|
Shell Technology Centre
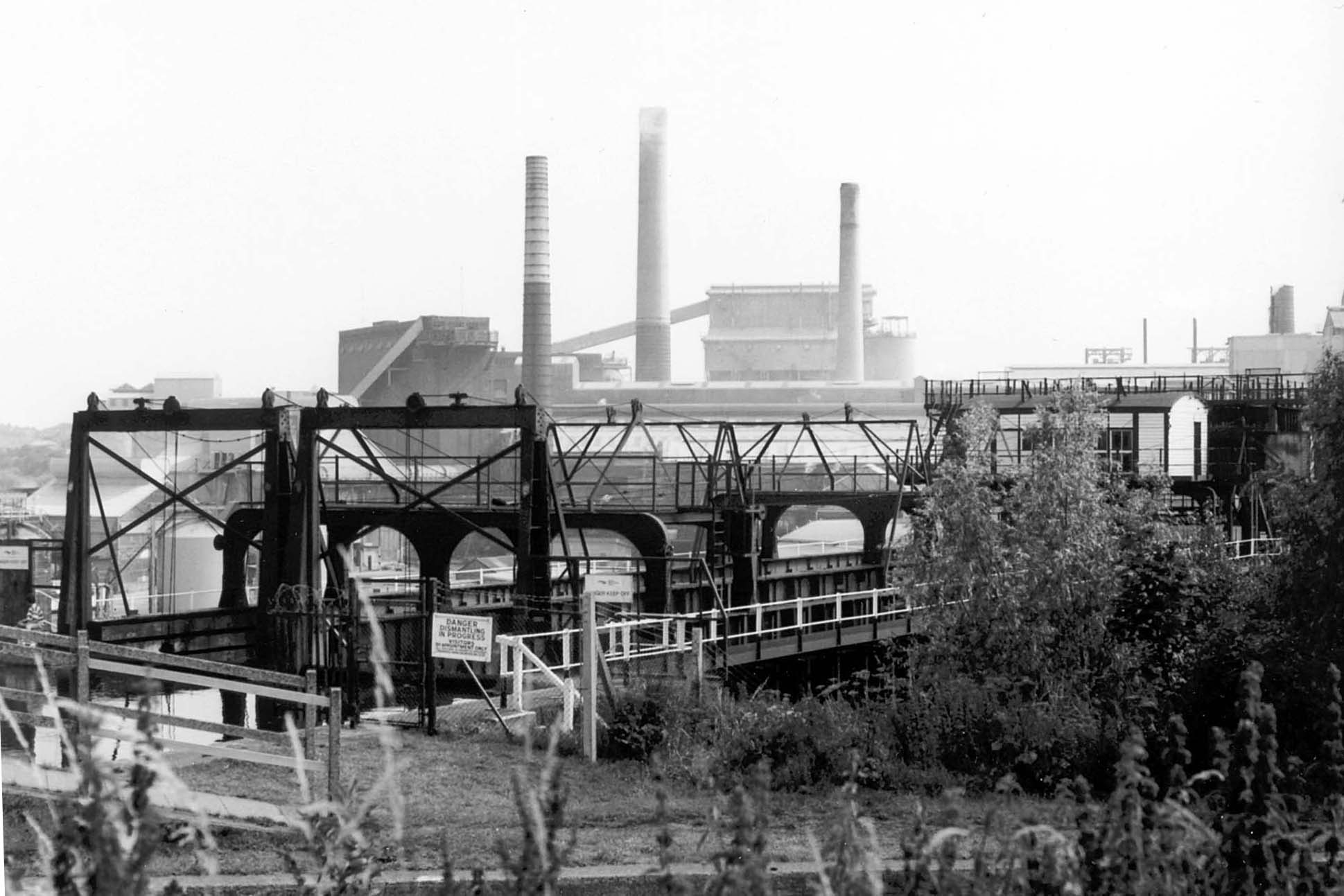
The Shell Technology Centre was a chemical and oil products research institute in northern Cheshire, near Stanlow, owned by Anglo-Dutch Shell. History World War II The site was first set up by Shell for the Ministry of Aircraft Production as the Aero Engine Research Laboratory. Vehicle engineering It returned to Shell ownership in April 1947. The site had 70 scientists, and around 250 technicians working on quartz combustion tubes, direct fuel injection, butane fuel and the atomisation of fuel. The neighbouring oil refinery opened in 1949, although a smaller plant had been there since 1924. In the 1950s it was one of three main Shell research sites in the UK, the others being in Kent and Buckinghamshire. In 1962, Shell spent £25m on research, with 19 worldwide research centres, 8 in Europe, and 11 in the US. By the early 1960s Shell also had its Central Laboratories in Surrey (which opened in 1956), the Tunstall Laboratory, and Chemical Enzymology Laboratory at Sitting ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Cheshire
Cheshire ( ) is a ceremonial and historic county in North West England, bordered by Wales to the west, Merseyside and Greater Manchester to the north, Derbyshire to the east, and Staffordshire and Shropshire to the south. Cheshire's county town is the cathedral city of Chester, while its largest town by population is Warrington. Other towns in the county include Alsager, Congleton, Crewe, Ellesmere Port, Frodsham, Knutsford, Macclesfield, Middlewich, Nantwich, Neston, Northwich, Poynton, Runcorn, Sandbach, Widnes, Wilmslow, and Winsford. Cheshire is split into the administrative districts of Cheshire West and Chester, Cheshire East, Halton, and Warrington. The county covers and has a population of around 1.1 million as of 2021. It is mostly rural, with a number of towns and villages supporting the agricultural and chemical industries; it is primarily known for producing chemicals, Cheshire cheese, salt, and silk. It has also had an impact on popular culture, producin ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
A5117 Road
The A5117 is a road in Cheshire, England. It runs between Shotwick and Helsby and connects the A550 at Woodbank to the M56. As such it forms a northerly bypass to Chester and a shorter route between the North West and North Wales than the A55. History The road, which was originally known as the "Shotwick – Helsby Bypass", was completed in the mid-1930s. The construction was contemporaneous to other transport major projects in the region such as the East Lanc Road and the opening of the first Mersey tunnel. The road was envisaged to become part of a link that connected the A56 from Manchester to North Wales via the Jubilee Bridge at Queensferry, Flintshire. Several sections of the road were constructed in concrete. Vehicles experience an up and down vertical motion due to the need for "summit and valley" drainage as the road crosses the flood plain of the River Gowy. Poplar trees were planted along the road (most are now only adjacent to the short section passed St ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Laboratories In The United Kingdom
A laboratory (; ; colloquially lab) is a facility that provides controlled conditions in which scientific or technological research, experiments, and measurement may be performed. Laboratory services are provided in a variety of settings: physicians' offices, clinics, hospitals, and regional and national referral centers. Overview The organisation and contents of laboratories are determined by the differing requirements of the specialists working within. A physics laboratory might contain a particle accelerator or vacuum chamber, while a metallurgy laboratory could have apparatus for casting or refining metals or for testing their strength. A chemist or biologist might use a wet laboratory, while a psychologist's laboratory might be a room with one-way mirrors and hidden cameras in which to observe behavior. In some laboratories, such as those commonly used by computer scientists, computers (sometimes supercomputers) are used for either simulations or the analysis of data. S ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
History Of The Petroleum Industry In The United Kingdom
History (derived ) is the systematic study and the documentation of the human activity. The time period of event before the invention of writing systems is considered prehistory. "History" is an umbrella term comprising past events as well as the memory, discovery, collection, organization, presentation, and interpretation of these events. Historians seek knowledge of the past using historical sources such as written documents, oral accounts, art and material artifacts, and ecological markers. History is not complete and still has debatable mysteries. History is also an academic discipline which uses narrative to describe, examine, question, and analyze past events, and investigate their patterns of cause and effect. Historians often debate which narrative best explains an event, as well as the significance of different causes and effects. Historians also debate the nature of history as an end in itself, as well as its usefulness to give perspective on the problems of the p ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Engineering Research Institutes
Engineering is the use of scientific method, scientific principles to design and build machines, structures, and other items, including bridges, tunnels, roads, vehicles, and buildings. The discipline of engineering encompasses a broad range of more specialized List of engineering branches, fields of engineering, each with a more specific emphasis on particular areas of applied mathematics, applied science, and types of application. See glossary of engineering. The term ''engineering'' is derived from the Latin ''ingenium'', meaning "cleverness" and ''ingeniare'', meaning "to contrive, devise". Definition The American Engineers' Council for Professional Development (ECPD, the predecessor of Accreditation Board for Engineering and Technology, ABET) has defined "engineering" as: The creative application of scientific principles to design or develop structures, machines, apparatus, or manufacturing processes, or works utilizing them singly or in combination; or to construct o ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Engine Technology
An engine or motor is a machine designed to convert one or more forms of energy into mechanical energy. Available energy sources include potential energy (e.g. energy of the Earth's gravitational field as exploited in hydroelectric power generation), heat energy (e.g. geothermal), chemical energy, electric potential and nuclear energy (from nuclear fission or nuclear fusion). Many of these processes generate heat as an intermediate energy form, so heat engines have special importance. Some natural processes, such as atmospheric convection cells convert environmental heat into motion (e.g. in the form of rising air currents). Mechanical energy is of particular importance in transportation, but also plays a role in many industrial processes such as cutting, grinding, crushing, and mixing. Mechanical heat engines convert heat into work via various thermodynamic processes. The internal combustion engine is perhaps the most common example of a mechanical heat engine, in whi ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Energy Research Institutes
In physics, energy (from Ancient Greek: ἐνέργεια, ''enérgeia'', “activity”) is the quantitative property that is transferred to a body or to a physical system, recognizable in the performance of work and in the form of heat and light. Energy is a conserved quantity—the law of conservation of energy states that energy can be converted in form, but not created or destroyed. The unit of measurement for energy in the International System of Units (SI) is the joule (J). Common forms of energy include the kinetic energy of a moving object, the potential energy stored by an object (for instance due to its position in a field), the elastic energy stored in a solid object, chemical energy associated with chemical reactions, the radiant energy carried by electromagnetic radiation, and the internal energy contained within a thermodynamic system. All living organisms constantly take in and release energy. Due to mass–energy equivalence, any object that has mass when ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Chemical Research Institutes
A chemical substance is a form of matter having constant chemical composition and characteristic properties. Some references add that chemical substance cannot be separated into its constituent elements by physical separation methods, i.e., without breaking chemical bonds. Chemical substances can be simple substances (substances consisting of a single chemical element), chemical compounds, or alloys. Chemical substances are often called 'pure' to set them apart from mixtures. A common example of a chemical substance is pure water; it has the same properties and the same ratio of hydrogen to oxygen whether it is isolated from a river or made in a laboratory. Other chemical substances commonly encountered in pure form are diamond (carbon), gold, table salt (sodium chloride) and refined sugar (sucrose). However, in practice, no substance is entirely pure, and chemical purity is specified according to the intended use of the chemical. Chemical substances exist as solids, liquids, g ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Chemical Industry In The United Kingdom
The chemical industry in the United Kingdom is one of the UK's main manufacturing industries. At one time, the UK's chemical industry was a world leader. The industry has also been environmentally damaging, and includes radioactive nuclear industries. History Sir William Henry Perkin FRS discovered the first synthetic dye mauveine in 1856, produced from aniline, having tried to synthesise quinine at his home on Cable Street in east London. Perkin's work, alone, led the way to the British chemical industry. 21% of the UK's chemical industry is in North West England, notably around Runcorn and Widnes. The chemical industry is 6.8% of UK manufacturing; around 85% of the UK chemical industry is in England. It employs 500,000, including 350,000 indirectly. It accounts for around 20% of the UK's research and development. Output In 2015, the UK chemical industry exported £50bn of products. The industry employs about 30,000 in research and development. Regulation Regulation of ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Automotive Industry In The United Kingdom
The automotive industry in the United Kingdom is now best known for premium and sports car marques including Aston Martin, Bentley, Caterham Cars, Daimler, Jaguar, Lagonda, Land Rover, Lister Cars, Lotus, McLaren, MG, Mini, Morgan and Rolls-Royce. Volume car manufacturers with a major presence in the UK include Honda, Nissan, Toyota and Vauxhall Motors (subsidiary of Opel, itself a subsidiary of Stellantis). Commercial vehicle manufacturers active in the UK include Alexander Dennis, Ford, IBC Vehicles (owned by Stellantis), Leyland Trucks (owned by Paccar) and London Electric Vehicle Company (owned by Geely). In 2018 the UK automotive manufacturing sector had a turnover of £82 billion, generated £18.6 billion in value to the UK economy and produced around 1.5 million passenger vehicles and 85,000 commercial vehicles. In that year around 168,000 people were directly employed in automotive manufacturing in the UK, with a further 823,000 people employed in ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Winnington Laboratory
The Winnington Laboratory was a former chemical laboratory at Winnington, near Northwich, in Cheshire, England. History The Winnington Works were built in 1874. The laboratory was set up by the ICI Alkali Division of Imperial Chemical Industries. The chemist Francis Arthur Freeth arrived in 1907, and became head of the laboratory. ICI was formed in 1926. Discovery of polythene On 24 March 1933 two scientists conducted an experiment that produced polythene (polyethylene). Benzaldehyde was reacted with ethene ( ethylene) at 2,000 atmospheres pressure. Sir Michael Perrin worked with this group of scientists from October 1933 until 1938. In December 1935 he conducted an experiment that allowed polythene to be created. Polythene is the world's most widespread plastic. In 1958, manufacture of polythene was moved to ICI's plant in Hertfordshire (ICI Plastics). Structure The laboratory was off the A533 next to the River Weaver and south of Barnton, Cheshire. The nearby chem ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Widnes Laboratory
The Widnes Laboratory was a research institute in northern Cheshire, run by Imperial Chemical Industries. History The site opened in 1891 as the Central Laboratory. On Monday 7 August 1950, an explosion at the site killed one man and injured another. Discovery of halothane Work was carried out at Widnes Laboratory from 1951 to 1956 which led to the discovery of halothane in 1955. Halothane gas was the most common anaesthetic for many years. There had been deaths with halothane and liver damage, and was discontinued from the 1980s. Anaesthetic deployment in hospitals is mostly with intravenous compounds and then isoflurane gas, discovered by Ross Terrell in the US. Structure The site was demolished, and now lies under the A533. See also * Winnington Laboratory The Winnington Laboratory was a former chemical laboratory at Winnington, near Northwich, in Cheshire, England. History The Winnington Works were built in 1874. The laboratory was set up by the ICI Alkali Divis ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |

.jpg)