|
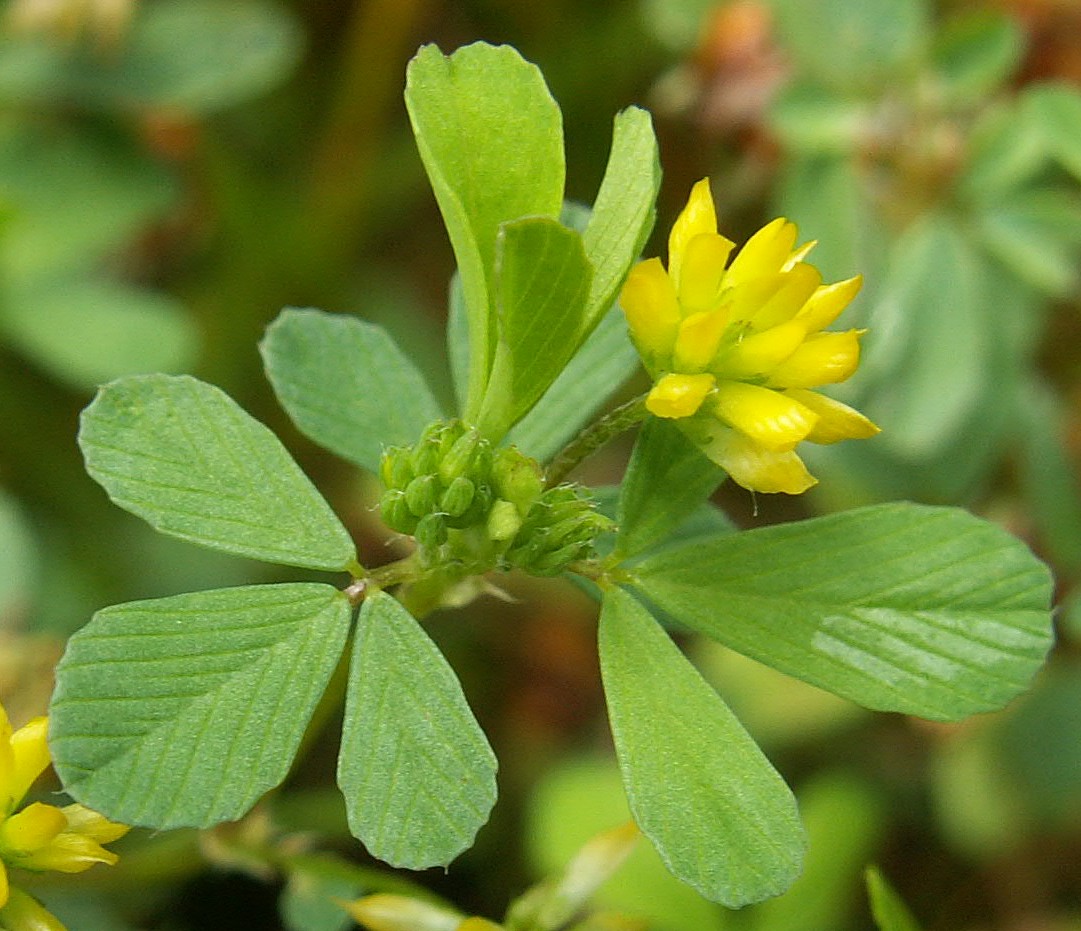
Shamrock Poor Boy
A shamrock is a young sprig, used as a symbol of Ireland. Saint Patrick, Ireland's patron saint, is said to have used it as a metaphor for the Christian Holy Trinity. The name ''shamrock'' comes from Irish (), which is the diminutive of the Irish word and simply means "young clover". At most times'', Shamrock'' refers to either the species (lesser clover, Irish: ) or (white clover, Irish: ). However, other three-leaved plants—such as , , and —are sometimes called shamrocks. The shamrock was traditionally used for its medicinal properties and was a popular motif in Victorian times. Botanical species There is still not a consensus over the precise botanical species of clover that is the "true" shamrock. John Gerard in his herbal of 1597 defined the shamrock as ''Trifolium pratense'' or ''Trifolium pratense flore albo'', meaning red or white clover. He described the plant in English as "Three leaved grasse" or "Medow Trefoile", "which are called in Irish ''Sha ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Irish Clover
A shamrock is a young sprig, used as a symbol of Ireland. Saint Patrick, Ireland's patron saint, is said to have used it as a metaphor for the Christian Holy Trinity. The name ''shamrock'' comes from Irish (), which is the diminutive of the Irish word and simply means "young clover". At most times'', Shamrock'' refers to either the species (lesser clover, Irish: ) or (white clover, Irish: ). However, other three-leaved plants—such as , , and —are sometimes called shamrocks. The shamrock was traditionally used for its medicinal properties and was a popular motif in Victorian times. Botanical species There is still not a consensus over the precise botanical species of clover that is the "true" shamrock. John Gerard in his herbal of 1597 defined the shamrock as ''Trifolium pratense'' or ''Trifolium pratense flore albo'', meaning red or white clover. He described the plant in English as "Three leaved grasse" or "Medow Trefoile", "which are called in Irish '' ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Botany
Botany, also called , plant biology or phytology, is the science of plant life and a branch of biology. A botanist, plant scientist or phytologist is a scientist who specialises in this field. The term "botany" comes from the Ancient Greek word (''botanē'') meaning " pasture", " herbs" "grass", or " fodder"; is in turn derived from (), "to feed" or "to graze". Traditionally, botany has also included the study of fungi and algae by mycologists and phycologists respectively, with the study of these three groups of organisms remaining within the sphere of interest of the International Botanical Congress. Nowadays, botanists (in the strict sense) study approximately 410,000 species of land plants of which some 391,000 species are vascular plants (including approximately 369,000 species of flowering plants), and approximately 20,000 are bryophytes. Botany originated in prehistory as herbalism with the efforts of early humans to identify – and later cultivate – ed ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
The Irish Naturalist
''The Irish Naturalist'' was a scientific journal that was published in Dublin, Ireland, from April 1892 until December 1924. History The journal owed its establishment to the efforts of several leading Dublin naturalists, notably George H. Carpenter and R. M. Barrington. The first editors were Carpenter and Robert Lloyd Praeger, of the National Library of Ireland. The journal was supported by a number of societies, including the Royal Zoological Society of Ireland, the Dublin Microscopical Club, the Belfast Naturalists' Field Club, and the Dublin Naturalists' Field Club. ''The Irish Naturalist'' was published for 33 years and contained in total over 3000 pages. The journal ceased publication in December 1924. It had been having some financial problems, but the final blow came when Carpenter took up his appointment to the keepership of the Manchester Museum in 1923. The journal was succeeded in 1925 by the '' Irish Naturalists' Journal''. Contributors Among notable c ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Trifolium Repens Leaf April 2, 2010
Clover or trefoil are common names for plants of the genus ''Trifolium'' (from Latin ''tres'' 'three' + ''folium'' 'leaf'), consisting of about 300 species of flowering plants in the legume or pea family Fabaceae originating in Europe. The genus has a cosmopolitan distribution with highest diversity in the temperate Northern Hemisphere, but many species also occur in South America and Africa, including at high altitudes on mountains in the tropics. They are small annual, biennial, or short-lived perennial herbaceous plants, typically growing up to 30 cm tall. The leaves are trifoliate (rarely quatrefoiled; see four-leaf clover), monofoil, bifoil, cinquefoil, hexafoil, septfoil, etcetera, with stipules adnate to the leaf-stalk, and heads or dense spikes of small red, purple, white, or yellow flowers; the small, few-seeded pods are enclosed in the calyx. Other closely related genera often called clovers include ''Melilotus'' (sweet clover) and ''Medicago'' (alfalfa or Calvary clover) ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Saint Patrick's Day
Saint Patrick's Day, or the Feast of Saint Patrick ( ga, Lá Fhéile Pádraig, lit=the Day of the Festival of Patrick), is a cultural and religious celebration held on 17 March, the traditional death date of Saint Patrick (), the foremost patron saint of Ireland. Saint Patrick's Day was made an official Christian feast day in the early 17th century and is observed by the Catholic Church, the Anglican Communion (especially the Church of Ireland), the Eastern Orthodox Church, and the Lutheran Church. The day commemorates Saint Patrick and the arrival of Christianity in Ireland, and celebrates the heritage and culture of the Irish in general. Celebrations generally involve public parades and festivals, céilithe, and the wearing of green attire or shamrocks. Christians who belong to liturgical denominations also attend church services and historically the Lenten restrictions on eating and drinking alcohol were lifted for the day, which has encouraged and propagated the holida ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Covent Garden
Covent Garden is a district in London, on the eastern fringes of the West End, between St Martin's Lane and Drury Lane. It is associated with the former fruit-and-vegetable market in the central square, now a popular shopping and tourist site, and with the Royal Opera House, itself known as "Covent Garden". The district is divided by the main thoroughfare of Long Acre, north of which is given over to independent shops centred on Neal's Yard and Seven Dials, while the south contains the central square with its street performers and most of the historical buildings, theatres and entertainment facilities, including the London Transport Museum and the Theatre Royal, Drury Lane. The area was fields until briefly settled in the 7th century when it became the heart of the Anglo-Saxon trading town of Lundenwic, then abandoned at the end of the 9th century after which it returned to fields. By 1200 part of it had been walled off by the Abbot of Westminster Abbey for use as arable l ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
James Britten
James Britten (3 May 1846 – 8 October 1924) was an English botanist. Biography Born in Chelsea, London, he moved to High Wycombe in 1865 to begin a medical career. However he became increasingly interested in botany, and began writing papers on the subject. His first publication was probably that published in the '' Journal of Botany'' in 1863. He became a Catholic in 1867, and was involved at various times in social work and training choirs in Brentford, Isleworth, and Southwark. In 1869, he was appointed a junior at the Herbarium at the Royal Botanic Gardens, Kew. In 1871, he joined the Department of Botany at the British Museum and remained in this position until his retirement in 1909. In 1879, he succeeded Henry Trimen as editor of the ''Journal of Botany, British and Foreign''. He would hold the editorship for around 45 years. Botanist Norman Hall wrote of Britten: "Britten threw himself fully into the editorship, although his pungent remarks on papers submitted were ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
James Ebenezer Bicheno
James Ebenezer Bicheno (25 January 1785 – 25 February 1851) was a British author and colonial official. Bicheno was born in Newbury, Berkshire, the son of the Rev. James Bicheno, who was minister of the Baptist Church there. He was called to the bar in 1822 but seems to have spent most of his time until 1832 in writing and natural history pursuits, especially with the Linnean Society. He was elected a Fellow of the Royal Society in May, 1827. In 1832 he left London to live at Ty Maen, South Cornelly, Glamorgan, where he had been one of the founders of the Maesteg Ironworks in 1826. and where he was a friend of Lewis Weston Dillwyn. This investment ultimately failed and he needed to look for an income. During his years in south Wales Bicheno held conservative views at a time of considerable social and economic change. He was certainly anti-Chartist as his correspondence with the Marquis of Bute, the Lord Lieutenant of Glamorgan, clearly shows. He was ever vigilant regard ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Wood Sorrel
''Oxalis'' ( (American English) or (British English)) is a large genus of flowering plants in the wood-sorrel family Oxalidaceae, comprising over 550 species. The genus occurs throughout most of the world, except for the polar areas; species diversity is particularly rich in tropical Brazil, Mexico, and South Africa. Many of the species are known as wood sorrels (sometimes written "woodsorrels" or "wood-sorrels") as they have an acidic taste reminiscent of the sorrel proper ('' Rumex acetosa''), which is only distantly related. Some species are called yellow sorrels or pink sorrels after the color of their flowers instead. Other species are colloquially known as false shamrocks, and some called sourgrasses. For the genus as a whole, the term oxalises is also used. Description and ecology These plants are annual or perennial. The leaves are divided into three to ten or more obovate and top-notched leaflets, arranged palmately with all the leaflets of roughly equal size. The maj ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Edmund Spenser
Edmund Spenser (; 1552/1553 – 13 January 1599) was an English poet best known for ''The Faerie Queene'', an epic poem and fantastical allegory celebrating the Tudor dynasty and Elizabeth I. He is recognized as one of the premier craftsmen of nascent Modern English verse and is often considered one of the greatest poets in the English language. Life Edmund Spenser was born in East Smithfield, London, around the year 1552; however, there is still some ambiguity as to the exact date of his birth. His parenthood is obscure, but he was probably the son of John Spenser, a journeyman clothmaker. As a young boy, he was educated in London at the Merchant Taylors' School and matriculated as a sizar at Pembroke College, Cambridge. While at Cambridge he became a friend of Gabriel Harvey and later consulted him, despite their differing views on poetry. In 1578, he became for a short time secretary to John Young, Bishop of Rochester. In 1579, he published ''The Shepheardes Calender'' and ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Shamrock Plant In Bloom
A shamrock is a young sprig, used as a symbol of Ireland. Saint Patrick, Ireland's patron saint, is said to have used it as a metaphor for the Christian Holy Trinity. The name ''shamrock'' comes from Irish (), which is the diminutive of the Irish word and simply means "young clover". At most times'', Shamrock'' refers to either the species (lesser clover, Irish: ) or (white clover, Irish: ). However, other three-leaved plants—such as , , and —are sometimes called shamrocks. The shamrock was traditionally used for its medicinal properties and was a popular motif in Victorian times. Botanical species There is still not a consensus over the precise botanical species of clover that is the "true" shamrock. John Gerard in his herbal of 1597 defined the shamrock as ''Trifolium pratense'' or ''Trifolium pratense flore albo'', meaning red or white clover. He described the plant in English as "Three leaved grasse" or "Medow Trefoile", "which are called in Irish ''Sha ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Flora Lapponica
''Flora Lapponica'' (Amsterdam, 1737) is an account of the plants of Lapland written by botanist, zoologist and naturalist Carl Linnaeus (1707-1788) following his expedition to Lapland. Over the period from 12 May 1732 to 10 September 1732, and with a grant from the Royal Society of Sciences in Uppsala for his journey, Anderson (1997), pp. 42–43. Blunt (2001), p. 38. Linnaeus was able to combine his interest in medicine with that of natural history to travel for five months in Lapland collecting animals, plants, and minerals. In ''Flora Lapponica'' Linnaeus's ideas about nomenclature and classification were first used in a practical way, making this the first proto-modern flora. The account covered 534 species, used the Linnaean classification system and included, for the described species, geographical distribution and taxonomic notes. It was Augustin Pyramus de Candolle who attributed Linnaeus with ''Flora Lapponica'' as the first example in the botanical genre of Flora writ ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |









.jpg)