|
Shanweiniao
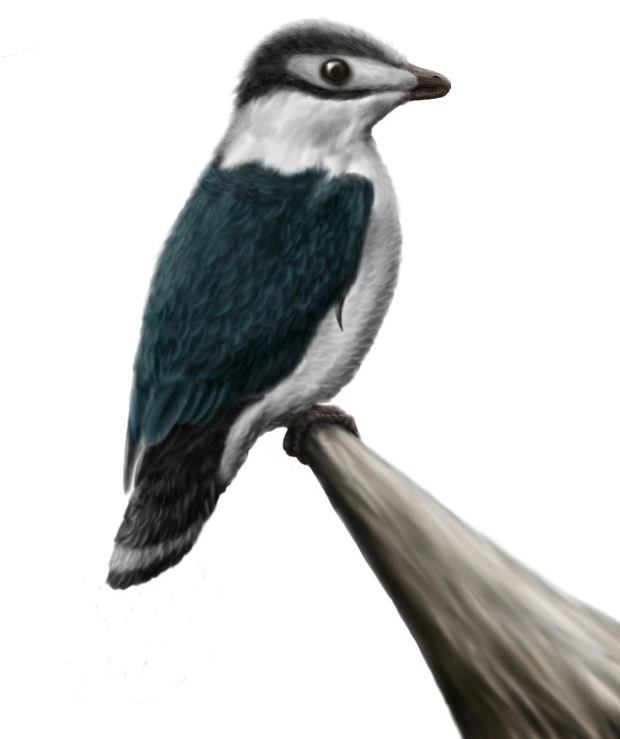
''Shanweiniao'' is a genus of long-snouted enantiornithean birds from Early Cretaceous China. One species is known, ''Shanweiniao cooperorum''. There is one known fossil, a slab and counterslab. The fossil is in the collection of the Dalian Natural History Museum, and has accession number DNHM D1878/1 and DNHM1878/2. It was collected from the Lower Cretaceous Dawangzhengzi Beds, middle Yixian Formation, from Lingyuan in the Liaoning Province, China. O'Connor et al. (2010) found that ''Shanweiniao'' is a close relative of ''Longipteryx'', ''Longirostravis'', and ''Rapaxavis'', which together form a clade of long-beaked enantiornithean birds, the Longipterygidae. The genus name ''Shanweiniao'' () means "fan-tailed bird" in Chinese. The authors report that ''Shanweiniao'' is the only known enantiornithean bird with a tail surface capable of generating lift, as in modern birds. They also report that only one other Mesozoic bird, '' Yixianornis grabaui'', which is a basal ornithur ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Longipterygidae
Longipterygidae is a family of early enantiornithean avialans from the Early Cretaceous epoch of China. All known specimens come from the Jiufotang Formation and Yixian Formation, dating to the early Aptian age, 125-120 million years ago. Description Longipterygids are characterized by an extremely long, toothed snout (making up over 60% of the total skull length), in which the teeth are restricted to the tips of the jaws. The snouts were straight but slightly concave at a point behind the nostrils, and the bones of the snout tip were solid. Their pygostyles, the series of fused vertebrae in the tail, were unusually large, and longer than the foot bones. The feet of longipterygids were also specialized relative to other enantiornitheans. Where most enantiornitheans had a long middle toe with a "knuckle" (trochlea) that extended beyond the outer two, the toes of longipterygids were even in length, and attached to the rest of the foot at the same level. This configuration is also ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Enantiornithean
The Enantiornithes, also known as enantiornithines or enantiornitheans in literature, are a group of extinct avialans ("birds" in the broad sense), the most abundant and diverse group known from the Mesozoic era. Almost all retained teeth and clawed fingers on each wing, but otherwise looked much like modern birds externally. Over eighty species of Enantiornithes have been named, but some names represent only single bones, so it is likely that not all are valid. The Enantiornithes became extinct at the Cretaceous–Paleogene boundary, along with Hesperornithes and all other non-avian dinosaurs. Discovery and naming The first Enantiornithes to be discovered were incorrectly referred to modern bird groups. For example, the first known species of Enantiornithes, '' Gobipteryx minuta'', was originally considered a paleognath related to ostriches and tinamou. The Enantiornithes were first recognized as a distinct lineage, or "subclass" of birds, by Cyril A. Walker in 1981. Walker mad ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Paraprotopteryx
''Paraprotopteryx'' is a genus of enantiornithean birds from the Mesozoic of China.Zheng, X. Zhang, Z. & Hou, L. (2007) A new enantiornithine bird with four long rectrices from the Early Cretaceous of northern Hebei, China. ''Acta Geologica Sinica'' 81(5):703-708. In 2007, the type species ''Paraprotopeteryx gracilis'' was named and described by Zheng Xiaoting, Zhang Zihui and Hou Lianhai. The generic name means "near '' Protopteryx''", in reference to a presumed similarity with that genus. The specific name is intended to mean "pretty". The holotype is specimen STM V001. It consists of a skeleton with skull on a plate and counterplate. The investigation preceding the description of the species proved that fossil traders had added the skull of a different individual to the torso. The description is based on the rump parts. Feathers have been preserved. The rump represents a subadult individual. Though initially reported to be from the Early Cretaceous Yixian Formation, la ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Longipteryx
''Longipteryx'' is a genus of prehistoric bird which lived during the Early Cretaceous (Aptian stage, 120.3 million years ago). It contains a single species, ''Longipteryx chaoyangensis''. Its remains have been recovered from the Jiufotang Formation at Chaoyang in Liaoning Province, China. Apart from the holotype IVPP V 12325 - a fine and nearly complete skeleton — another entire skeleton (IPPV V 12552) and some isolated bones (a humerus and furcula, specimens IPPV V 12553, and an ulna, IPPV V 12554) are known to date. The name ''Longipteryx'' means "one with long feathers", from Latin ''longus'', "long" + Ancient Greek ''pteryx'' (πτέρυξ), "wing", "feather" or "pinion". The specific name ''chaoyangensis'' is from the Latin for "from Chaoyang". Description Excluding the tail, ''Longipteryx'' was some 15 cm long overall in life. It had a long bill — longer than the rest of the head — with a few hooked teeth at the tip, and, as the name implies ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Yixianornis Grabaui
''Yixianornis'' (meaning "Yixian Formation bird") is a bird genus from the early Cretaceous period. Its remains have been found in the Jiufotang Formation at Chaoyang (People's Republic of China) dated to the early Aptian age, around 120 million years ago. Only one species, ''Yixianornis grabaui'', is known at present. The specific name, ''grabaui'', is named after American paleontologist Amadeus William Grabau, who surveyed China in the early 20th century. Description The type specimen (and only specimen found to date) of ''Yixianornis'', catalog number IVPP V12631 in the collections of the Institute of Vertebrate Paleontology and Paleoanthropology, is one of the most well-preserved bird fossils known from the Jehol group. It is nearly complete and, unlike many other fossils, the bones are mostly uncrushed and were not split in half when the stone slabs were initially separated. It is also one of the few known Mesozoic ornithuran bird specimens that preserve clear impressions of ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Early Cretaceous
The Early Cretaceous ( geochronological name) or the Lower Cretaceous (chronostratigraphic name), is the earlier or lower of the two major divisions of the Cretaceous. It is usually considered to stretch from 145 Ma to 100.5 Ma. Geology Proposals for the exact age of the Barremian-Aptian boundary ranged from 126 to 117 Ma until recently (as of 2019), but based on drillholes in Svalbard the defining early Aptian Oceanic Anoxic Event 1a (OAE1a) was carbon isotope dated to 123.1±0.3 Ma, limiting the possible range for the boundary to c. 122–121 Ma. There is a possible link between this anoxic event and a series of Early Cretaceous large igneous provinces (LIP). The Ontong Java-Manihiki-Hikurangi large igneous province, emplaced in the South Pacific at c. 120 Ma, is by far the largest LIP in Earth's history. The Ontong Java Plateau today covers an area of 1,860,000 km2. In the Indian Ocean another LIP began to form at c. 120 Ma, the Kerguelen P ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Mesozoic
The Mesozoic Era ( ), also called the Age of Reptiles, the Age of Conifers, and colloquially as the Age of the Dinosaurs is the second-to-last era of Earth's geological history, lasting from about , comprising the Triassic, Jurassic and Cretaceous Period (geology), Periods. It is characterized by the dominance of archosaurian reptiles, like the dinosaurs; an abundance of conifers and ferns; a hot Greenhouse and icehouse earth, greenhouse climate; and the tectonic break-up of Pangaea. The Mesozoic is the middle of the three eras since Cambrian explosion, complex life evolved: the Paleozoic, the Mesozoic, and the Cenozoic. The era began in the wake of the Permian–Triassic extinction event, the largest well-documented mass extinction in Earth's history, and ended with the Cretaceous–Paleogene extinction event, another mass extinction whose victims included the non-avian dinosaurs, Pterosaur, pterosaurs, Mosasaur, mosasaurs, and Plesiosaur, plesiosaurs. The Mesozoic was a time of ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Specific Name (zoology)
In zoological nomenclature, the specific name (also specific epithet or species epithet) is the second part (the second name) within the scientific name of a species (a binomen). The first part of the name of a species is the name of the genus or the generic name. The rules and regulations governing the giving of a new species name are explained in the article species description. For example, the scientific name for humans is ''Homo sapiens'', which is the species name, consisting of two names: ''Homo'' is the " generic name" (the name of the genus) and ''sapiens'' is the "specific name". Historically, ''specific name'' referred to the combination of what are now called the generic and specific names. Carl Linnaeus, who formalized binomial nomenclature, made explicit distinctions between specific, generic, and trivial names. The generic name was that of the genus, the first in the binomial, the trivial name was the second name in the binomial, and the specific the proper term for ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Rachis
In biology, a rachis (from the grc, ῥάχις [], "backbone, spine") is a main axis or "shaft". In zoology and microbiology In vertebrates, ''rachis'' can refer to the series of articulated vertebrae, which encase the spinal cord. In this case the ''rachis'' usually forms the supporting axis of the body and is then called the spine or vertebral column. ''Rachis'' can also mean the central shaft of pennaceous feathers. In the gonad of the invertebrate nematode '' Caenorhabditis elegans'', a rachis is the central cell-free core or axis of the gonadal arm of both adult males and hermaphrodites where the germ cells have achieved pachytene and are attached to the walls of the gonadal tube. The rachis is filled with cytoplasm. In botany In plants, a rachis is the main axis of a compound structure. It can be the main stem of a compound leaf, such as in ''Acacia'' or ferns, or the main, flower-bearing portion of an inflorescence above a supporting peduncle. Where it subdivides ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Ornithuromorpha
Euornithes (from Greek ' meaning "true birds") is a natural group which includes the most recent common ancestor of all avialans closer to modern birds than to ''Sinornis''. Description Clarke ''et al''. (2006) found that the most primitive known euornithians (the Yanornithiformes) had a mosaic of advanced and primitive features. These species retained primitive features like gastralia and a pubic symphysis. They also showed the first fully modern pygostyles, and the type specimen of ''Yixianornis'' (IVPP 13631) preserves eight elongated rectrices (tail feathers) in a modern arrangement. No earlier pygostylians are known which preserve a fan of tail feathers of this sort; instead, they showed only paired plumes or a tuft of short feathers. Classification The name Euornithes has been used for a wide variety of avialan groups since it was first named by Edward Drinker Cope in 1889. It was first defined as a clade in 1998 by Paul Sereno, who made it the group of all animals close ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Chiappeavis
''Chiappeavis'' is a genus of enantiornithean bird from Early Cretaceous of northeastern China. The only species is ''Chiappeavis magnapremaxillo''. ''Chiappeavis'' is classified within the family Pengornithidae. It is known from a single, almost complete skeleton including feather impressions discovered in the Jiufotang Formation of the Jehol Group. Long feathers formed a fan-shaped tail that was probably employed in flight. The genus name honors Luis Chiappe for his extensive research on Mesozoic birds. The specific name ''magnapremaxillo'' ("large premaxilla") alludes to the unusually large size of the premaxillary bone, the frontmost bone of the upper jaw. The only specimen (holotype, STM29-11), of a subadult individual, was discovered on a single slab in Jianchang County, Liaoning. Is housed in the Shandong Tianyu Museum of Nature in Pingyi County, Shandong. Description ''Chiappeavis'' was large for a pengornithid. The skull was triangular in side view with a blun ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Sapeornis
''Sapeornis'' is a monotypic genus of avialan which lived during the early Cretaceous period ( late Barremian to early Aptian, roughly 125-120 mya). ''Sapeornis'' contains only one species, ''Sapeornis chaoyangensis''. Description ''Sapeornis'' was large for an early avialan, about long in life, excluding the tail feathers. The hand of ''Sapeornis'' was far more derived than that of ''Archaeopteryx''. It had three fingers, the outer ones with two and the middle one with three phalanges, and a well-fused carpometacarpus. Its arms were about half again as long as the legs, suggesting a large wing area. On the other hand, its shoulder girdle was apparently ill-adapted to flapping flight and its furcula was unusual, with a hypocleidum similar to more advanced avialans but a general anatomy even more basal than in ''Archaeopteryx''. The humerus was large and bore holes, apparently to save weight, as in the Confuciusornithidae. The skull has a handful of teeth in the upper jawtip ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |