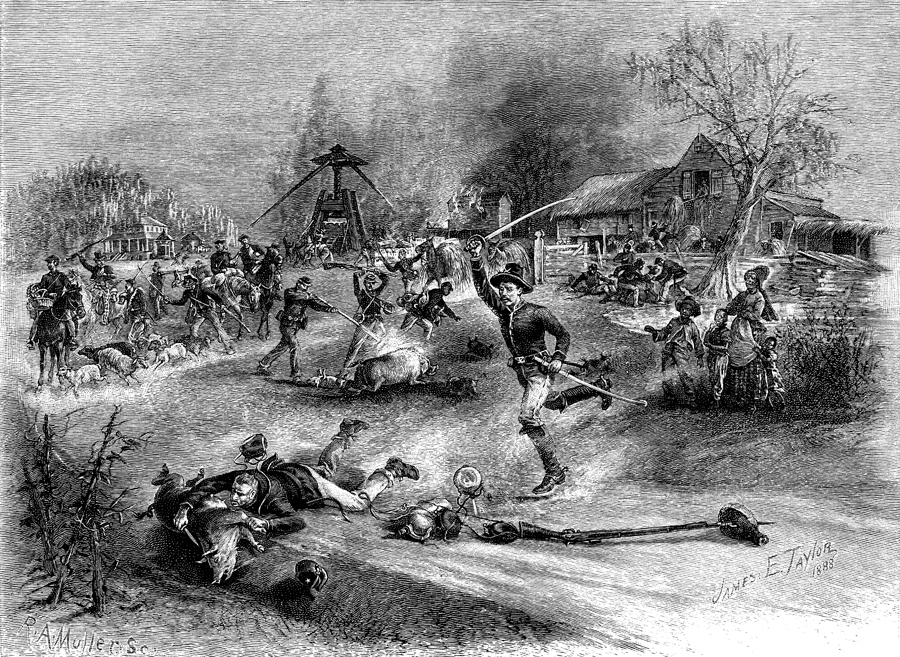|
Sherman’s March To The Sea
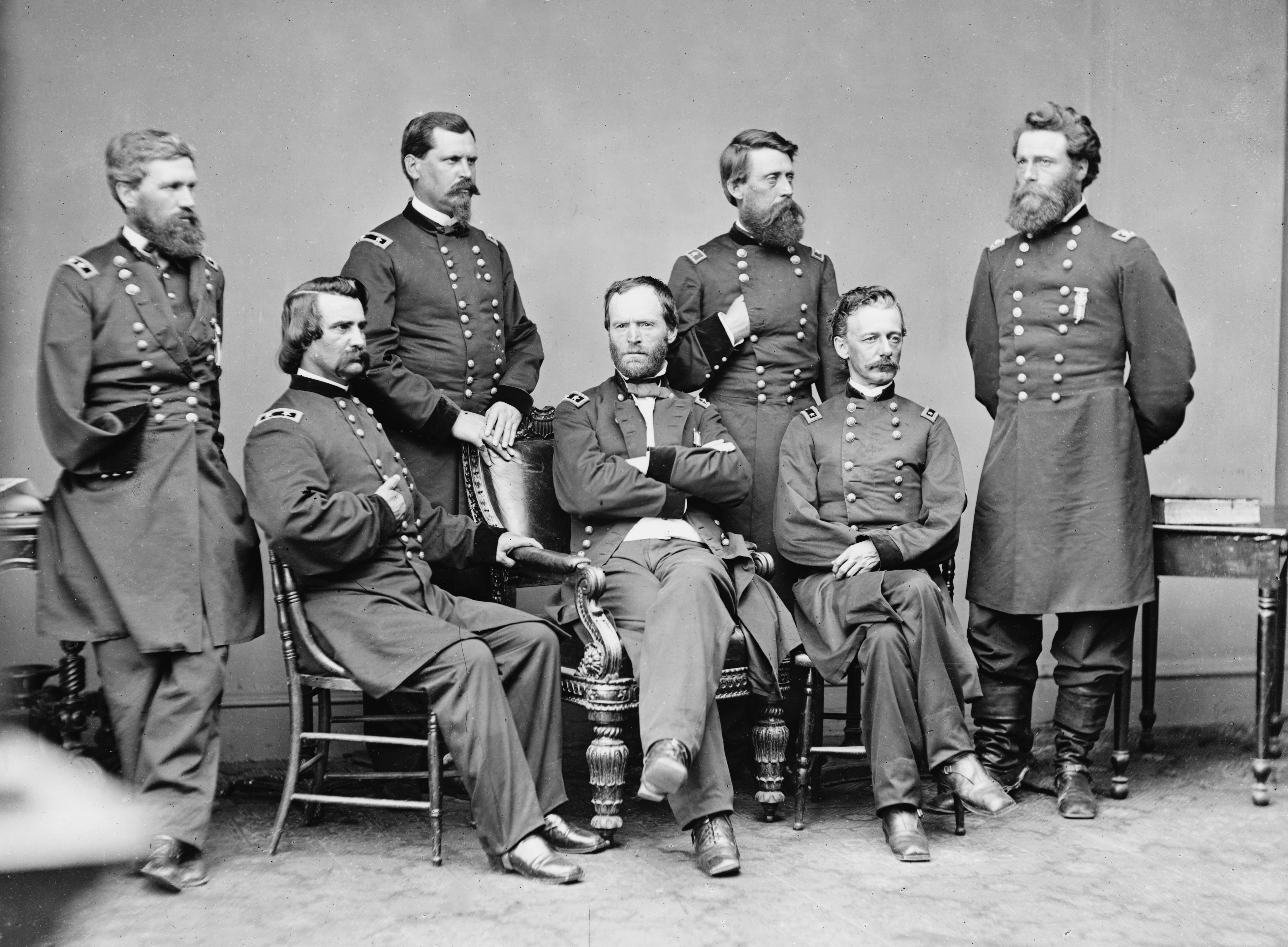
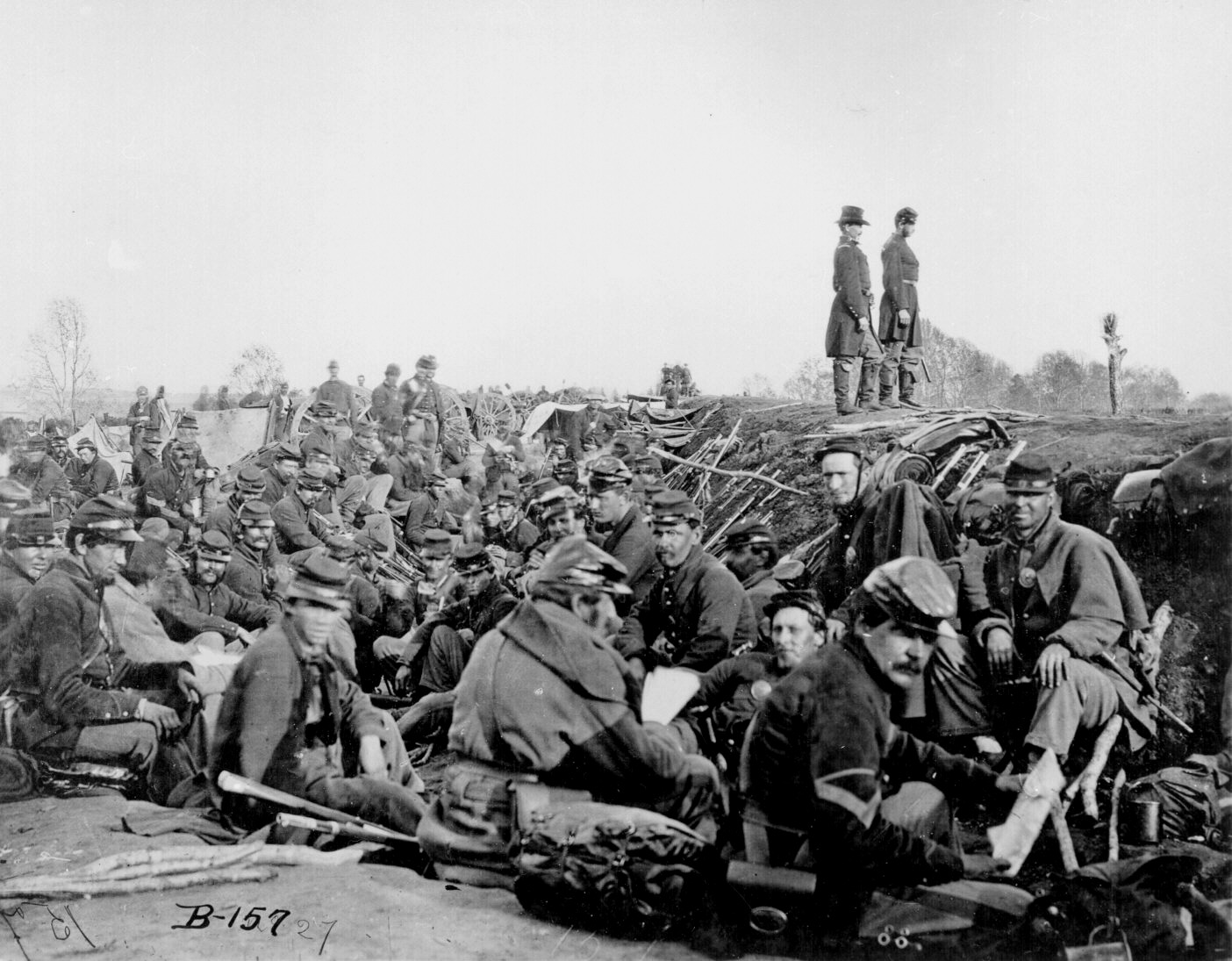
Sherman's March to the Sea (also known as the Savannah campaign or simply Sherman's March) was a military campaign of the American Civil War conducted through Georgia from November 15 until December 21, 1864, by William Tecumseh Sherman, major general of the Union Army. The campaign began with Sherman's troops leaving the captured city of Atlanta on November 15 and ended with the capture of the port of Savannah on December 21. His forces followed a "scorched earth" policy, destroying military targets as well as industry, infrastructure, and civilian property, disrupting the Confederacy's economy and transportation networks. The operation debilitated the Confederacy and helped lead to its eventual surrender. Sherman's decision to operate deep within enemy territory without supply lines was unusual for its time, and the campaign is regarded by some historians as an early example of modern warfare or total war. Background and objectives Military situation Sherman's "March to ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
American Civil War
The American Civil War (April 12, 1861 – May 26, 1865; also known by other names) was a civil war in the United States. It was fought between the Union ("the North") and the Confederacy ("the South"), the latter formed by states that had seceded. The central cause of the war was the dispute over whether slavery would be permitted to expand into the western territories, leading to more slave states, or be prevented from doing so, which was widely believed would place slavery on a course of ultimate extinction. Decades of political controversy over slavery were brought to a head by the victory in the 1860 U.S. presidential election of Abraham Lincoln, who opposed slavery's expansion into the west. An initial seven southern slave states responded to Lincoln's victory by seceding from the United States and, in 1861, forming the Confederacy. The Confederacy seized U.S. forts and other federal assets within their borders. Led by Confederate President Jefferson Davis, ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Scorched Earth
A scorched-earth policy is a military strategy that aims to destroy anything that might be useful to the enemy. Any assets that could be used by the enemy may be targeted, which usually includes obvious weapons, transport vehicles, communication sites, and industrial resources. However, anything useful to the advancing enemy may be targeted, including food stores and agricultural areas, water sources, and even the local people themselves, though the last has been banned under the 1977 Geneva Conventions. The practice can be carried out by the military in enemy territory or in its own home territory while it is being invaded. It may overlap with, but is not the same as, punitive destruction of the enemy's resources, which is usually done as part of political strategy, rather than operational strategy. Notable historic examples of scorched-earth tactics include William Tecumseh Sherman's March to the Sea in the American Civil War, Kit Carson's subjugation of the America ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Railroad
Rail transport (also known as train transport) is a means of transport that transfers passengers and goods on wheeled vehicles running on rails, which are incorporated in tracks. In contrast to road transport, where the vehicles run on a prepared flat surface, rail vehicles (rolling stock) are directionally guided by the tracks on which they run. Tracks usually consist of steel rails, installed on sleepers (ties) set in ballast, on which the rolling stock, usually fitted with metal wheels, moves. Other variations are also possible, such as "slab track", in which the rails are fastened to a concrete foundation resting on a prepared subsurface. Rolling stock in a rail transport system generally encounters lower frictional resistance than rubber-tyred road vehicles, so passenger and freight cars (carriages and wagons) can be coupled into longer trains. The operation is carried out by a railway company, providing transport between train stations or freight customer facili ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Bummers
Bummers was a nickname applied to foragers of Maj. Gen. William Tecumseh Sherman's Union army during its March to the Sea and north through South Carolina and North Carolina during the American Civil War. History Origin The designation "bummers" was used, both by soldiers and civilians, to describe Sherman's soldiers, official and unofficial, who "requisitioned" food from Southern homes along the route of the Army's march. Often highly destructive in nature, bummers became notorious among Southerners for looting and vandalism, and they did much to shatter the illusion that the Confederate Army was successfully defending its territory on all fronts. The bummers' activities in Georgia and the Carolinas helped ensure that the South would be unable to sustain its war effort; additionally, bummers' destruction of industrial property rendered the garrisoning of southern cities largely unnecessary by destroying most, if not all, of those facilities in their path that replenished the ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Meridian Campaign
The Meridian campaign or Meridian expedition took place from February 3 – March 6, 1864, from Vicksburg, Mississippi to Meridian, Mississippi, by the Union Army of the Tennessee, led by Maj. Gen. William Tecumseh Sherman. Sherman captured Meridian, Mississippi, inflicting heavy damage to it. The campaign is viewed by historians as a prelude to Sherman's March to the Sea (Savannah campaign) in that a large swath of damage and destruction was inflicted on Central Mississippi as Sherman marched across the state and back. Two supporting columns were under the command of Brigadier General William Sooy Smith and Colonel James Henry Coates. Smith's expedition was tasked to destroy a rebel cavalry commanded by Major General Nathan Bedford Forrest, maintain communications with Middle Tennessee and take men from the defense on the Mississippi River to the Atlanta campaign. To maintain communications, it was to protect the Mobile and Ohio Railroad. Coates' expedition moved up the Yazoo ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Vicksburg Campaign
The Vicksburg campaign was a series of maneuvers and battles in the Western Theater of the American Civil War directed against Vicksburg, Mississippi, a fortress city that dominated the last Confederate-controlled section of the Mississippi River. The Union Army of the Tennessee under Major General Ulysses S. Grant gained control of the river by capturing this stronghold and defeating Lieutenant General John C. Pemberton's forces stationed there. The campaign consisted of many important naval operations, troop maneuvers, failed initiatives, and eleven distinct battles from December 26, 1862, to July 4, 1863. Military historians divide the campaign into two formal phases: operations against Vicksburg (December 1862 – January 1863) and Grant's operations against Vicksburg (March–July 1863). Grant initially planned a two-pronged approach in which half of his army, under Maj. Gen. William Tecumseh Sherman, would advance to the Yazoo River and attempt to reach Vic ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Siege Of Petersburg
The Richmond–Petersburg campaign was a series of battles around Petersburg, Virginia, fought from June 9, 1864, to March 25, 1865, during the American Civil War. Although it is more popularly known as the Siege of Petersburg, it was not a classic military siege, in which a city is usually surrounded and all supply lines are cut off, nor was it strictly limited to actions against Petersburg. The campaign consisted of nine months of trench warfare in which Union forces commanded by Lt. Gen. Ulysses S. Grant assaulted Petersburg unsuccessfully and then constructed trench lines that eventually extended over from the eastern outskirts of Richmond, Virginia, to around the eastern and southern outskirts of Petersburg. Petersburg was crucial to the supply of Confederate Gen. Robert E. Lee's army and the Confederate capital of Richmond. Numerous raids were conducted and battles fought in attempts to cut off the Richmond and Petersburg Railroad. Many of these battles caused the leng ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Robert E
The name Robert is an ancient Germanic given name, from Proto-Germanic "fame" and "bright" (''Hrōþiberhtaz''). Compare Old Dutch ''Robrecht'' and Old High German ''Hrodebert'' (a compound of '' Hruod'' ( non, Hróðr) "fame, glory, honour, praise, renown" and ''berht'' "bright, light, shining"). It is the second most frequently used given name of ancient Germanic origin. It is also in use as a surname. Another commonly used form of the name is Rupert. After becoming widely used in Continental Europe it entered England in its Old French form ''Robert'', where an Old English cognate form (''Hrēodbēorht'', ''Hrodberht'', ''Hrēodbēorð'', ''Hrœdbœrð'', ''Hrœdberð'', ''Hrōðberχtŕ'') had existed before the Norman Conquest. The feminine version is Roberta. The Italian, Portuguese, and Spanish form is Roberto. Robert is also a common name in many Germanic languages, including English, German, Dutch, Norwegian, Swedish, Scots, Danish, and Icelandic. It can be use ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Ulysses S
Ulysses is one form of the Roman name for Odysseus, a hero in ancient Greek literature. Ulysses may also refer to: People * Ulysses (given name), including a list of people with this name Places in the United States * Ulysses, Kansas * Ulysses, Kentucky * Ulysses, Nebraska * Ulysses Township, Butler County, Nebraska * Ulysses, New York *Ulysses, Pennsylvania * Ulysses Township, Potter County, Pennsylvania Arts and entertainment Literature * "Ulysses" (poem), by Alfred Lord Tennyson * ''Ulysses'' (play), a 1705 play by Nicholas Rowe * ''Ulysses'', a 1902 play by Stephen Phillips * ''Ulysses'' (novel), by James Joyce * ''HMS Ulysses'' (novel), by Alistair Maclean * Ulysses (comics), two members of a fictional group in the Marvel Comics universe * Ulysses Klaue, a character in Marvel comic books * Ulysses: Jeanne d'Arc and the Alchemist Knight, a light novel Film and television * ''Ulysses'' (1954 film), starring Kirk Douglas based on the story of Homer's ''Odysse ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Lieutenant General (United States)
In the United States Armed Forces, a lieutenant general is a three-star general officer in the United States Army, Marine Corps, Air Force, and Space Force. A lieutenant general ranks above a major general and below a general. The pay grade of lieutenant general is O-9. It is equivalent to the rank of vice admiral in the other United States uniformed services which use naval ranks. It is abbreviated as LTG in the Army, LtGen in the Marine Corps, and Lt Gen in the Air Force and Space Force. Statutory limits The United States Code explicitly limits the total number of generals that may be concurrently active to 231 for the Army, 62 for the Marine Corps, and 198 for the Air Force. For the Army and Air Force, no more than about 25% of the service's active duty general officers may have more than two stars. [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |