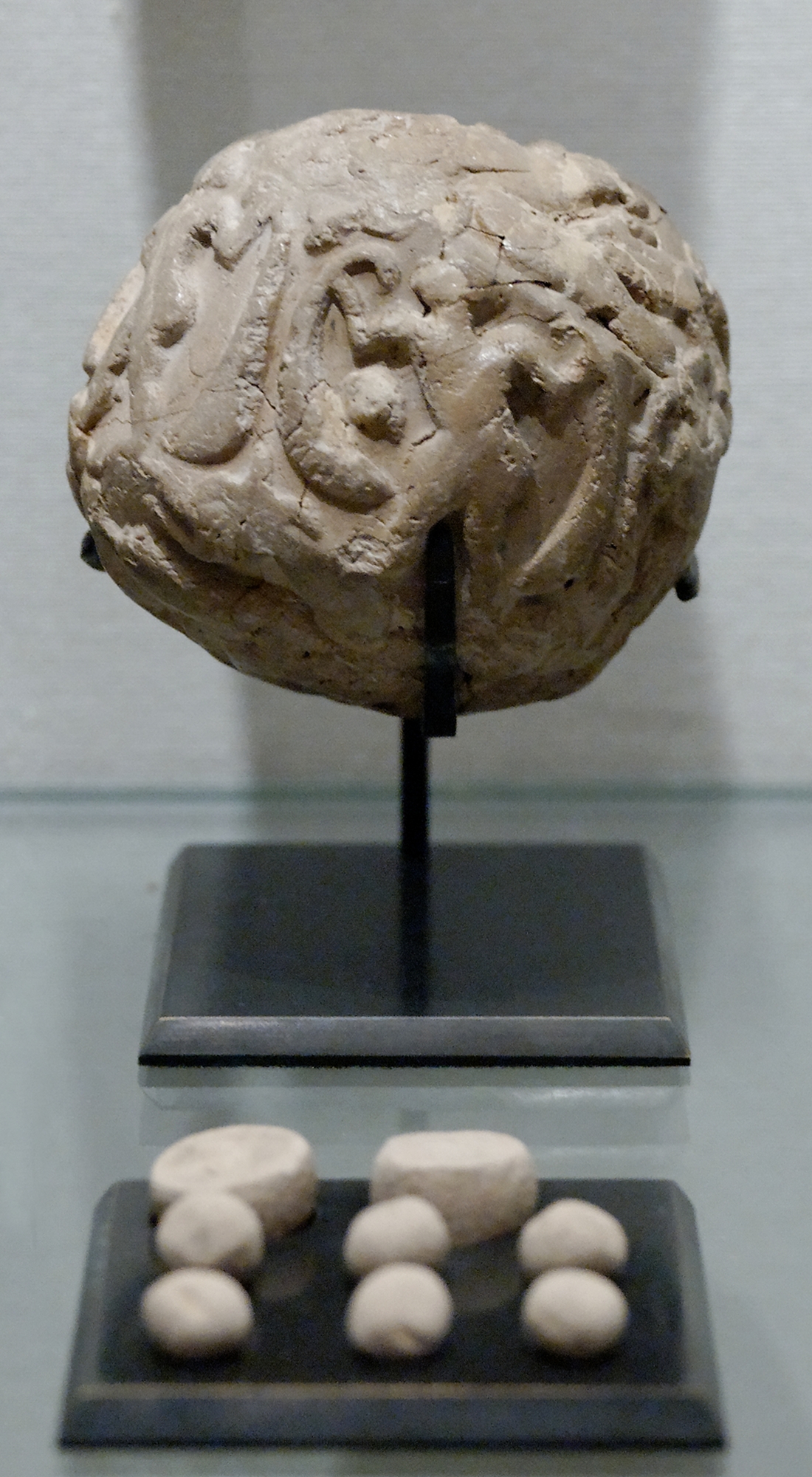
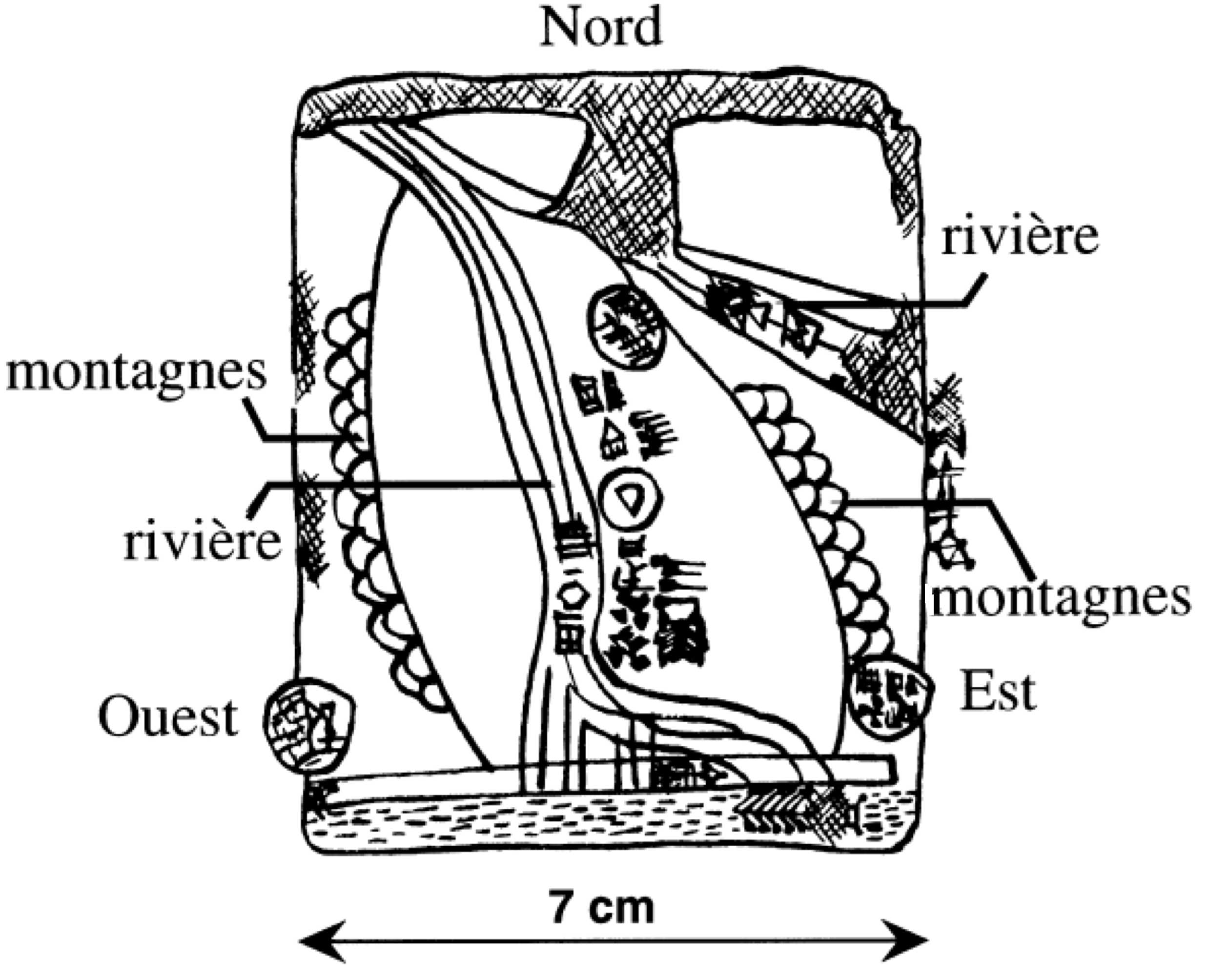
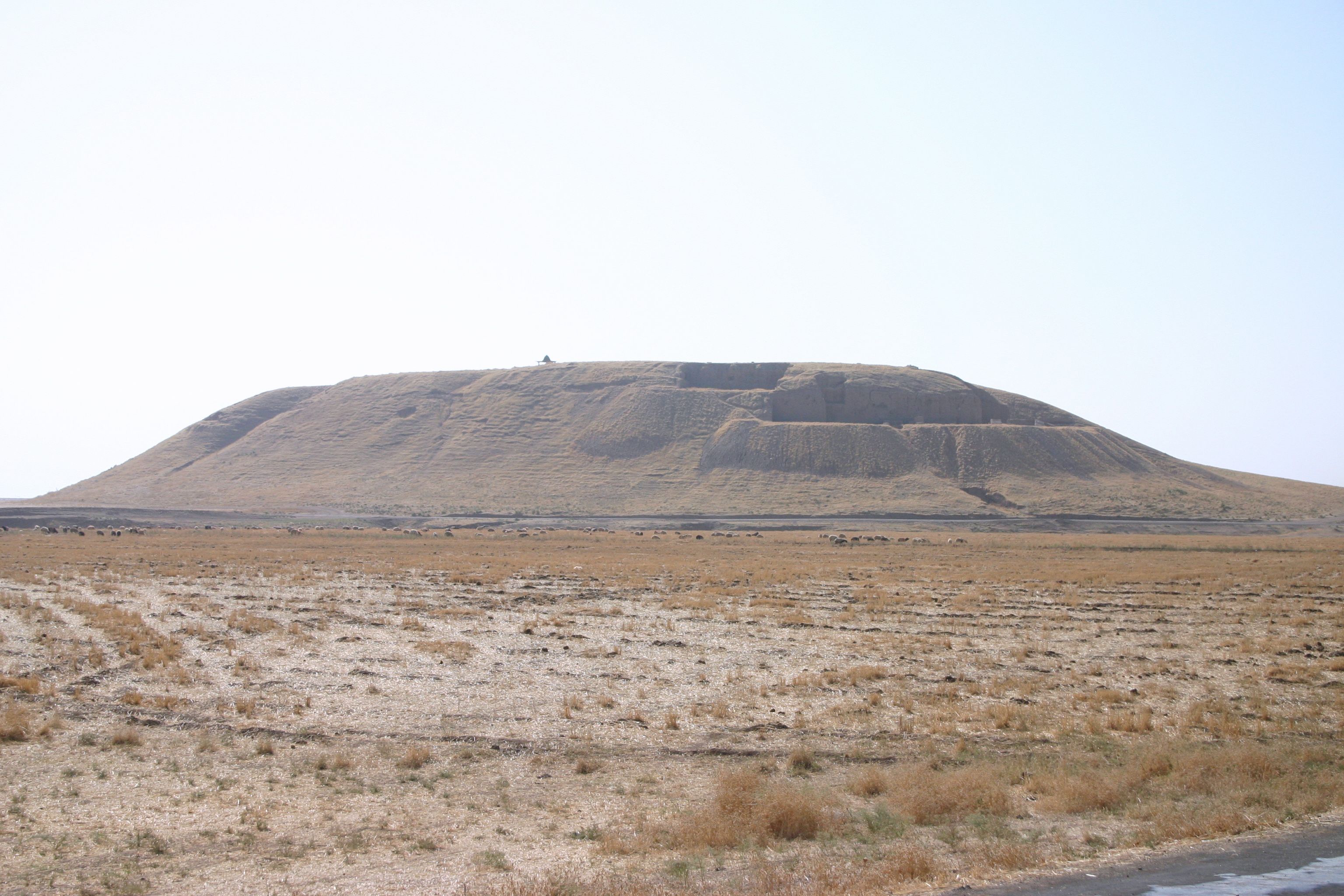
Tell Billa (also Tell Billah and Baasheikhah) is an archaeological site near Bashiqa in Nineveh Province (Iraq) 20 kilometers northeast of Mosul. Beginning in Middle Assyrian times the ancient city, not far from Assur, was named Shibaniba. Its earlier name is not known. In 2022 it was proposed that Tell Billa was the site of the Ur III period Hurrian city Šimānum (known as Asimānum during the Akkadian Empire). History of archaeological research After some minor soundings done by Austen Henry Layard around 1850, Tell Billa was excavated between 1930 and 1934 by a team from the University of Pennsylvania and the American Schools of Oriental Research. The excavation was led by Ephraim Avigdor Speiser with Charles Bache. The work was complicated by the fact that the mound was divided up among 18 owners including a Jacobite church. At the same time, these scholars explored the related nearby ancient site of Tepe Gawra, which is located about northeast of Billa. Tell Billa and it ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Cities Of The Ancient Near East
The earliest cities in history were in the ancient Near East, an area covering roughly that of the modern Middle East: its history began in the 4th millennium BC and ended, depending on the interpretation of the term, either with the conquest by the Achaemenid Empire in the 6th century BC or with that by Alexander the Great in the 4th century BC. The largest cities of the Bronze Age Near East housed several tens of thousands of people. Memphis in the Early Bronze Age, with some 30,000 inhabitants, was the largest city of the time by far. Ebla is estimated to have had a population of 40,000 inhabitants in the Intermediate Bronze age. Ur in the Middle Bronze Age is estimated to have had some 65,000 inhabitants; Babylon in the Late Bronze Age similarly had a population of some 50,000–60,000. Niniveh had some 20,000–30,000, reaching 100,000 only in the Iron Age (around 700 BC). In Akkadian and Hittite orthography, URU became a determinative sign denoting a city, or combi ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Ephraim Avigdor Speiser
Ephraim Avigdor Speiser (January 24, 1902 – June 15, 1965) was a Polish-born American Assyriologist. He discovered the ancient site of Tepe Gawra in 1927 and supervised its excavation between 1931 and 1938. Speiser was married to Sue Gimbel Dannenbaum, granddaughter of Charles Gimbel of the Gimbel Brothers. They had two children together, Jean and Joel. Early life Speiser was born in Skalat, Galicia (then in Austrian Poland, now Ukraine) on January 24, 1902. He went to school in Lemberg (later called Lwow, now Lviv), attending the Imperial Gymnasium of Lemberg and later graduating from the College of Lemberg in 1918. Two years later, at the age of 18, he emigrated to the United States and eventually became a US citizen in 1926. In the United States, Speiser received his M.A. in Semitics at the University of Pennsylvania in 1923, studying under J.A. Montgomery and Max Margolis. He continued his studies under Max Margolis and earned his Ph.D. from Dropsie College in Philade ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Nineveh Province
Nineveh Governorate ( ar, محافظة نينوى, syr, ܗܘܦܪܟܝܐ ܕܢܝܢܘܐ, Hoparkiya d’Ninwe, ckb, پارێزگای نەینەوا, Parêzgeha Neynewa), also known as Ninawa Governorate, is a Governorates of Iraq, governorate in northern Iraq. It has an area of and an estimated population of 2,453,000 people as of 2003. Its largest city and provincial capital is Mosul, which lies across the Tigris river from the ruins of ancient Nineveh. Before 1976, it was called ''Mosul Province'' and included the present-day Dohuk Governorate. The second largest city is Tal Afar, which has an almost exclusively Iraqi Turkmen, Turkmen population. An ethnically, religiously and culturally diverse region, it was partly conquered by Islamic State of Iraq and the Levant, ISIS in 2014. Iraqi government forces Battle of Mosul (2016–2017), retook the city of Mosul in 2017. Recent history and administration Its two cities endured the 2003 Invasion of Iraq, 2003 U.S.-led invasion of ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Hurrian
The Hurrians (; cuneiform: ; transliteration: ''Ḫu-ur-ri''; also called Hari, Khurrites, Hourri, Churri, Hurri or Hurriter) were a people of the Bronze Age Near East. They spoke a Hurrian language and lived in Anatolia, Syria and Northern Mesopotamia. The largest and most influential Hurrian nation was the kingdom of Mitanni, its ruling class perhaps being Indo-Aryan speakers. The population of the Hittite Empire in Anatolia included a large population of Hurrians, and there is significant Hurrian influence in Hittite mythology. By the Early Iron Age, the Hurrians had been assimilated with other peoples. The state of Urartu later covered some of the same area. Language The Hurrian language is closely related to the Urartian language, the language of the ancient kingdom of Urartu. Together they form the Hurro-Urartian language family. The external connections of the Hurro-Urartian languages are disputed. There exist various proposals for a genetic relationship to ot ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Archaeological Sites In Iraq
Archaeology or archeology is the scientific study of human activity through the recovery and analysis of material culture. The archaeological record consists of artifacts, architecture, biofacts or ecofacts, sites, and cultural landscapes. Archaeology can be considered both a social science and a branch of the humanities. It is usually considered an independent academic discipline, but may also be classified as part of anthropology (in North America – the four-field approach), history or geography. Archaeologists study human prehistory and history, from the development of the first stone tools at Lomekwi in East Africa 3.3 million years ago up until recent decades. Archaeology is distinct from palaeontology, which is the study of fossil remains. Archaeology is particularly important for learning about prehistoric societies, for which, by definition, there are no written records. Prehistory includes over 99% of the human past, from the Paleolithic until the advent of ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Tells (archaeology)
In archaeology, a tell or tel (borrowed into English from ar, تَلّ, ', 'mound' or 'small hill'), is an artificial topographical feature, a species of mound consisting of the accumulated and stratified debris of a succession of consecutive settlements at the same site, the refuse of generations of people who built and inhabited them, and of natural sediment. (Very limited snippet view).Matthews (2020)Introduction and Definition/ref> Tells are most commonly associated with the ancient Near East, but they are also found elsewhere, such as Southern and parts of Central Europe, from Greece and Bulgaria to Hungary and SpainBlanco-González & Kienlin, eds (2020), 6th page of chapter 1, see map. and in North Africa. Within the Near East, they are concentrated in less arid regions, including Upper Mesopotamia, the Southern Levant, Anatolia and Iran, which had more continuous settlement. Eurasian tells date to the Neolithic,Blanco-González & Kienlin, eds (2020), 2nd page of chapter 1, ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Parthian Empire
The Parthian Empire (), also known as the Arsacid Empire (), was a major Iranian political and cultural power in ancient Iran from 247 BC to 224 AD. Its latter name comes from its founder, Arsaces I, who led the Parni tribe in conquering the region of Parthia in Iran's northeast, then a satrapy (province) under Andragoras, who was rebelling against the Seleucid Empire. Mithridates I (r. c. 171–132 BC) greatly expanded the empire by seizing Media and Mesopotamia from the Seleucids. At its height, the Parthian Empire stretched from the northern reaches of the Euphrates, in what is now central-eastern Turkey, to present-day Afghanistan and western Pakistan. The empire, located on the Silk Road trade route between the Roman Empire in the Mediterranean Basin and the Han dynasty of China, became a center of trade and commerce. The Parthians largely adopted the art, architecture, religious beliefs, and royal insignia of their culturally heterogene ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Faience
Faience or faïence (; ) is the general English language term for fine tin-glazed pottery. The invention of a white pottery glaze suitable for painted decoration, by the addition of an oxide of tin to the slip of a lead glaze, was a major advance in the history of pottery. The invention seems to have been made in Iran or the Middle East before the ninth century. A kiln capable of producing temperatures exceeding was required to achieve this result, the result of millennia of refined pottery-making traditions. The term is now used for a wide variety of pottery from several parts of the world, including many types of European painted wares, often produced as cheaper versions of porcelain styles. English generally uses various other terms for well-known sub-types of faience. Italian tin-glazed earthenware, at least the early forms, is called maiolica in English, Dutch wares are called Delftware, and their English equivalents English delftware, leaving "faience" as the normal te ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Neo-Assyrian
The Neo-Assyrian Empire was the fourth and penultimate stage of ancient Assyrian history and the final and greatest phase of Assyria as an independent state. Beginning with the accession of Adad-nirari II in 911 BC, the Neo-Assyrian Empire grew to dominate the ancient Near East throughout much of the 8th and 7th centuries BC, becoming the largest empire in history up to that point. Because of its geopolitical dominance and ideology based in world domination, the Neo-Assyrian Empire is by many researchers regarded to have been the first world empire in history. At its height, the empire was the strongest military power in the world and ruled over all of Mesopotamia, the Levant and Egypt, as well as portions of Anatolia, Arabia and modern-day Iran and Armenia. The early Neo-Assyrian kings were chiefly concerned with restoring Assyrian control over much of northern Mesopotamia and Syria, since significant portions of the preceding Middle Assyrian Empire had been lost during a long p ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Late Bronze Age
The Bronze Age is a historic period, lasting approximately from 3300 BC to 1200 BC, characterized by the use of bronze, the presence of writing in some areas, and other early features of urban civilization. The Bronze Age is the second principal period of the three-age system proposed in 1836 by Christian Jürgensen Thomsen for classifying and studying ancient societies and history. An ancient civilization is deemed to be part of the Bronze Age because it either produced bronze by smelting its own copper and alloying it with tin, arsenic, or other metals, or traded other items for bronze from production areas elsewhere. Bronze is harder and more durable than the other metals available at the time, allowing Bronze Age civilizations to gain a technological advantage. While terrestrial iron is naturally abundant, the higher temperature required for smelting, , in addition to the greater difficulty of working with the metal, placed it out of reach of common use until the end o ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Nuzi
Nuzi (or Nuzu; Akkadian Gasur; modern Yorghan Tepe, Iraq) was an ancient Mesopotamian city southwest of the city of Arrapha (modern Kirkuk), located near the Tigris river. The site consists of one medium-sized multiperiod tell and two small single period mounds. History The site showed occupation as far back as the late Uruk period. The city, then named Gasur, was founded in the third millennium during the time of the Akkadian Empire. In the middle of the second millennium the Hurrians gained control of the town and renamed it Nuzi. The history of the site during the intervening period is unclear, though the presence of a few cuneiform tablets from the Old Assyrian Empire indicates that trade with nearby Assur was taking place. After the fall of the Hurrian kingdom of Mitanni to Ashur-uballit I of the Middle Assyrian Empire, Nuzi went into gradual decline. Note that while the Hurrian period is well known from full excavation of those strata, the earlier history is not as reliab ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
History Of Ancient Numeral Systems
Number systems have progressed from the use of fingers and tally marks, perhaps more than 40,000 years ago, to the use of sets of glyphs able to represent any conceivable number efficiently. The earliest known unambiguous notations for numbers emerged in Mesopotamia about 5000 or 6000 years ago. Prehistory Counting initially involves the fingers, given that digit-tallying is common in number systems that are emerging today, as is the use of the hands to express the numbers five and ten. In addition, the majority of the world's number systems are organized by tens, fives, and twenties, suggesting the use of the hands and feet in counting, and cross-linguistically, terms for these amounts are etymologically based on the hands and feet. Finally, there are neurological connections between the parts of the brain that appreciate quantity and the part that "knows" the fingers (finger gnosia), and these suggest that humans are neurologically predisposed to use their hands in counti ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
%2C_(033)_der_geladene_Gastredner_Athiel_al-Nudschafi%2C_Gouverneur_von_Ninive.jpg)

.jpg)

%2C_Nisa_mint.jpg)
.jpg)