|
Seyitgazi
Seyitgazi is a town and district of Eskişehir Province in the Central Anatolia region of Turkey. The central town of Seyitgazi lies at a distance of towards the south from the province capital of Eskişehir. According to 2010 census, population of the district is 16,222 of which 2,890 live in the town of Seyitgazi. The district covers an area of , and the average elevation is . Apart from the central town of Seyitgazi, the district has two dependent townships with own municipalities. These are Kırka and Doğançayır. The district also has 46 villages. Places of interest The town occupies the site of the Byzantine city of Nakoleia, and was named after the 8th-century Muslim saint (''seyyid'') and warrior Battal Gazi, who fell in a battle nearby in 740. A complex ( tr, külliye) dedicated to Battal Gazi and containing his tomb, a mosque, a medrese, cells and ceremonial rooms for dervishes as well as charitable services for the community such as kitchens and a bakery was built ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Doğançayır
Doğançayır is a town in Seyitgazi district, Eskişehir Province, Turkey. Formerly known as Arapören. Location Doğançayır is about from Eskişehir and from Seyitgazi. Hamidiye junction on the Eskişehir-Ankara highway is away from Doğançayır. Geography Doğançayır is a considered to be a plain. The land owned by the people living currently in Doğançayır is about 90 hectares. The Kırkkız Mountain, where the TV transmitter is located, is the only peak around the town which has an approximate height of 1800 m. The town is established on the foot of the mountain. The Seydisuyu, an important branch of the Sakarya River, passes through the town. Two bridges in Doğançayır connect the banks of the river. Although there used to be the danger of floods from the river in the spring, after the construction of the Çatıören Dam, it is possible to pass across the river using stepping stones on the water. Economy Economic activities in Doğançayır are mostly limited ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Battal Gazi
Seyyid Battal Ghazi is a Turkish warrior based in Anatolia (associated primarily with Malatya, where his father, Hüseyin Gazi, was the ruler,) based on the real-life exploits of the 8th-century Umayyad military leader Abdallah al-Battal. His attributed legends, which also form the bulk of the information available on the historic personality, later became an important part of Turkish folk literature. His title Seyyid, as well as being an Arabic honorific, may refer, in the form "Seyyid", to family ties to Muhammad. The legends Sources available on the historical personality of Abdallah al-Battal consist of legends often written in the mesnevi style, and which may comport historically correct elements or points that support each other, as well as contradictions. For example, he is cited as having participated in his twenties to the Second Arab Siege of Constantinople in 718, and the legends name his Byzantine enemy as ''Leon'', which could be no other than Leo III the Isaurian, ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
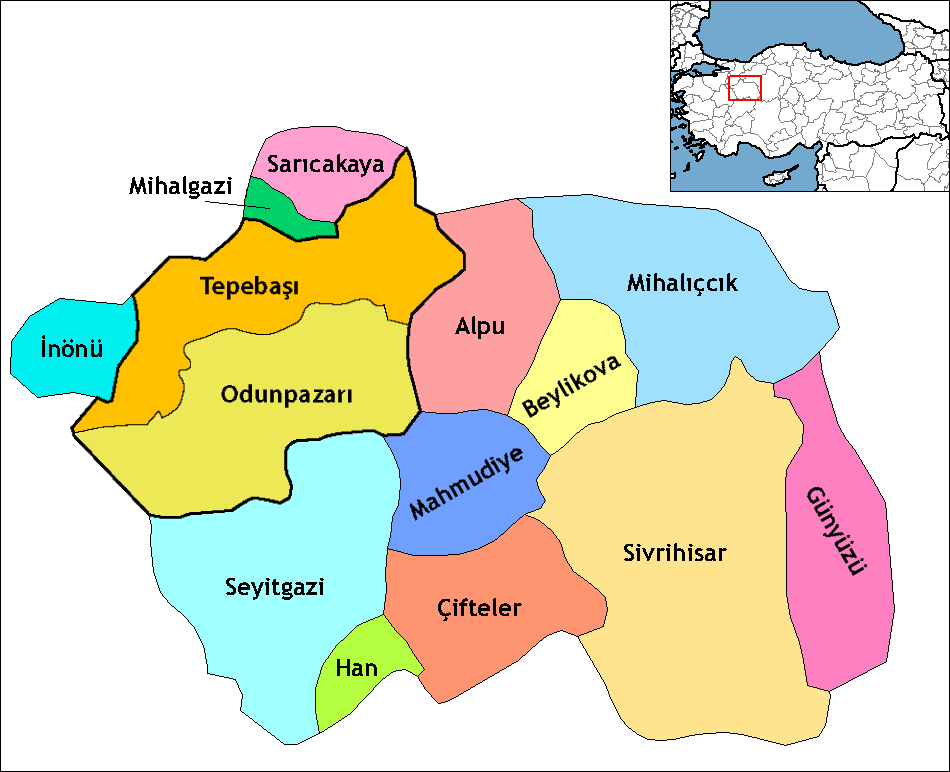
Eskişehir Province
Eskişehir Province ( tr, ) is a province in northwestern Turkey. Its adjacent provinces are Bilecik to the northwest, Kütahya to the west, Afyon to the southwest, Konya to the south, Ankara to the east, and Bolu to the north. The provincial capital is Eskişehir. Most of the province is laid down in Central Anatolia Region. Northern parts of Mihalıççık district and ones of Mihalgazi and Sarıcakaya are located in the Black Sea Region and one of them belong to the Aegean Region. Eskişehir is an old, culturally developed province of Turkey. It has a population of 844,842. Its urban population is 734,837. Eskişehir has 2 universities, Eskişehir Osmangazi University and Anadolu University, which is the largest university in Turkey and which has some branch offices in Europe. Districts Eskişehir province is divided into 14 districts, two of which are included in the greater municipality of Eskişehir (shown in boldface letters). *Odunpazarı * Tepebaşı *Alpu *Beyli ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Seyyid Battal Gazi Complex
Seyyid Battal Gazi Complex ( tr, Seyyid Battal Gazi Külliyesi) is a külliye, historic religious social complex, in Seyitgazi district of Eskişehir Province, Turkey. A mosque and a shrine in honor of Seyyid Battal Gazi, a legendary Muslim folk hero, who fell in a battle against the Byzantine army in this area in 720, was built in 1207/08 at a place southeast of Eskişehir, known today as Seyitgazi. It was donated by Ümmühan Hatun, mother of the Seljuq Sultan of Rûm Alaeddin Keyjubat I (1188–1237). During the Ottoman Empire era, social complex buildings were added around the mosque, including madrasa, almshouse and dervish lodge. Ottoman sultans Mehmed the Conqueror (reigned 1444–1446, 1451–1481), Bayezid II (r. 1481–1512) and Selim I (r. 1512–1520) enriched the complex by additional buildings. Suleiman the Magnificent (r. 1520–1566) and his army camped at the site before the Baghdad Campaign (1534). Murad IV (r. 1623–1640) built a caravanserai on the way to Y ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Eskişehir
Eskişehir ( , ; from "old" and "city") is a city in northwestern Turkey and the capital of the Eskişehir Province. The urban population of the city is 898,369 with a metropolitan population of 797,708. The city is located on the banks of the Porsuk River, 792 m above sea level, where it overlooks the fertile Phrygian Valley. In the nearby hills one can find hot springs. The city is to the west of Ankara, to the southeast of Istanbul and to the northeast of Kütahya. It is located in the vicinity of the ancient city of Dorylaeum. Known as a university town; Eskişehir Technical University, Eskişehir Osmangazi University, and Anadolu University are based in Eskişehir. The province covers an area of . Name The name literally means 'Old City' in Turkish. History The city was founded by the Phrygians in at least 1000 BC, although it has been estimated to be older than 4000 years old. The current city lies about a mile from the ancient Phrygian city of Dorylaeum. Many Ph ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Nakoleia
Nakoleia ( el, Νακώλεια and Νακόλεια) also known as Nakolaion (Νακώλαιον), Latinized as Nacolia or Nacolea, was an ancient and medieval city in Phrygia. It corresponds to present-day Seyitgazi, Eskişehir Province in the Central Anatolia region of Turkey. History It was a town of Phrygia Salutaris, taking its name in legend from the nymph Nacole (Νακώλη and Νακόλη), and had no history in antiquity. The area was known for its fertility in late Roman times, thanks to the river Parthenios (Seyit Su), and was wooded in the late 4th century (it is now deforested). It was there that Valens defeated the usurper Procopius in 366 AD (see Battle of Thyatira); under Arcadius it was occupied by a garrison of Goths under Tribigild who revolted against the emperor in 399 AD. In 782, it was temporarily captured by the Abbasid Caliphate. Bishopric At first a suffragan of Synnada, the see of Nakoleia became important in the early 8th century, when its bish ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Towns In Turkey
A town is a human settlement. Towns are generally larger than villages and smaller than cities, though the criteria to distinguish between them vary considerably in different parts of the world. Origin and use The word "town" shares an origin with the German word , the Dutch word , and the Old Norse . The original Proto-Germanic word, *''tūnan'', is thought to be an early borrowing from Proto-Celtic *''dūnom'' (cf. Old Irish , Welsh ). The original sense of the word in both Germanic and Celtic was that of a fortress or an enclosure. Cognates of ''town'' in many modern Germanic languages designate a fence or a hedge. In English and Dutch, the meaning of the word took on the sense of the space which these fences enclosed, and through which a track must run. In England, a town was a small community that could not afford or was not allowed to build walls or other larger fortifications, and built a palisade or stockade instead. In the Netherlands, this space was a garden, mor ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Sarcophagus
A sarcophagus (plural sarcophagi or sarcophaguses) is a box-like funeral receptacle for a corpse, most commonly carved in stone, and usually displayed above ground, though it may also be buried. The word ''sarcophagus'' comes from the Greek σάρξ ' meaning "flesh", and φαγεῖν ' meaning "to eat"; hence ''sarcophagus'' means "flesh-eating", from the phrase ''lithos sarkophagos'' ( λίθος σαρκοφάγος), "flesh-eating stone". The word also came to refer to a particular kind of limestone that was thought to rapidly facilitate the decomposition of the flesh of corpses contained within it due to the chemical properties of the limestone itself. History of the sarcophagus Sarcophagi were most often designed to remain above ground. The earliest stone sarcophagi were used by Egyptian pharaohs of the 3rd dynasty, which reigned from about 2686 to 2613 B.C. The Hagia Triada sarcophagus is a stone sarcophagus elaborately painted in fresco; one style of later A ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Marble
Marble is a metamorphic rock composed of recrystallized carbonate minerals, most commonly calcite or Dolomite (mineral), dolomite. Marble is typically not Foliation (geology), foliated (layered), although there are exceptions. In geology, the term ''marble'' refers to metamorphosed limestone, but its use in stonemasonry more broadly encompasses unmetamorphosed limestone. Marble is commonly used for Marble sculpture, sculpture and as a building material. Etymology The word "marble" derives from the Ancient Greek (), from (), "crystalline rock, shining stone", perhaps from the verb (), "to flash, sparkle, gleam"; Robert S. P. Beekes, R. S. P. Beekes has suggested that a "Pre-Greek origin is probable". This Stem (linguistics), stem is also the ancestor of the English language, English word "marmoreal," meaning "marble-like." While the English term "marble" resembles the French language, French , most other European languages (with words like "marmoreal") more closely resemb ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Bayezid II
Bayezid II ( ota, بايزيد ثانى, Bāyezīd-i s̱ānī, 3 December 1447 – 26 May 1512, Turkish: ''II. Bayezid'') was the eldest son and successor of Mehmed II, ruling as Sultan of the Ottoman Empire from 1481 to 1512. During his reign, Bayezid II consolidated the Ottoman Empire and thwarted a Safavid rebellion soon before abdicating his throne to his son, Selim I. He evacuated Sephardi Jews from Spain after the proclamation of the Alhambra Decree, and resettled them throughout Ottoman lands, especially in Salonica. Early life Bayezid II was the son of Mehmed II (1432–1481) and Gülbahar Hatun, she is generally accepted as the real mother of Bayezid II. There are sources that claim that Bayezid was the son of Sittişah Hatun. This would make Ayşe Gülbahar Hatun a first cousin of Bayezid II. However, the marriage of Sittisah Hatun took place two years after Bayezid was born and the whole arrangement was not to Mehmed's liking. Born in Demotika, Bayezid II was e ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Ottoman Empire
The Ottoman Empire, * ; is an archaic version. The definite article forms and were synonymous * and el, Оθωμανική Αυτοκρατορία, Othōmanikē Avtokratoria, label=none * info page on book at Martin Luther University) // CITED: p. 36 (PDF p. 38/338) also known as the Turkish Empire, was an empire that controlled much of Southeast Europe, Western Asia, and Northern Africa between the 14th and early 20th centuries. It was founded at the end of the 13th century in northwestern Anatolia in the town of Söğüt (modern-day Bilecik Province) by the Turkoman tribal leader Osman I. After 1354, the Ottomans crossed into Europe and, with the conquest of the Balkans, the Ottoman beylik was transformed into a transcontinental empire. The Ottomans ended the Byzantine Empire with the conquest of Constantinople in 1453 by Mehmed the Conqueror. Under the reign of Suleiman the Magnificent, the Ottoman Empire marked the peak of its power and prosperity, as well a ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Gıyaseddin Keyhüsrev I
Kaykhusraw I ( 1ca, كَیخُسرو or Ghiyāth ad-Dīn Kaykhusraw ibn Kilij Arslān; fa, غياث الدين كيخسرو بن قلج ارسلان), the eleventh and youngest son of Kilij Arslan II, was Seljuk Sultan of Rûm. He succeeded his father in 1192, but had to fight his brothers for control of the Sultanate, losing to his brother Suleiman II in 1196. He ruled it 1192–1196 and 1205–1211. Name The name "Kaykhusraw" is based on the name of the legendary ''Shahnameh'' hero Kay Khosrow. Background Kaykhusraw's date of birth is unknown. He was the eleventh and youngest son of Kilij Arslan II (). His mother was of Byzantine ancestry. Kaykhusraw received a good education during his upbringing, learning other languages besides his native Turkish, which was Persian, Arabic, and Greek. Marriage Kaykhusraw married a daughter of Manuel Maurozomes. Manuel Maurozomes would hold the castles of Chonae and Laodicea as a vassal of Kaykhusraw. Reign In 1192/93, Kaykhusraw retu ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
_-_3.jpg)
.jpg)


