|
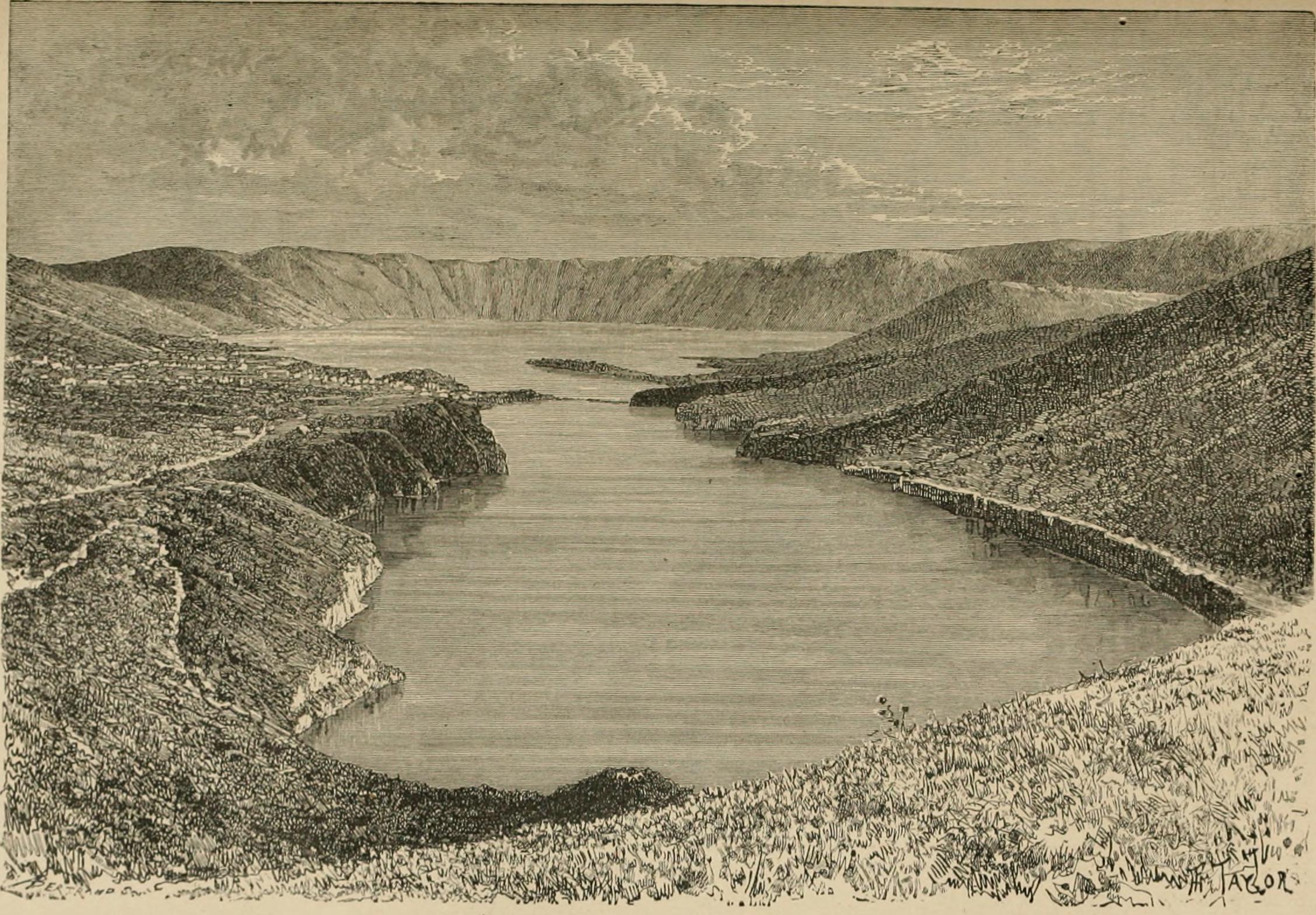
Sete Cidades Massif
Sete Cidades Massif is a stratovolcanic complex, referring to a polygenetic volcano and caldera, located in western part of the island of São Miguel, in the Portuguese archipelago of the Azores. More recognizable for the Lagoa das Sete Cidades at its centre, the volcanic complex includes centuries of geomorphological structures that include lava domes, cones, lava flows and maar geomorphology that have marked its history. History The almost circular caldera is a nested structure formed as a result of three separate caldera collapse episodes,Robert B. Moore (1990), p.603 each associated with explosive eruptions.Jose Pacheo et al. (2002), p.4-5 These caldera collapse episodes occurred following explosive eruptions that formed the ''Risco'', ''Bretanha'' and ''Santa Barbara'' pyroclastic fields.Jose Pacheo et al. (2002), p.5-6 The first phase occurred 35,700 years ago, and ceased with the collapse of the principal volcano. A secondary phase began around 28,750 years ago and w ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Lagoa Das Sete Cidades
Lagoa (Portuguese for ''lagoon'') may refer to the following: People *Barbara Lagoa, Cuban-American federal judge Places Brazil *Campina da Lagoa, Paraná * Lagoa, Paraíba, Paraíba *Lagoa, Rio de Janeiro, a quarter of Rio de Janeiro * Lagoa Alegre, Piauí * Lagoa d'Anta, Rio Grande do Norte * Lagoa do Barro do Piauí, Piauí * Lagoa da Canoa, Alagoas *Lagoa do Carro, Pernambuco *Lagoa da Conceição, in the city of Florianópolis, Santa Catarina state *Lagoa da Confusão, Tocantins * Lagoa de Dentro, Paraíba *Lagoa Dourada, Minas Gerais * Lagoa Formosa, Minas Gerais * Lagoa dos Gatos, Pernambuco * Lagoa Grande, Minas Gerais * Lagoa Grande, Pernambuco *Lagoa Grande do Maranhão, Maranhão *Lagoa do Itaenga, Pernambuco * Manguaba Lagoon, Alagoas * Lagoa do Mato, Maranhão *Lagoa do Mato, Ceará *Lagoa Mirim, Rio Grande do Sul *Mundaú Lagoon, Alagoas *Lagoa Nova, Rio Grande do Norte *Lagoa do Ouro, Pernambuco *Lagoa dos Patos, Rio Grande do Sul *Lagoa de Pedras, Rio Grande do No ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Explosive Eruption
In volcanology, an explosive eruption is a volcanic eruption of the most violent type. A notable example is the 1980 eruption of Mount St. Helens. Such eruptions result when sufficient gas has dissolved under pressure within a viscous magma such that expelled lava violently froths into volcanic ash when pressure is suddenly lowered at the vent. Sometimes a lava plug will block the conduit to the summit, and when this occurs, eruptions are more violent. Explosive eruptions can expel as much as per second of rocks, dust, gas and pyroclastic material, averaged over the duration of eruption, that travels at several hundred meters per second as high as into the atmosphere. This cloud may subsequently collapse, creating a fast-moving pyroclastic flow of hot volcanic matter. Stages of an explosive eruption An explosive eruption begins with some form of blockage in the crater of a volcano that prevents the release of gases trapped in highly viscous andesitic or rhyolitic magma. The pr ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Furnas
Furnas is a civil parish in the municipality of Povoação on the island of São Miguel in the Portuguese Azores. The population in 2011 was 1,439, in an area of 34.43 km2. The parish is one of the largest in the island and in the Azores. It is located east of Lagoa and Ponta Delgada, west of Povoação and southeast of Ribeira Grande. History One of the earliest references to Furnas came from the harvesting of trees in the valley of Furnas, in order to assist the construction of many of the homes destroyed by the 1522 earthquakes and landslides in Vila Franca do Campo. This includes numerous trees used to rebuild the parochial church, a project begun by Donatary-Captain Rui Gonçalves da Câmara. In 1553, his predecessor Manuel da Câmara, issued an edict to re-plant these trees after the area was nearly deforested, and roadways were expanded under his son, Rui Gonçalves da Câmara, in order to develop the area, allowing cattle herding in the valley after 1577. Still ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Hawaiian Eruption
A Hawaiian eruption is a type of volcanic eruption where lava flows from the vent in a relatively gentle, low level eruption; it is so named because it is characteristic of Hawaiian volcanoes. Typically they are effusive eruptions, with basaltic magmas of low viscosity, low content of gases, and high temperature at the vent. Very small amounts of volcanic ash are produced. This type of eruption occurs most often at hotspot volcanoes such as Kīlauea on Hawaii's big island and in Iceland, though it can occur near subduction zones (e.g. Medicine Lake Volcano in California, United States) and rift zones. Another example of Hawaiian eruptions occurred on the island of Surtsey in Iceland from 1964 to 1967, when molten lava flowed from the crater to the sea. Hawaiian eruptions may occur along fissure vents, such as during the eruption of Mauna Loa in 1950, or at a central vent, such as during the 1959 eruption in Kīlauea Iki Crater, which created a lava fountain 580 meters (1,900&n ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Pleistocene
The Pleistocene ( , often referred to as the ''Ice age'') is the geological Epoch (geology), epoch that lasted from about 2,580,000 to 11,700 years ago, spanning the Earth's most recent period of repeated glaciations. Before a change was finally confirmed in 2009 by the International Union of Geological Sciences, the cutoff of the Pleistocene and the preceding Pliocene was regarded as being 1.806 million years Before Present (BP). Publications from earlier years may use either definition of the period. The end of the Pleistocene corresponds with the end of the last glacial period and also with the end of the Paleolithic age used in archaeology. The name is a combination of Ancient Greek grc, label=none, πλεῖστος, pleīstos, most and grc, label=none, καινός, kainós (latinized as ), 'new'. At the end of the preceding Pliocene, the previously isolated North and South American continents were joined by the Isthmus of Panama, causing Great American Interchang ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Pyroclastic Cone
Volcanic cones are among the simplest volcanic landforms. They are built by ejecta from a volcanic vent, piling up around the vent in the shape of a cone with a central crater. Volcanic cones are of different types, depending upon the nature and size of the fragments ejected during the eruption. Types of volcanic cones include stratocones, spatter cones, tuff cones, and cinder cones. Stratocone Stratocones are large cone-shaped volcanoes made up of lava flows, explosively erupted pyroclastic rocks, and igneous intrusives that are typically centered around a cylindrical vent. Unlike shield volcanoes, they are characterized by a steep profile and periodic, often alternating, explosive eruptions and effusive eruptions. Some have collapsed craters called calderas. The central core of a stratocone is commonly dominated by a central core of intrusive rocks that range from around to over several kilometers in diameter. This central core is surrounded by multiple generations of lava f ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Holocene
The Holocene ( ) is the current geological epoch. It began approximately 11,650 cal years Before Present (), after the Last Glacial Period, which concluded with the Holocene glacial retreat. The Holocene and the preceding Pleistocene together form the Quaternary period. The Holocene has been identified with the current warm period, known as MIS 1. It is considered by some to be an interglacial period within the Pleistocene Epoch, called the Flandrian interglacial.Oxford University Press – Why Geography Matters: More Than Ever (book) – "Holocene Humanity" section https://books.google.com/books?id=7P0_sWIcBNsC The Holocene corresponds with the rapid proliferation, growth and impacts of the human species worldwide, including all of its written history, technological revolutions, development of major civilizations, and overall significant transition towards urban living in the present. The human impact on modern-era Earth and its ecosystems may be considered of global si ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Trachyte
Trachyte () is an extrusive igneous rock composed mostly of alkali feldspar. It is usually light-colored and aphanitic (fine-grained), with minor amounts of mafic minerals, and is formed by the rapid cooling of lava enriched with silica and alkali metals. It is the volcanic equivalent of syenite. Trachyte is common wherever alkali magma is erupted, including in late stages of ocean island volcanismMacDonald 1983, pp. 51-52 and in continental rift valleys, above mantle plumes,Philpotts and Ague 2009, pp. 390-394 and in areas of back-arc extension. Trachyte has also been found in Gale crater on Mars. Trachyte has been used as decorative building stone and was extensively used as dimension stone in the Roman Empire and the Republic of Venice. Chemical composition Trachyte has a silica content of 60 to 65% and an alkali oxide content of over 7%. This gives it less SiO2 than rhyolite and more (Na2O plus K2O) than dacite. These chemical differences are consistent with the positio ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Ignimbrite
Ignimbrite is a type of volcanic rock, consisting of hardened tuff. Ignimbrites form from the deposits of pyroclastic flows, which are a hot suspension of particles and gases flowing rapidly from a volcano, driven by being denser than the surrounding atmosphere. New Zealand geologist Patrick Marshall (1869-1950) coined the term ''ignimbrite'' from the Latin ''igni-'' [fire] and ''imbri-'' [rain]. Ignimbrites are made of a very poorly sorted mixture of volcanic ash (or tuff when Lithification, lithified) and pumice lapilli, commonly with scattered lithic fragments. The ash is composed of glass shards and crystal fragments. Ignimbrites may be loose and unconsolidated, or lithified (solidified) rock called lapilli-tuff. Near the volcanic source, ignimbrites often contain thick accumulations of lithic blocks, and distally, many show meter-thick accumulations of rounded cobbles of pumice. Ignimbrites may be white, grey, pink, beige, brown, or black depending on their composition and d ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Pyroclastic Flow
A pyroclastic flow (also known as a pyroclastic density current or a pyroclastic cloud) is a fast-moving current of hot gas and volcanic matter (collectively known as tephra) that flows along the ground away from a volcano at average speeds of but is capable of reaching speeds up to . The gases and tephra can reach temperatures of about . Pyroclastic flows are the most deadly of all volcanic hazards and are produced as a result of certain explosive eruptions; they normally touch the ground and hurtle downhill, or spread laterally under gravity. Their speed depends upon the density of the current, the volcanic output rate, and the gradient of the slope. Origin of term The word ''pyroclast'' is derived from the Greek (''pýr''), meaning "fire", and (''klastós''), meaning "broken in pieces". A name for pyroclastic flows which glow red in the dark is (French, "burning cloud"); this was notably used to describe the disastrous 1902 eruption of Mount Pelée on Martinique, a French ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |