|
Shahdad Chota
Shahdad ( fa, شهداد, also Romanized as Shahdād; formerly, Khabīs) is a city and capital of Shahdad District, in Kerman County, Kerman Province, Iran. At the 2006 census, its population was 4,097, in 1,010 families. District Shahdad is the center of Shahdad district which includes smaller cities and villages such as Sirch, Anduhjerd, Chahar Farsakh, Go-diz, Keshit, Ibrahim Abad, Joshan and Dehseif. The driving distance from Kerman city to Shahdad is 95 km. The local climate is hot and dry. The main agricultural produce is date fruits. There are many castles and caravanserais at Shahdad and around. Examples are the Shafee Abaad castle and the Godeez castle. The shrine of Imamzadeh Zeyd, in the south of the town, is a respected religious site. There is also the main mosque ''Masjed-e-Rasool'' (''Mosque of the Prophet'') where people go to offer namaz. Climate Shahdad has a hot desert climate ( Köppen climate classification ''BWh''). The city is located at ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Ab Anbar
An ''ab anbar'' ( fa, آبانبار, literally " Cistern") is a traditional reservoir or cistern of drinking water in Greater Iran in antiquity. Structure To withstand the pressure the water exerts on the containers of the storage tank, the storage itself was built below ground level. This also provides resistance to earthquakes. Many cities in Iran lie in a region that has been affected by very large earthquakes. Since almost all ab anbars are subterranean structures capped barely above ground level, they inherently possess stable structures. The construction material used for ab anbars were very tough and extensively used a special mortar called ''sarooj'' which was made of sand, clay, egg whites, lime, goat hair, and ash in specific proportions, depending on location and climate of the city. This mixture was thought to be completely water impenetrable. The walls of the storage were often 2 meters thick, and special bricks had to be used. These bricks were especially ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Castle
A castle is a type of fortified structure built during the Middle Ages predominantly by the nobility or royalty and by military orders. Scholars debate the scope of the word ''castle'', but usually consider it to be the private fortified residence of a lord or noble. This is distinct from a palace, which is not fortified; from a fortress, which was not always a residence for royalty or nobility; from a ''pleasance'' which was a walled-in residence for nobility, but not adequately fortified; and from a fortified settlement, which was a public defence – though there are many similarities among these types of construction. Use of the term has varied over time and has also been applied to structures such as hill forts and 19th-20th century homes built to resemble castles. Over the approximately 900 years when genuine castles were built, they took on a great many forms with many different features, although some, such as curtain walls, arrowslits, and portcullises, were ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Populated Places In Kerman County
Population typically refers to the number of people in a single area, whether it be a city or town, region, country, continent, or the world. Governments typically quantify the size of the resident population within their jurisdiction using a census, a process of collecting, analysing, compiling, and publishing data regarding a population. Perspectives of various disciplines Social sciences In sociology and population geography, population refers to a group of human beings with some predefined criterion in common, such as location, race, ethnicity, nationality, or religion. Demography is a social science which entails the statistical study of populations. Ecology In ecology, a population is a group of organisms of the same species who inhabit the same particular geographical area and are capable of interbreeding. The area of a sexual population is the area where inter-breeding is possible between any pair within the area and more probable than cross-breeding with ind ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
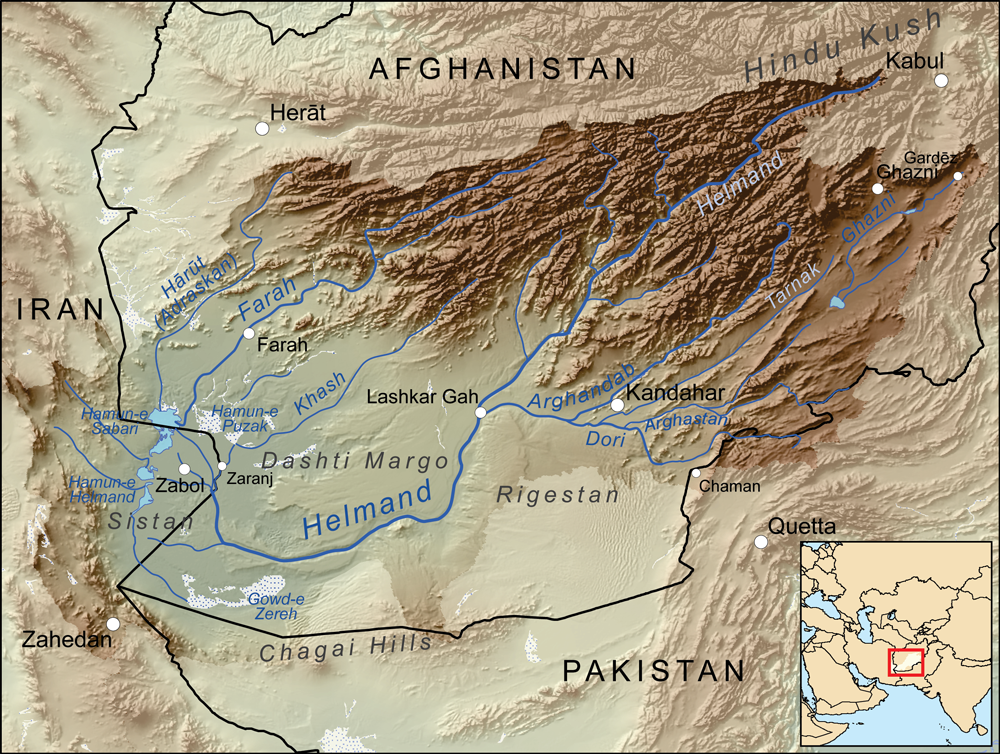
Sistan Basin
The Sistan Basin is an inland endorheic basin encompassing large parts of southwestern Afghanistan and minor parts of southeastern Iran, one of the driest regions in the world and an area subjected to prolonged droughts. Its watershed is a system of rivers flowing from the highlands of Afghanistan into freshwater lakes and marshes and then to its ultimate destination: Afghanistan's saline Godzareh depression, part of the extensive Sistan terminal basin. The Helmand River drains the basin's largest watershed, fed mainly by snowmelt from the mountains of Hindu Kush, but other rivers contribute also. A basalt hill, known as Mount Khajeh, rises beside the lakes and marshes of the basin. Lakes The lowest part of the Sistan Basin contains a series of shallow lakes, known as ''hamuns''. It appears that in the past there was a single Hamun Lake, but there are now three separate lakes. From north to south the lakes are: Hamun-e Puzak The Hamun-e Puzak lies mostly in Afghan ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Aratta
Aratta is a land that appears in Sumerian myths surrounding Enmerkar and Lugalbanda, two early and possibly mythical kings of Uruk also mentioned on the Sumerian king list. Role in Sumerian literature Aratta is described as follows in Sumerian literature: *It is a fabulously wealthy place full of gold, silver, lapis lazuli and other precious materials, as well as the artisans to craft them. *It is remote and difficult to reach. *It is home to the goddess Inana, who transfers her allegiance from Aratta to Uruk. *It is conquered by Enmerkar of Uruk. Mentions in Sumerian literature ''Enmerkar and the Lord of Aratta'' - The goddess Inanna resides in Aratta, but Enmerkar of Uruk pleases her more than does the lord of Aratta, who is not named in this epic. Enmerkar wants Aratta to submit to Uruk, bring stones down from the mountain, craft gold, silver and lapis lazuli, and send them, along with "kugmea" ore to Uruk to build a temple. Inana bids him send a messenger to Aratta, w ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Jiroft Civilization
The Jiroft cultureOscar White MuscarellaJiroft(2008), in: Encyclopedia Iranica. "For archeological accuracy the terms "Jiroft" or "Jiroft culture" employed to define a specific ancient Iranian culture and its artifacts should only be cited within quotation mark." also known as the Intercultural style or the Halilrud style, is a postulated early Bronze Age (late 3rd millennium BC) archaeological culture, located in the territory of present-day Sistan and Baluchestan and Kermān Provinces of Iran. The proposed type site is Konar Sandal, near Jiroft in the Halil River area. Other significant sites associated with the culture include Shahr-e Sukhteh (Burnt City), Tepe Bampur, Espiedej, Shahdad, Tal-i-Iblis and Tepe Yahya. The grouping of these sites as an "independent Bronze Age civilization with its own architecture and language", intermediate between Elam to the west and the Indus Valley civilization to the east, was first proposed by Yusef Majidzadeh, head of the archaeolog ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Shahr-i-Sokhta
Shahr-e Sukhteh ( fa, شهر سوخته, meaning "[The] Burnt City"), c. 3200–2350 BCE, also spelled as ''Shahr-e Sūkhté'' and ''Shahr-i Sōkhta'', is an archaeological site of a sizable Bronze Age urban settlement, associated with the Helmand culture. It is located in Sistan and Baluchistan Province, the southeastern part of Iran, on the bank of the Helmand River, near the Zahedan-Zabol road. It was placed on the UNESCO World Heritage List in June 2014. The reasons for the unexpected rise and fall of the city are still wrapped in mystery. Artifacts recovered from the city demonstrate a peculiar incongruity with nearby civilizations of the time and it has been speculated that Shahr-e-Sukhteh might ultimately provide concrete evidence of a civilization east of prehistoric Persia that was independent of ancient Mesopotamia. Archaeology Covering an area of 151 hectares, Shahr-e Sukhteh was one of the world's largest cities at the dawn of the urban era. It is located close to th ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Lut Desert
The Lut Desert, widely referred to as Dasht-e Lut ( fa, دشت لوت, "Emptiness Plain"), is a large salt desert located in the provinces of Kerman Province, Kerman and Sistan and Baluchestan Province, Sistan and Baluchestan, Iran. It is the List of deserts by area#Deserts over 50 000 km², world's 33rd-largest desert, and was included on UNESCO's World Heritage Site, World Heritage List on July 17, 2016. The name is derived from 'Lut' which means bare and empty in Persian language, Persian and 'dasht' which means plain in Persian language, Persian. The surface of its sand has been measured at temperatures as high as 70.7 °C (159.3 °F), making it one of the world's driest and hottest places. Description Iran is climatically part of the Afro-Asian belt of deserts, which stretches from Mauritania all the way to Mongolia. The patchy, elongated, light-colored feature in the foreground (parallel to the mountain range) is the northernmost of the Dasht dry lakes that stre ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Bronze Flag, Shadad Kerman, Iran
Bronze is an alloy consisting primarily of copper, commonly with about 12–12.5% tin and often with the addition of other metals (including aluminium, manganese, nickel, or zinc) and sometimes non-metals, such as phosphorus, or metalloids such as arsenic or silicon. These additions produce a range of alloys that may be harder than copper alone, or have other useful properties, such as strength, ductility, or machinability. The archaeological period in which bronze was the hardest metal in widespread use is known as the Bronze Age. The beginning of the Bronze Age in western Eurasia and India is conventionally dated to the mid-4th millennium BCE (~3500 BCE), and to the early 2nd millennium BCE in China; elsewhere it gradually spread across regions. The Bronze Age was followed by the Iron Age starting from about 1300 BCE and reaching most of Eurasia by about 500 BCE, although bronze continued to be much more widely used than it is in modern times. Because historical artworks were ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Dasht-e Lut
The Lut Desert, widely referred to as Dasht-e Lut ( fa, دشت لوت, "Emptiness Plain"), is a large salt desert located in the provinces of Kerman and Sistan and Baluchestan, Iran. It is the world's 33rd-largest desert, and was included on UNESCO's World Heritage List on July 17, 2016. The name is derived from 'Lut' which means bare and empty in Persian and 'dasht' which means plain in Persian. The surface of its sand has been measured at temperatures as high as 70.7 °C (159.3 °F), making it one of the world's driest and hottest places. Description Iran is climatically part of the Afro-Asian belt of deserts, which stretches from Mauritania all the way to Mongolia. The patchy, elongated, light-colored feature in the foreground (parallel to the mountain range) is the northernmost of the Dasht dry lakes that stretch southward . Iran's geography consists of a plateau surrounded by mountains and divided into drainage basins. Dasht-e Lut is one of the largest of the ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Köppen Climate Classification
The Köppen climate classification is one of the most widely used climate classification systems. It was first published by German-Russian climatologist Wladimir Köppen (1846–1940) in 1884, with several later modifications by Köppen, notably in 1918 and 1936. Later, the climatologist Rudolf Geiger (1894–1981) introduced some changes to the classification system, which is thus sometimes called the Köppen–Geiger climate classification system. The Köppen climate classification divides climates into five main climate groups, with each group being divided based on seasonal precipitation and temperature patterns. The five main groups are ''A'' (tropical), ''B'' (arid), ''C'' (temperate), ''D'' (continental), and ''E'' (polar). Each group and subgroup is represented by a letter. All climates are assigned a main group (the first letter). All climates except for those in the ''E'' group are assigned a seasonal precipitation subgroup (the second letter). For example, ''Af'' indi ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Namaz
(, plural , romanized: or Old Arabic [t͡sˤaˈloːh] , ( or Old Arabic [t͡sˤaˈloːtʰ] in construct state) ), also known as ( fa, نماز) and also spelled , are prayers performed by Muslims. Facing the , the direction of the Kaaba with respect to those praying, Muslims pray first standing and later kneeling or sitting on the ground, reciting prescribed prayers and phrases from the Quran as they bow and prostrate themselves in between. is composed of prescribed repetitive cycles of bows and prostrations, called ( ). The number of s, also known as units of prayer, varies from prayer to prayer. Ritual purity in Islam, Ritual purity and are prerequisites for performing the prayers. The daily obligatory prayers collectively form the second of the Five Pillars of Islam, five pillars in Islam, observed three or five times (the latter being the majority) every day at Salah times, prescribed times. These are usually (observed at dawn), (observed at noon), (observed la ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |