|
Shankaragana III
Shankaragana III ( IAST: Śankaragaṇa, r. c. 970-980 CE) was a ruler of the Kalachuri dynasty of Tripuri in central India. His kingdom was centered around the Chedi or Dahala region in present-day Madhya Pradesh. He defeated a weak Gurjara-Pratihara ruler, and seems to have died in a battle against the Chandelas. Reign Shankargana succeeded the Kalachuri king Lakshmanaraja around 970 CE. Shankaragana adopted an aggressive policy against his neighbours. According to a Jabalpur inscription, he defeated the contemporary Gurjara-Pratihara king. This rival king was probably Vijayapala. Shankaragana seems to have died in a battle against the Chandelas. A Bhilsa inscription boasts that the Chandela minister Vachaspati vanquished the king of Chedi (identified with Shankaragana) and his ally, a Shabara chief. Vachaspati was a subordinate of Krishnapa, the brother of the Chandela king Dhanga. A Maser inscription states that Narasimha of the Sulki family turned the wives of the Kalachu ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Kalachuris Of Tripuri
The Kalachuris of Tripuri ( IAST: ), also known the Kalachuris of Chedi, ruled parts of central India during 7th to 13th centuries. They are also known as the Later Kalachuris to distinguish them from their earlier namesakes, especially the Kalachuris of Mahishmati. Their core territory included the historical Chedi region (also known as Dahala-mandala), and their capital was located at Tripuri (present-day Tewar near Jabalpur, Madhya Pradesh). The origin of the dynasty is uncertain, although one theory connects them to the Kalachuris of Mahishmati. By the 10th century, the Kalachuris of Tripuri had consolidated their power by raiding neighbouring territories and by fighting wars with the Gurjara-Pratiharas, the Chandelas and the Paramaras. They also had matrimonial relations with the Rashtrakutas and the Chalukyas of Kalyani. In the 1030s, the Kalachuri king Gangeyadeva assumed imperial titles after achieving military successes at his eastern and northern frontiers. The ki ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Yuvarajadeva II
Yuvarajadeva II ( IAST: Yuva-rāja-deva, r. c. 980-990 CE) was a ruler of the Kalachuri dynasty of Tripuri in central India. His kingdom was centered around the Chedi or Dahala region in present-day Madhya Pradesh. He established matrimonial relations with the Chalukyas of Kalyani, and was defeated by their rival, the Paramara king Munja. Early life Yuvarajadeva succeeded his elder brother Shankaragana III, who was probably killed in a battle against the Chandelas. Reign The Karanbel inscription of Yuvarajadeva's descendant claims that he raided several countries, and presented the plundered wealth to lord Somnath. His ancestor Lakshmanaraja II is also credited with a similar achievement. According to historian V. V. Mirashi, these are conventional praises, and should not be taken as factual descriptions. The Karanbel inscription also boasts that Yuvarajadeva once fought and killed a tiger. Yuvarajadeva's sister Bonthadevi married the Kalyani Chalukya ruler Tailapa II, ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
IAST
The International Alphabet of Sanskrit Transliteration (IAST) is a transliteration scheme that allows the lossless romanisation of Indic scripts as employed by Sanskrit and related Indic languages. It is based on a scheme that emerged during the nineteenth century from suggestions by Charles Trevelyan, William Jones, Monier Monier-Williams and other scholars, and formalised by the Transliteration Committee of the Geneva Oriental Congress, in September 1894. IAST makes it possible for the reader to read the Indic text unambiguously, exactly as if it were in the original Indic script. It is this faithfulness to the original scripts that accounts for its continuing popularity amongst scholars. Usage Scholars commonly use IAST in publications that cite textual material in Sanskrit, Pāḷi and other classical Indian languages. IAST is also used for major e-text repositories such as SARIT, Muktabodha, GRETIL, and sanskritdocuments.org. The IAST scheme represents more than a ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Madhya Pradesh
Madhya Pradesh (, ; meaning 'central province') is a state in central India. Its capital is Bhopal, and the largest city is Indore, with Jabalpur, Ujjain, Gwalior, Sagar, and Rewa being the other major cities. Madhya Pradesh is the second largest Indian state by area and the fifth largest state by population with over 72 million residents. It borders the states of Uttar Pradesh to the northeast, Chhattisgarh to the east, Maharashtra to the south, Gujarat to the west, and Rajasthan to the northwest. The area covered by the present-day Madhya Pradesh includes the area of the ancient Avanti Mahajanapada, whose capital Ujjain (also known as Avantika) arose as a major city during the second wave of Indian urbanisation in the sixth century BCE. Subsequently, the region was ruled by the major dynasties of India. The Maratha Empire dominated the majority of the 18th century. After the Anglo-Maratha Wars in the 19th century, the region was divided into several princel ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Gurjara-Pratihara
The Gurjara-Pratihara was a dynasty that ruled much of Hindustan, Northern India from the mid-8th to the 11th century. They ruled first at Ujjain and later at Kannauj. The Gurjara-Pratiharas were instrumental in containing Arab armies moving east of the Indus River. Nagabhata I defeated the Arab army under Junaid and Tamin in the Caliphate campaigns in India. Under Nagabhata II, the Gurjara-Pratiharas became the most powerful dynasty in northern India. He was succeeded by his son Ramabhadra, who ruled briefly before being succeeded by his son, Mihira Bhoja. Under Bhoja and his successor Mahendrapala I, the Gurjara-Pratihara dynasty reached its peak of prosperity and power. By the time of Mahendrapala, the extent of its territory rivalled that of the Gupta Empire stretching from the border of Sindh in the west to Bengal in the east and from the Himalayas in the north to areas past the Narmada in the south. The expansion triggered a Tripartite Struggle, tripartite power struggle ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Chandela
The Chandelas of Jejakabhukti was an Indian dynasty in Central India. The Chandelas ruled much of the Bundelkhand region (then called ''Jejakabhukti'') between the 9th and the 13th centuries. They belonged to the Chandel clan of the Rajputs. The Chandelas initially ruled as feudatories of the Gurjara-Pratiharas of Kanyakubja (Kannauj). The 10th century Chandela ruler Yashovarman became practically independent, although he continued to acknowledge the Pratihara suzerainty. By the time of his successor Dhanga, the Chandelas had become a sovereign power. Their power rose and declined as they fought battles with the neighbouring dynasties, especially the Paramaras of Malwa and the Kalachuris of Tripuri. From the 11th century onwards, the Chandelas faced raids by the northern Muslim dynasties, including the Ghaznavids and the Ghurids. The Chandela power effectively ended around the beginning of the 13th century, following Chahamana and Ghurid invasions. The Chandelas are well known ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Jabalpur
Jabalpur is a city situated on the banks of Narmada River in the state of Madhya Pradesh, India. According to the 2011 census, it is the third-largest urban agglomeration in Madhya Pradesh and the country's 38th-largest urban agglomeration. Jabalpur is an important administrative, industrial and business center of Madhya Pradesh. It is the judicial capital of Madhya Pradesh as The Madhya Pradesh High Court along with other important administrative headquarters of India and Madhya Pradesh are located in Jabalpur. It is generally accepted that the game of Snooker originated in Jabalpur. Jabalpur is the administrative headquarters of Jabalpur district (the second-most-populous district in Madhya Pradesh) and the Jabalpur division. It also is a major education centre in India. The city is known for the marble rocks on the river Narmada at Bhedaghat. Etymology According to a prevalent theory, Jabalpur was named after a sage named Jabali, who meditated on the banks of the Narmada ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
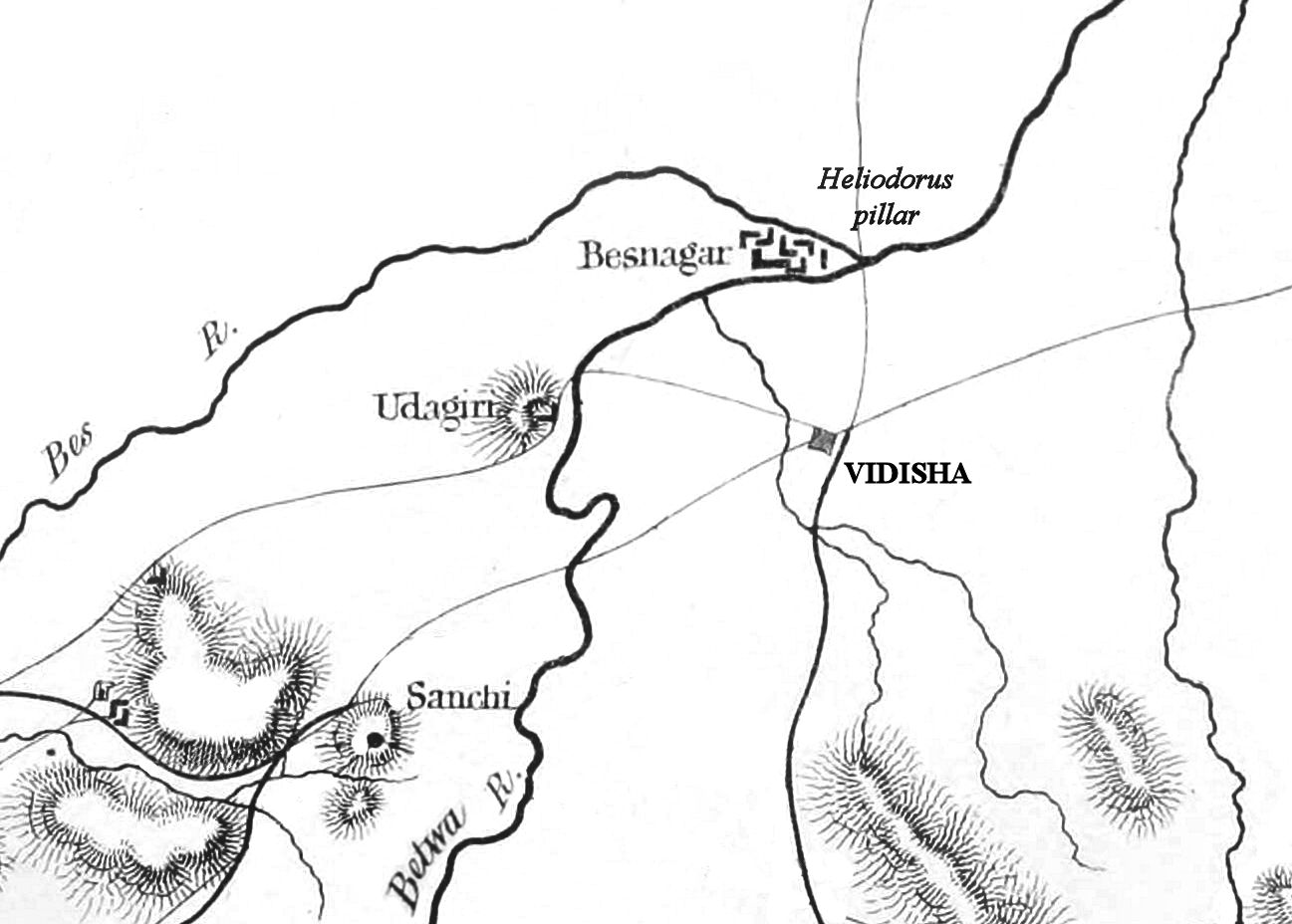
Bhilsa
Vidisha (विदिशा, formerly known as Bhelsa and known as Besnagar in ancient times) is a city in central Madhya Pradesh, India. It is located 62.5 km northeast of the state capital, Bhopal. The name "Vidisha" is derived from the nearby river "Bais", mentioned in the Puranas. The district was created as Bhilsa District in 1904 by joining the tehsils of Vidisha (also known as Bhilsa) and Basoda (but not Basoda State) which were then part of Gwalior state. After India's independence in 1947, the former princely state of Gwalior became part of Madhya Bharat state, which was formed in 1948. Vidishā was the administrative headquarters of Bhelsa, or Bhilsa, during the Medieval period. It was renamed Vidisha in 1956. Vidisha is also amongst the 112 Aspirational District in the Aspirational District Programme launched by NITI Aayog in 2018. Demographics As of the 2011 Census of India, Vidisha had a population of 155,959. Males constitute 53.21% of the population and ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Sabar People
The Sabar people (also Shabar and Saora) are one of the Adivasi of Munda ethnic group tribe who live mainly in Odisha and West Bengal. During the colonial period, they were classed as one of the 'criminal tribes' under Criminal Tribes Act 1871, and suffer from social stigma and ostracism in modern times. Also known as Saora, the Sabar tribe finds mention in the Hindu epic Mahabharata, while in some parts of East Singhbhum district mainly in Musabani, they are known as in Kariya. Noted writer and activist Mahasweta Devi is known for working with these forest tribals. This reclusive tribe is found primarily in Odisha and in Midnapore District of West Bengal. The traditionally forest-dwelling tribe lack experience in agriculture, and rely on the forests for their livelihood. In recent years, with the spread of the Naxalite rebellion in the area, the police often restrict their access to the forest. In 2004, five persons in the Sabar village of Amlasole, in Midnapore distr ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Dhanga
Dhanga (r. c. 950-999 CE), also known as Dhaṇgadeva in inscriptions, was a king of the Chandela dynasty of India. He ruled in the Jejakabhukti region (Bundelkhand in present-day Madhya Pradesh). Dhanga established the sovereignty of the Chandelas, who had served as vassals to the Pratiharas until his reign. He is also notable for having commissioned magnificent temples at Khajuraho, including the Vishvanatha temple. Early life According to the Khajuraho Inscription No. IV, Dhanga was born to the Chandella (Chandratreya) king Yashovarman and his queen Puppā (Puṣpā) Devī. The earliest inscription set up during Dhanga's reign is the Chaturbhuj inscription of 953-954 CE (1011 VS). Dhanga must have ascended the throne sometime before this. His ascension was probably undisputed, as his brother Krishna had been deputed to protect the kingdom's Malwa frontier. Other inscriptions from Dhanga's reign include the Nanaora (or Nanyaura) inscription (998 CE) and the Lalaji inscr ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |


_male.jpg)

_(8638391942).jpg)